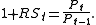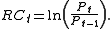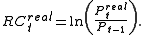Continuously Compounded Nominal and Real Returns
Encyclopedia
Nominal return
Let Pt be the price of a security at time t, including any cash dividends or interestInterest
Interest is a fee paid by a borrower of assets to the owner as a form of compensation for the use of the assets. It is most commonly the price paid for the use of borrowed money, or money earned by deposited funds....
, and let Pt − 1 be its price at t − 1. Let RSt be the simple rate of return on the security from t − 1 to t. Then
The continuously compounded rate of return or instantaneous rate of return RCt obtained during that period is
If this instantaneous return is received continuously for one period, then the initial value Pt-1 will grow to
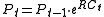 during that period. See also continuous compounding
during that period. See also continuous compoundingCompound interest
Compound interest arises when interest is added to the principal, so that from that moment on, the interest that has been added also itself earns interest. This addition of interest to the principal is called compounding...
.
Since this analysis did not adjust for the effects of inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
on the purchasing power of Pt, RS and RC are referred to as nominal rates of return.
Real return
Let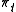 be the purchasing power of a dollar at time t (the number of bundles of consumption that can be purchased for $1). Then
be the purchasing power of a dollar at time t (the number of bundles of consumption that can be purchased for $1). Then 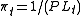 , where PLt is the price level at t (the dollar price of a bundle of consumption goods). The simple inflation rate ISt from t –1 to t is
, where PLt is the price level at t (the dollar price of a bundle of consumption goods). The simple inflation rate ISt from t –1 to t is 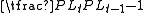 . Thus, continuing the above nominal example, the final value of the investment expressed in real terms is
. Thus, continuing the above nominal example, the final value of the investment expressed in real terms is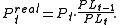
Then the continuously compounded real rate of return
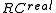 is
isThe continuously compounded real rate of return is just the continuously compounded nominal rate of return minus the continuously compounded inflation rate.