Computer supported cooperative work
Encyclopedia
The term computer-supported cooperative work (CSCW) was first coined by Irene Greif and Paul M. Cashman in 1984, at a workshop attended by individuals interested in using technology to support people in their work. At about this same time, in 1987 Dr. Charles Findley presented the concept of Collaborative Learning-Work.
According to Carstensen and Schmidt, CSCW addresses "how collaborative activities and their coordination can be supported by means of computer systems." On the one hand, many authors consider that CSCW and groupware are synonyms. On the other hand, different authors claim that while groupware refers to real computer-based systems, CSCW focuses on the study of tools and techniques of groupware as well as their psychological, social, and organizational effects. The definition of Wilson (1991) expresses the difference between these two concepts:
Over the years, CSCW researchers have identified a number of core dimensions of cooperative work. A non-exhaustive list includes:
These concepts have largely been derived through the analysis of systems designed by researchers in the CSCW community, or through studies of existing systems (for example, Wikipedia). CSCW researchers that design and build systems try to address core concepts in novel ways. However, the complexity of the domain makes it difficult to produce conclusive results; the success of CSCW systems are often so contingent on the peculiarities of the social context that it is hard to generalize. Consequently, CSCW systems that are based on the design of successful ones may fail to be appropriated in other seemingly similar contexts for a variety of reasons that are nearly impossible to identify a priori. CSCW researcher Mark Ackerman calls this "divide between what we know we must support socially and what we can support technically" the socio-technical gap and describes CSCW's main research agenda to be "exploring, understanding, and hopefully ameliorating" this gap.
CSCW has traditionally held a conference every two years, supported by the ACM. Beginning in 2010, the conference will be held annually.
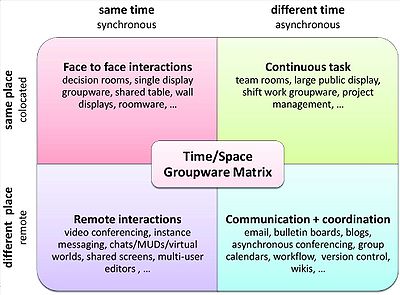 One of the most common ways of conceptualizing CSCW systems is to consider the context of a system's use. One such conceptualization is the CSCW Matrix, first introduced in 1988 by Johansen; it also appears in Baecker (1995). The matrix considers work contexts along two dimensions: first, whether collaboration is co-located or geographically distributed, and second, whether individuals collaborate synchronously (same time) or asynchronously (not depending on others to be around at the same time).
One of the most common ways of conceptualizing CSCW systems is to consider the context of a system's use. One such conceptualization is the CSCW Matrix, first introduced in 1988 by Johansen; it also appears in Baecker (1995). The matrix considers work contexts along two dimensions: first, whether collaboration is co-located or geographically distributed, and second, whether individuals collaborate synchronously (same time) or asynchronously (not depending on others to be around at the same time).
According to Carstensen and Schmidt, CSCW addresses "how collaborative activities and their coordination can be supported by means of computer systems." On the one hand, many authors consider that CSCW and groupware are synonyms. On the other hand, different authors claim that while groupware refers to real computer-based systems, CSCW focuses on the study of tools and techniques of groupware as well as their psychological, social, and organizational effects. The definition of Wilson (1991) expresses the difference between these two concepts:
Central concerns of CSCW
CSCW is a design-oriented academic field bringing together social psychologists, sociologists, anthropologists and computer scientists, among others. Despite the variety of disciplines, CSCW is an identifiable research field focused on understanding characteristics of interdependent group work with the objective of designing adequate computer-based technology to support such cooperative work.Over the years, CSCW researchers have identified a number of core dimensions of cooperative work. A non-exhaustive list includes:
- Awareness: individuals working together need to be able to gain some level of shared knowledge about each other's activities.
- Articulation work: cooperating individuals must somehow be able to partition work into units, divide it amongst themselves and, after the work is performed, reintegrate it.
- Appropriation (or tailorability): how an individual or group adapts a technology to their own particular situation; the technology may be appropriated in a manner completely unintended by the designers.
These concepts have largely been derived through the analysis of systems designed by researchers in the CSCW community, or through studies of existing systems (for example, Wikipedia). CSCW researchers that design and build systems try to address core concepts in novel ways. However, the complexity of the domain makes it difficult to produce conclusive results; the success of CSCW systems are often so contingent on the peculiarities of the social context that it is hard to generalize. Consequently, CSCW systems that are based on the design of successful ones may fail to be appropriated in other seemingly similar contexts for a variety of reasons that are nearly impossible to identify a priori. CSCW researcher Mark Ackerman calls this "divide between what we know we must support socially and what we can support technically" the socio-technical gap and describes CSCW's main research agenda to be "exploring, understanding, and hopefully ameliorating" this gap.
CSCW has traditionally held a conference every two years, supported by the ACM. Beginning in 2010, the conference will be held annually.
