
Cooling flow
Encyclopedia
A cooling flow occurs according to the theory that the intracluster medium
(ICM) in the centres of galaxy clusters should be rapidly cooling at the rate of tens to thousands of solar masses per year. This should happen as the ICM (a plasma
) is quickly losing its energy by the emission of X-rays. The X-ray brightness of the ICM is proportional to the square of its density, which rises steeply towards the centres of many clusters. Also the temperature falls to typically a third or a half of the temperature in the outskirts of the cluster. The typical timescale for the ICM to cool is relatively short, less than a billion years. As material in the centre of the cluster cools out, the pressure of the overlying ICM should cause more material to flow inwards (the cooling flow).
In a steady state, the rate of mass deposition, i.e. the rate at which the plasma cools, is given by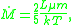
where L is the bolometric (i.e. over the entire spectrum) luminosity
of the cooling region, T is its temperature, k is the Boltzmann constant and μm is the mean molecular mass.
It is currently thought that the very large amounts of expected cooling are in reality much smaller, as there is little evidence for cool X-ray emitting gas in many of these systems. This is the cooling flow problem. Theories for why there is little evidence of cooling include
Heating by AGN is the most popular explanation, as they emit a lot of energy over their lifetimes, and some of the alternatives listed have theoretical problems.
Intracluster medium
In astronomy, the intracluster medium is the superheated plasma present at the center of a galaxy cluster. This is gas heated to temperatures of between roughly 10 and 100 megakelvins and consisting mainly of ionised hydrogen and helium, containing most of the baryonic material in the cluster...
(ICM) in the centres of galaxy clusters should be rapidly cooling at the rate of tens to thousands of solar masses per year. This should happen as the ICM (a plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
) is quickly losing its energy by the emission of X-rays. The X-ray brightness of the ICM is proportional to the square of its density, which rises steeply towards the centres of many clusters. Also the temperature falls to typically a third or a half of the temperature in the outskirts of the cluster. The typical timescale for the ICM to cool is relatively short, less than a billion years. As material in the centre of the cluster cools out, the pressure of the overlying ICM should cause more material to flow inwards (the cooling flow).
In a steady state, the rate of mass deposition, i.e. the rate at which the plasma cools, is given by
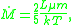
where L is the bolometric (i.e. over the entire spectrum) luminosity
Luminosity
Luminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
of the cooling region, T is its temperature, k is the Boltzmann constant and μm is the mean molecular mass.
It is currently thought that the very large amounts of expected cooling are in reality much smaller, as there is little evidence for cool X-ray emitting gas in many of these systems. This is the cooling flow problem. Theories for why there is little evidence of cooling include
- Heating by the central Active galactic nucleusActive galactic nucleusAn active galactic nucleus is a compact region at the centre of a galaxy that has a much higher than normal luminosity over at least some portion, and possibly all, of the electromagnetic spectrum. Such excess emission has been observed in the radio, infrared, optical, ultra-violet, X-ray and...
(AGN) in clusters, possibly via sound waves (seen in the PerseusPerseus ClusterThe Perseus Cluster is a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Perseus. It has a recession speed of 5,366 km/s and a diameter of 863′...
and Virgo clusterVirgo ClusterThe Virgo Cluster is a cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly away in the constellation Virgo. Comprising approximately 1300 member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger Local Supercluster, of which the Local Group is an outlying member...
s) - Thermal conduction of heat from the outer parts of clusters
- Cosmic rayCosmic rayCosmic rays are energetic charged subatomic particles, originating from outer space. They may produce secondary particles that penetrate the Earth's atmosphere and surface. The term ray is historical as cosmic rays were thought to be electromagnetic radiation...
heating - Hiding cool gas by absorbing material
- Mixing of cool gas with hotter material
Heating by AGN is the most popular explanation, as they emit a lot of energy over their lifetimes, and some of the alternatives listed have theoretical problems.

