
Confusion of the inverse
Encyclopedia
Confusion of the inverse, also called the conditional probability fallacy, is a logical fallacy whereupon a conditional probability
is equivocated
with its inverse: That is, given two events A and B, the probability Pr(A | B) is assumed to be approximately equal to Pr(B | A).
of occurring and a positive test result from a diagnostic known to be 80% accurate with a 10% false positive rate for that type of test . 95 out of 100 physicians responded the probability of malignancy would be around 75%, apparently because the physicians believed that the chances of malignancy given a positive test result were approximately the same as the chances of a positive test result given malignancy.
The correct probability of malignancy given a positive test result as stated above is 7.5%, derived via Bayes' theorem
:
Conditional probability
In probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
is equivocated
Equivocation
Equivocation is classified as both a formal and informal logical fallacy. It is the misleading use of a term with more than one meaning or sense...
with its inverse: That is, given two events A and B, the probability Pr(A | B) is assumed to be approximately equal to Pr(B | A).
Example 1
In one study, physicians were asked what the chances of malignancy with a 1% prior probabilityPrior probability
In Bayesian statistical inference, a prior probability distribution, often called simply the prior, of an uncertain quantity p is the probability distribution that would express one's uncertainty about p before the "data"...
of occurring and a positive test result from a diagnostic known to be 80% accurate with a 10% false positive rate for that type of test . 95 out of 100 physicians responded the probability of malignancy would be around 75%, apparently because the physicians believed that the chances of malignancy given a positive test result were approximately the same as the chances of a positive test result given malignancy.
The correct probability of malignancy given a positive test result as stated above is 7.5%, derived via Bayes' theorem
Bayes' theorem
In probability theory and applications, Bayes' theorem relates the conditional probabilities P and P. It is commonly used in science and engineering. The theorem is named for Thomas Bayes ....
:
-
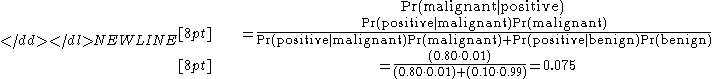
Other examples of confusion include:
- Hard drug users tend to use marijuana; therefore, marijuana users tend to use hard drugs (the first probability is marijuana use given hard drug use, the second is hard drug use given marijuana use).
- Most accidents occur within 25 miles from home; therefore, you are safest when you are far from home.
- Terrorists tend to have an engineering background; so, engineers have a tendency towards terrorism.
For other errors in conditional probability, see the Monty Hall problem and the base rate fallacyBase rate fallacyThe base rate fallacy, also called base rate neglect or base rate bias, is an error that occurs when the conditional probability of some hypothesis H given some evidence E is assessed without taking into account the "base rate" or "prior probability" of H and the total probability of evidence...
. Compare to illicit conversion.
Example 2
In order to identify individuals having a serious disease in an early curable form, one may consider screening a large group of people. While the benefits are obvious, an argument against such screenings is the disturbance caused by false positive screening results: If a person not having the disease is incorrectly found to have it by the initial test, they will most likely be distressed, and even if they subsequently take a more careful test and are told they are well, their lives may still be affected negatively. If they undertake unnecessary treatment for the disease, they may be harmed by the treatment's side effects and costs.
The magnitude of this problem is best understood in terms of conditional probabilities.
Suppose 1% of the group suffer from the disease, and the rest are well. Choosing an individual at random,
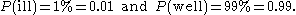
Suppose that when the screening test is applied to a person not having the disease, there is a 1% chance of getting a false positive result (and hence 99% chance of getting a true negative result), i.e.
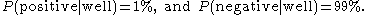
Finally, suppose that when the test is applied to a person having the disease, there is a 1% chance of a false negative result (and 99% chance of getting a true positive result), i.e.
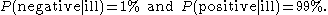
Calculations
The fraction of individuals in the whole group who are well and test negative (true negative):
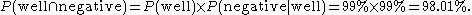
The fraction of individuals in the whole group who are ill and test positive (true positive):
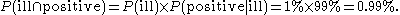
The fraction of individuals in the whole group who have false positive results:
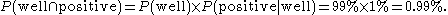
The fraction of individuals in the whole group who have false negative results:
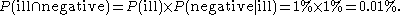
Furthermore, the fraction of individuals in the whole group who test positive:
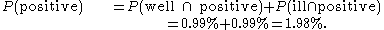
Finally, the probability that an individual actually has the disease, given that the test result is positive:
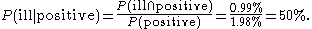
Conclusion
In this example, it should be easy to relate to the difference between the conditional probabilities P(positive | ill) which with the assumed probabilities is 99%, and P(ill | positive) which is 50%: the first is the probability that an individual who has the disease tests positive; the second is the probability that an individual who tests positive actually has the disease. Thus, it is to be expected that roughly the same number of individuals receive the benefits of early treatment as are distressed by false negatives; these positive and negative effects can then be considered in deciding whether to carry out the screening.
External links

