
Core recovery parameters
Encyclopedia
Total core recovery
Total core recovery (TCR) is the borehole core recovery percentage.TCR is defined as the quotient:
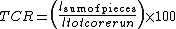 %
%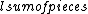 = Sum of length of core pieces
= Sum of length of core pieces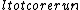 = Total length of core run
= Total length of core runSolid core recovery
Solid core recovery (SCR) is the borehole core recovery percentage of solid, cylindrical, pieces of rock core.SCR is defined as the quotient:
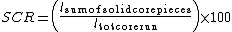 %
%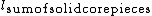 = Sum of length of solid, cylindrical, core pieces
= Sum of length of solid, cylindrical, core pieces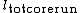 = Total length of core run
= Total length of core runRock quality designation
rock-quality designation (RQD) Rough measure of the degree of jointing or fracture in a rock mass, measured as a percentage of the drill core in lengths of 10 cm or more. High-quality rock has an RQD of more than 75%, low quality of less than 50%.Rock quality designation (RQD) has several definitions. The most widely used definition was developed in 1964 by D. U. Deere. It is the borehole core recovery percentage incorporating only pieces of solid core that are longer than 100 mm in length measured along the centerline of the core. In this respect pieces of core that are not hard and sound should not be counted though they are 100 mm in length. RQD was originally introduced for use with core diameters of 54.7 mm (NX-size core). RQD has considerable value in estimating support of rock tunnels. RQD forms a basic element in some of the most used rock mass classification systems: Rock Mass Rating system (RMR
RMR
RMR, a three-letter acronym meaning:*Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive layout*Recurring Monthly Revenue*Registered Merit Reporter, a certification offered by the National Court Reporters Association*Resting Metabolic Rate, see basal metabolic rate...
) and Q-system
RQD is defined as the quotient:
 %
%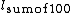 = Sum of length of core sticks longer than 100 mm measured along the center line of the core
= Sum of length of core sticks longer than 100 mm measured along the center line of the core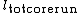 = Total length of core run
= Total length of core runClassification table
From the RQD index the rock mass can be classified as follows:| RQD | Rock mass quality |
|---|---|
| <25% | very poor |
| 25-50% | poor |
| 50-75% | fair |
| 75-90% | good |
| 90-100% | excellent |
Rock mass classification
Many rock mass classificationRock mass classification
Rock mass classification systems are used for various engineering design and stability analysis. These are based on empirical relations between rock mass parameters and engineering applications, such as tunnels, slopes, foundations, and excavatability...
systems use core recovery parameters as input parameter, such as Rock Mass Rating
Rock mass rating
The rock mass rating system is a geomechanical classification system for rocks, developed by Z. T. Bieniawski between 1972 and 1973.-Definition:The following six parameters are used to classify a rock mass using the RMR system...
and Q-system
Q-system (geotechnical engineering)
The Q-system for rock mass classification is developed by Barton, Lien, and Lunde. It expresses the quality of the rock mass in the so-called Q-value, on which are based design and support recommendations for underground excavations....
.

