
Craniopharyngioma
Encyclopedia
Craniopharyngioma is a type of brain tumor
derived from pituitary gland
embryonic tissue, that occurs most commonly in children but also in men and women in their 50s and 60s.
It arises from nests of odontogenic (tooth-forming) epithelium within the suprasellar/diencephalic region and, therefore, contains deposits of calcium
, which are evident on an x-ray
.
Histologically, craniopharyngiomas resemble adamantinomas (the most common tumors of the tooth). Patients may present with bitemporal inferior quadrantanopia leading to bitemporal hemianopia, as the tumor may compress the optic chiasm
.
It has a point prevalence
of approximately 2/100,000.
Craniopharyngiomas are also known as Rathke pouch tumors, hypophyseal duct tumors, or adamantinomas.
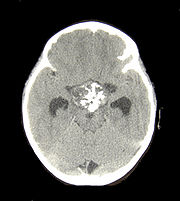 Craniopharyngiomas are typically very slow growing tumors. They arise from the cells along the pituitary stalk
Craniopharyngiomas are typically very slow growing tumors. They arise from the cells along the pituitary stalk
. They are classified by histology as benign
; however, as with many brain tumors, their treatment can be difficult, and significant morbidities are associated with both the tumor and treatment.
Craniopharyngioma is a rare, usually suprasellar neoplasm, which may be cystic, that develops from rests of epithelium derived from Rathke's pouch
. Rathke's pouch is an embryonic precursor of the anterior pituitary.
bordered by radially arranged cells. It is frequently accompanied by calcium deposition and may have a microscopic papillary architecture.
Two distinct types are recognized:
In the adamantinomatous type, calcifications are visible on neuroimaging and are helpful in diagnosis.
The papillary type rarely calcifies.
On macroscopic examination, craniopharyngiomas are cystic or partially-cystic with solid areas. On light microscopy, the cysts are seen to be lined by stratified squamous epithelium. Keratin pearls may also be seen. The cysts are usually filled with a yellow, viscous fluid which is rich in cholesterol crystals. In addition to a long list of possible symptoms, the most common presentation include: headaches, growth failure, and bitemporal hemianopsia
.
The histologic pattern consists of nesting of squamous epithelium
bordered by radially arranged cells. It is frequently accompanied by calcium deposition and may have a microscopic papillary architecture.
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
derived from pituitary gland
Pituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 g , in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain, and rests in a small, bony cavity covered by a dural fold...
embryonic tissue, that occurs most commonly in children but also in men and women in their 50s and 60s.
It arises from nests of odontogenic (tooth-forming) epithelium within the suprasellar/diencephalic region and, therefore, contains deposits of calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
, which are evident on an x-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
.
Histologically, craniopharyngiomas resemble adamantinomas (the most common tumors of the tooth). Patients may present with bitemporal inferior quadrantanopia leading to bitemporal hemianopia, as the tumor may compress the optic chiasm
Optic chiasm
The optic chiasm or optic chiasma is the part of the brain where the optic nerves partially cross...
.
It has a point prevalence
Prevalence
In epidemiology, the prevalence of a health-related state in a statistical population is defined as the total number of cases of the risk factor in the population at a given time, or the total number of cases in the population, divided by the number of individuals in the population...
of approximately 2/100,000.
Craniopharyngiomas are also known as Rathke pouch tumors, hypophyseal duct tumors, or adamantinomas.
Presentation

Pituitary stalk
The pituitary stalk is the connection between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary....
. They are classified by histology as benign
Benign
A benign tumor is a tumor that lacks the ability to metastasize. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.The term "benign" implies a mild and nonprogressive disease. Indeed, many kinds of benign tumors are harmless to human health...
; however, as with many brain tumors, their treatment can be difficult, and significant morbidities are associated with both the tumor and treatment.
Craniopharyngioma is a rare, usually suprasellar neoplasm, which may be cystic, that develops from rests of epithelium derived from Rathke's pouch
Rathke's pouch
In embryogenesis, Rathke's pouch is a depression in the roof of the developing mouth in front of the buccopharyngeal membrane. It gives rise to the anterior pituitary , a part of the endocrine system.-Development:...
