
Crotyl
Encyclopedia
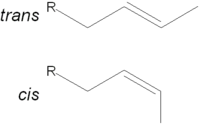
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
with the formula RCH2CH=CHCH3. Systematically, it is called a but-2-en-1-yl group and exhibits geometric isomerism
Geometric isomerism
In organic chemistry, cis/trans isomerism or geometric isomerism or configuration isomerism or E/Z isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism describing the orientation of functional groups within a molecule...
, being either cis (Z) or trans (E). There are many simple compounds in which the crotyl group forms base carbon chain: crotyl alcohol, crotonaldehyde
Crotonaldehyde
Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common...
, crotonic acid
Crotonic acid
Crotonic acid, or trans-2-butenoic acid, is a short-chain unsaturated carboxylic acid, described by the formula CH3CH=CHCO2H. Crotonic acid is so named because it was erroneously thought to be a saponification product of croton oil...
, and crotyl acrylate are examples.
Synthesis of crotylates
Crotylate (crotyl anions) can be synthesised from 2-butene2-Butene
2-Butene is an acyclic alkene with four carbon atoms. It is the simplest alkene exhibiting cis/trans-isomerism ; that is, it exists as two geometrical isomers cis-2-butene , shown at the right, and trans-2-butene , not shown.It is a petrochemical, produced by the catalytic cracking of crude oil...
(either isomer): this reaction must be performed in the presence of organometallic reagents, as a base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
, usually alkyl lithium
Lithium
Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly...
, or any alkylates of s-block
S-block
The s-block of the periodic table of elements consists of the first two groups: the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, plus hydrogen and helium.Except in hydrogen and helium, these electrons are very easily lost to form positive ions...
metals, in a solvent, typically THF
ThF
Follicular B helper T cells , are antigen-experienced CD4+ T cells found in the B cell follicles of secondary lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, spleens and Peyer's patches, and are identified by their constitutive expression of the B cell follicle homing receptor CXCR5...
, and at low temperatures, generally below -20°C. The negative charge is delocalised over three of the carbon atoms of the crotylate group and there is resonance between the two possible delocalised forms (one for each terminal carbon).
Crotylation reactions
Crotylation readily occurs with alkoxy boronates to form crotylboronates.Crotylboronates are useful reagents in the formation of crotyl alcohols. They react with the acidic protons of aldehydes to form alcohols. The mechanism involves a six-membered ring involving the carbonyl oxygen and boron in a chair-like structure. Such reactions are highly diastereoselective.

