
Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry
Encyclopedia
There are numerous commonly used terms of relationship and comparison that refer to different aspects of teeth and are frequently utilized in articles about dentistry
. Many of them are included below as a sort of glossary
to assist with understanding the many articles that include these types of words
.
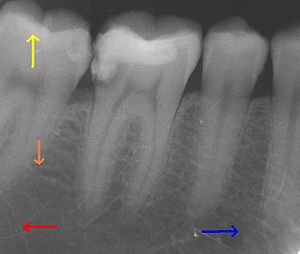 Anterior refers to the direction towards an individual's lips, as opposed to posterior, which refers to the directions towards the back of an individual's head. The term anterior teeth
Anterior refers to the direction towards an individual's lips, as opposed to posterior, which refers to the directions towards the back of an individual's head. The term anterior teeth
refers to incisor
s and canines
, as opposed to premolars and molars, which are posterior teeth.
Apical refers to the direction towards the root tip(s) of a tooth, as opposed to coronal, which refers to the direction towards the crown. It may also refer to something relating to the roots, such as apical support. When referring to direction in relation to entities on or of the crown, this term can be synonymous with both cervical and gingival.
Axial refers to a plane
parallel to the surface of a tooth. For example, if a drill bur would be inserted into a tooth from any side (proximal, facial or lingual), the depth of the hole is defined by the axial wall of the hole.
Buccal refers to the side of a tooth that is adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the cheek
, as opposed to lingual or palatal, which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the tongue
or palate
, respectively. Although technically referring only to posterior teeth (where the cheeks are present instead of lips, use of this term may extend to all teeth, anterior and posterior), this term may be employed to describe the facial surface of (or directions in relation to) anterior teeth as well.
Cervical, which simply means neck in Latin
(as in cervical vertebrae
), refers to the narrowing of the contours of the tooth surface at or near the CEJ
, where the crown meets the root. When referring to direction in relation to entities on or of the crown, it is nearly synonymous with both apical and gingival.
Coronal refers to the direction towards the crown of a tooth, as opposed to apical, which refers to the direction towards the tip(s) of the root(s). It may also refer to something relating to the crown, such as coronal forces.
Distal refers to the direction towards the last tooth in each quadrant of a dental arch, as opposed to mesial, which refers to the direction towards the anterior midline
. Each tooth can be described as having a distal surface and, for posterior teeth, a distobuccal (DB) and a distolingual (DL) corner or cusp
.
Facial refers to the side of a tooth that is adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the cheek
or lip
s, as opposed to lingual or palatal, which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the tongue
or palate
, respectively. This term is an umbrella term
for both the term buccal and labial.
Gingival refers to the direction towards the gingiva
(gums), synonymous with cervical and similar to apical. However, locations on teeth already more apical to the interface of the crown and root, referred to as the CEJ
, tend not to be described using this term, as it would lead to confusion, as the exact definition is ambiguous. Additionally, this term would not be used when referring to a tooth ex vivo
.
Incisal refers either to the direction towards the biting edge of anterior teeth or to something relating to this edge, such as the terms incisal guidance or incisal edge. This is the sister term to occlusal, which related to the analogous location on posterior teeth.
Inferior, as usual, refers to the direction towards the feet of a human's body, as opposed to superior, which refers to the direction towards the head. However, use of these terms should enjoy only limited usage when discussing features of a tooth, as, for example, something more inferior on a mandibular tooth will be situated more superior on a maxilla
ry tooth, as they exhibit an inverted relationship. It is for this reason that the terms coronal and apical are substituted.
Labial refers to the side of a tooth that is adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the lip
, as opposed to lingual or palatal, which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the tongue
or palate
, respectively. Although technically referring only to anterior teeth (where the lips are present instead of cheeks), use of the term buccal may extend to all teeth, anterior and posterior.
Lingual refers to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the tongue, as opposed to buccal, labial or facial which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the cheek or lips, respectively. Although this term is technically specific to the mandible, it enjoys extensive use in reference to the maxilla
as well (see Palatal.)