. Rathke's pouch is an embryonic precursor of the anterior pituitary.
Histology
The histologic pattern consists of nesting of squamous epitheliumEpithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
bordered by radially arranged cells. It is frequently accompanied by calcium deposition and may have a microscopic papillary architecture.
Two distinct types are recognized:
- Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma and,
- Papillary craniopharyngioma.
In the adamantinomatous type, calcifications are visible on neuroimaging and are helpful in diagnosis.
The papillary type rarely calcifies.
On macroscopic examination, craniopharyngiomas are cystic or partially-cystic with solid areas. On light microscopy, the cysts are seen to be lined by stratified squamous epithelium. Keratin pearls may also be seen. The cysts are usually filled with a yellow, viscous fluid which is rich in cholesterol crystals. In addition to a long list of possible symptoms, the most common presentation include: headaches, growth failure, and bitemporal hemianopsia
Bitemporal hemianopsia
Bitemporal hemianopsia is the medical description of a type of partial blindness where vision is missing in the outer half of both the right and left visual field...
.
The histologic pattern consists of nesting of squamous epithelium
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
bordered by radially arranged cells. It is frequently accompanied by calcium deposition and may have a microscopic papillary architecture.
Treatment
Treatment generally consists of subfrontal or transsphenoidal excision. Adjuvant radiotherapy is also used if total removal is not possible. Due to the morbidities associated with damage to the pituitary and hypothalmus from surgical removal and radiation, experimental therapies using intracavitary P32, yttrium or bleomycin delivered via an external reservoir are frequently employed, especially in young patients.Possible symptoms
- AnorexiaAnorexia (symptom)Anorexia is the decreased sensation of appetite...
- Balance disorderBalance disorderA balance disorder is a disturbance that causes an individual to feel unsteady, for example when standing or walking. It may be accompanied by feelings of giddiness or wooziness, or having a sensation of movement, spinning, or floating...
- Dry skin
- FatigueFatigue (physical)Fatigue is a state of awareness describing a range of afflictions, usually associated with physical and/or mental weakness, though varying from a general state of lethargy to a specific work-induced burning sensation within one's muscles...
- FeverFeverFever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
- HeadacheHeadacheA headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
(obstructive hydrocephalusHydrocephalusHydrocephalus , also known as "water in the brain," is a medical condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, or cavities, of the brain. This may cause increased intracranial pressure inside the skull and progressive enlargement of the head,...
) - Lethargy
- MyxedemaMyxedemaMyxedema describes a specific form of cutaneous and dermal edema secondary to increased deposition of connective tissue components in subcutaneous tissue as seen in various forms of hypothyroidism and Graves' disease. It is more common in women than in men...
- NauseaNauseaNausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
- Short statureShort statureShort stature refers to a height of a human being which is below expected. Shortness is a vague term without a precise definition and with significant relativity to context...
- PolydipsiaPolydipsiaPolydipsia is a medical symptom in which the patient displays excessive thirst. The word derives from the Greek πολυδιψία, which is derived from πολύς + δίψα...
- PolyuriaPolyuriaPolyuria is a condition usually defined as excessive or abnormally large production or passage of urine . Frequent urination is sometimes included by definition, but is nonetheless usually an accompanying symptom...
(diabetes insipidusDiabetes insipidusDiabetes insipidus is a condition characterized by excessive thirst and excretion of large amounts of severely diluted urine, with reduction of fluid intake having no effect on the concentration of the urine. There are several different types of DI, each with a different cause...
) - Vision lossVision lossVision loss or visual loss is the absence of vision where it existed before, which can happen either acutely or chronically .-Ranges of vision loss:...
(bitemporal hemianopia) - VomitingVomitingVomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
- Weight gainWeight gainWeight gain is an increase in body weight. This can be either an increase in muscle mass, fat deposits, or excess fluids such as water.-Description:...
- Amenorrhea

