
Coupon collector's problem (generating function approach)
Encyclopedia
The coupon collector's problem
can be solved in several different ways. The generating function
approach is a combinatorial technique that allows to obtain precise results.
We introduce the probability generating function (PGF)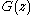 where
where  is the probability that we take q steps to collect the n coupons i.e.
is the probability that we take q steps to collect the n coupons i.e.  and the expectation is given by
and the expectation is given by

We can calculate explicitly. We have
explicitly. We have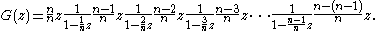
To see what this means, note that
so that this is the PGF of an event that has probability p occurring zero or more times, with the exponent of z counting the number of times. We split the sequence of coupons into segments. A new segment begins every time a new coupon is retrieved for the first time. The PGF is the product of the PGFs of the individual segments. Applying this to , we see that it represents the following sequence of events:
, we see that it represents the following sequence of events:
In the following, and
and  denote harmonic numbers.
denote harmonic numbers.
The function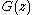 if first simplified before deriving the expectation. First:
if first simplified before deriving the expectation. First: .
.
THe use is made of the fact that
to obtain the derivative of
 .
.
This yields
or

Finally, some simplification:
so that
The PGF makes it possible to obtain an exact value for the variance
makes it possible to obtain an exact value for the variance
. Start with

which consists entirely of factorial moments that can be calculated from the PGF. We already have the value of . For the remainder, use
. For the remainder, use

The derivative is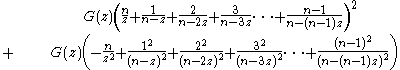
Evaluation at yields
yields
The conclusion is that

Coupon collector's problem
In probability theory, the coupon collector's problem describes the "collect all coupons and win" contests. It asks the following question: Suppose that there are n coupons, from which coupons are being collected with replacement...
can be solved in several different ways. The generating function
Generating function
In mathematics, a generating function is a formal power series in one indeterminate, whose coefficients encode information about a sequence of numbers an that is indexed by the natural numbers. Generating functions were first introduced by Abraham de Moivre in 1730, in order to solve the general...
approach is a combinatorial technique that allows to obtain precise results.
We introduce the probability generating function (PGF)
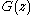 where
where  is the probability that we take q steps to collect the n coupons i.e.
is the probability that we take q steps to collect the n coupons i.e.  and the expectation is given by
and the expectation is given by
We can calculate
 explicitly. We have
explicitly. We have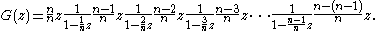
To see what this means, note that

so that this is the PGF of an event that has probability p occurring zero or more times, with the exponent of z counting the number of times. We split the sequence of coupons into segments. A new segment begins every time a new coupon is retrieved for the first time. The PGF is the product of the PGFs of the individual segments. Applying this to
 , we see that it represents the following sequence of events:
, we see that it represents the following sequence of events:- retrieve the first coupon (no restrictions at this time)
- retrieve the first coupon some number of times
- retrieve the second coupon (probability
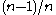 )
) - retrieve a mix of the first and second coupons some number of times
- retrieve the third coupon (probability
 )
) - retrieve a mix of the first, second, and third coupons some number of times
- retrieve the fourth coupon (probability
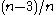 )
) -

- retrieve the last coupon (probability
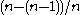 ).
).
In the following,
 and
and  denote harmonic numbers.
denote harmonic numbers.The function
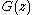 if first simplified before deriving the expectation. First:
if first simplified before deriving the expectation. First: .
.THe use is made of the fact that

to obtain the derivative of

 .
.This yields

or

Finally, some simplification:

so that

The PGF
 makes it possible to obtain an exact value for the variance
makes it possible to obtain an exact value for the varianceVariance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
. Start with

which consists entirely of factorial moments that can be calculated from the PGF. We already have the value of
 . For the remainder, use
. For the remainder, use
The derivative is
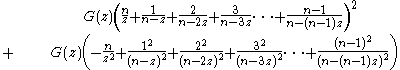
Evaluation at
 yields
yields
The conclusion is that


