
Coreflexive relation
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a coreflexive relation is a binary relation
that is a subset of the identity relation. Thus if a is related to b (aRb) then a is equal to b (a = b), but if c is equal to d (c = d) it does not necessarily hold that c is related to d (cRd).
In mathematical notation
, this is:
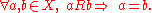
The identity relation is coreflexive by definition. Any relation that is coreflexive is thus a subset of the identity relation.
For example, consider the relation R as "equal to and odd". Over the set of positive integers, the relationship R holds over the pairs {(1, 1), (3, 3), ...} but does not hold over {(2, 2), (4, 4), ...}.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a coreflexive relation is a binary relation
Binary relation
In mathematics, a binary relation on a set A is a collection of ordered pairs of elements of A. In other words, it is a subset of the Cartesian product A2 = . More generally, a binary relation between two sets A and B is a subset of...
that is a subset of the identity relation. Thus if a is related to b (aRb) then a is equal to b (a = b), but if c is equal to d (c = d) it does not necessarily hold that c is related to d (cRd).
In mathematical notation
Mathematical notation
Mathematical notation is a system of symbolic representations of mathematical objects and ideas. Mathematical notations are used in mathematics, the physical sciences, engineering, and economics...
, this is:
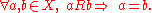
The identity relation is coreflexive by definition. Any relation that is coreflexive is thus a subset of the identity relation.
For example, consider the relation R as "equal to and odd". Over the set of positive integers, the relationship R holds over the pairs {(1, 1), (3, 3), ...} but does not hold over {(2, 2), (4, 4), ...}.