CSCW Matrix

Same time/same place
Face to face interaction- Roomware
- Shared tables, wall displays
- Digital whiteboards
- Electronic meeting systemElectronic meeting systemAn electronic meeting system is a type of computer software that facilitates creative problem solving and decision-making of groups within or across organizations. The term was coined by Jay Nunamaker et al. in 1991. The term is synonymous with Group Support Systems and essentially synonymous...
s - Single display groupware
Same time/different place
Remote interaction- Electronic meeting systemElectronic meeting systemAn electronic meeting system is a type of computer software that facilitates creative problem solving and decision-making of groups within or across organizations. The term was coined by Jay Nunamaker et al. in 1991. The term is synonymous with Group Support Systems and essentially synonymous...
s - VideoconferencingVideoconferencingVideoconferencing is the conduct of a videoconference by a set of telecommunication technologies which allow two or more locations to interact via two-way video and audio transmissions simultaneously...
- Real-time groupware
- Messaging (instant messagingInstant messagingInstant Messaging is a form of real-time direct text-based chatting communication in push mode between two or more people using personal computers or other devices, along with shared clients. The user's text is conveyed over a network, such as the Internet...
, emailEmailElectronic mail, commonly known as email or e-mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients. Modern email operates across the Internet or other computer networks. Some early email systems required that the author and the recipient both be online at the...
, chatOnline chatOnline chat may refer to any kind of communication over the Internet, that offers an instantaneous transmission of text-based messages from sender to receiver, hence the delay for visual access to the sent message shall not hamper the flow of communications in any of the directions...
)
Different time/different place
Communication + Coordination- Electronic meeting systemElectronic meeting systemAn electronic meeting system is a type of computer software that facilitates creative problem solving and decision-making of groups within or across organizations. The term was coined by Jay Nunamaker et al. in 1991. The term is synonymous with Group Support Systems and essentially synonymous...
s - WikiWikiA wiki is a website that allows the creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text editor. Wikis are typically powered by wiki software and are often used collaboratively by multiple users. Examples include...
- Blogs
- WorkflowWorkflowA workflow consists of a sequence of connected steps. It is a depiction of a sequence of operations, declared as work of a person, a group of persons, an organization of staff, or one or more simple or complex mechanisms. Workflow may be seen as any abstraction of real work...
- Version control
See also
- Collaborative working environmentCollaborative Working EnvironmentA collaborative working environment supports people in their individual and cooperative work. Research in CWE involves organisational, technical, and social issues....
- Collaborative working systemCollaborative working systemA collaborative work system is an organizational unit that emerges any time that collaboration takes place, whether it is formal or informal, intentional or unintentional.- Overview :...
- Collaborative softwareCollaborative softwareCollaborative software is computer software designed to help people involved in a common task achieve goals...
- Collaborative innovation network
- Computer-supported collaborationComputer-supported collaborationComputer-supported collaboration research focuses on technology that affects groups, organizations, communities and societies, e.g., voice mail and text chat. It grew from cooperative work study of supporting people's work activities and working relationships...
- Collaborative information seekingCollaborative information seekingCollaborative information seeking is a field of research that involves studying situations, motivations, and methods for people working in collaborative groups for information seeking projects, as well as building systems for supporting such activities. Such projects often involve information...
- Electronic meeting systemElectronic meeting systemAn electronic meeting system is a type of computer software that facilitates creative problem solving and decision-making of groups within or across organizations. The term was coined by Jay Nunamaker et al. in 1991. The term is synonymous with Group Support Systems and essentially synonymous...
- E-professionalE-professionalE-professional or "eprofessional" or even "eProfessional" is a term used in Europe to describe a professional whose work relies on concepts of telework or telecommuting: working at a distance using information and communication technologies, as well as online Collaboration E-professional or...
- E-work
- Integrated collaboration environmentIntegrated Collaboration EnvironmentAn integrated collaboration environment is an environment in which a virtual team do their work. Such environments allow companies to realize a number of competitive advantages by using their existing computers and network infrastructure for group and personal collaboration...
- Knowledge managementKnowledge managementKnowledge management comprises a range of strategies and practices used in an organization to identify, create, represent, distribute, and enable adoption of insights and experiences...
- Participatory designParticipatory designParticipatory design is an approach to design attempting to actively involve all stakeholders in the design process in order to help ensure the product designed meets their needs and is usable. The term is used in a variety of fields e.g...
CSCW most cited papers
The 47 CSCW Handbook Papers. This paper list is the result of a citation graph analysis of the CSCW Conference. It has been established in 2006 and reviewed by the CSCW Community. This list only contains papers published in one conference; papers published at other venues have also had significant impact on the CSCW community.
The “CSCW handbook” papers were chosen as the overall most
cited within the CSCW conference <...> It led to a list of 47 papers, corresponding to about 11% of
all papers.