Mandibular refers to entities related to the mandible.
Marginal may be used to refer to a number of different 'margins' that are involved in dentistry. The edge of tooth structure that is prepared to meet the edge of a prosthetic crown
is called a margin, as is the aforementioned edge of the crown; an example of this usage would be "a poorly fitting crown might exhibit marginal leakage." The gingiva
and bone that abut the teeth are referred to as 'marginal', as in marginal periodontitis. The bulk of tooth structure on the occlusal surface at the point of contact of posterior teeth is referred to as the marginal ridge.
Maxillary refers to entities related to the maxilla
.
 Mesial refers to the direction towards the anterior midline
Mesial refers to the direction towards the anterior midline
in a dental arch, as opposed to distal, which refers to the direction towards the last tooth in each quadrant. Each tooth can be described as having a mesial surface and, for posterior teeth, a mesiobuccal (MB) and a mesiolingual (ML) corner or cusp
.
Occlusal
refers either to the direction towards the biting surface of posterior teeth or to something relating to this surface, such as the terms occlusal interference or occlusal surface. This is the sister term to incisal, which related to the analogous location on anterior teeth. Restorations are designated by their location on a tooth, and abbreviated as such. Thus, for example, an amalgam
restoration on the distal-occlusal of a tooth would be termed a DO amalgam.
Palatal refers to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the palate
, as opposed to buccal, labial or facial which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the cheek or lips, respectively. This term is strictly used in the maxilla
.
Posterior refers to the direction towards the back of an individual's head, as opposed to anterior, which refers to the directions towards an individual's lips. The term posterior teeth
refers to premolar
s and molars
, as opposed to incisor
s and canines
, which are anterior teeth.
Proximal refers to the surfaces of teeth that normally lie adjacent to another tooth. It is an umbrella term
which includes both mesial and distal, such as when referring to the proximal surfaces of teeth.
Superior, as usual, refers to the direction towards the head of a human's body, as opposed to inferior, which refers to the direction towards the feet. However, use of these terms should enjoy only limited usage when discussing features of a tooth, as, for example, something more superior on a mandibular tooth will be situated more inferior on a maxilla
ry tooth, as they exhibit an inverted relationship. It is for this reason that the terms coronal and apical are substituted.
Dentistry
Dentistry is the branch of medicine that is involved in the study, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases, disorders and conditions of the oral cavity, maxillofacial area and the adjacent and associated structures and their impact on the human body. Dentistry is widely considered...
. Many of them are included below as a sort of glossary
Glossary
A glossary, also known as an idioticon, vocabulary, or clavis, is an alphabetical list of terms in a particular domain of knowledge with the definitions for those terms...
to assist with understanding the many articles that include these types of words
Jargon
Jargon is terminology which is especially defined in relationship to a specific activity, profession, group, or event. The philosophe Condillac observed in 1782 that "Every science requires a special language because every science has its own ideas." As a rationalist member of the Enlightenment he...
.
Terms

Anterior teeth
In dentistry, the term anterior teeth can refer to:*Incisors in upper or lower jaw*Canines in upper or lower jaw...
refers to incisor
Incisor
Incisors are the first kind of tooth in heterodont mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and mandible below.-Function:...
s and canines
Canine tooth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, fangs, or eye teeth, are relatively long, pointed teeth...
, as opposed to premolars and molars, which are posterior teeth.
Apical refers to the direction towards the root tip(s) of a tooth, as opposed to coronal, which refers to the direction towards the crown. It may also refer to something relating to the roots, such as apical support. When referring to direction in relation to entities on or of the crown, this term can be synonymous with both cervical and gingival.
Axial refers to a plane
Plane (mathematics)
In mathematics, a plane is a flat, two-dimensional surface. A plane is the two dimensional analogue of a point , a line and a space...
parallel to the surface of a tooth. For example, if a drill bur would be inserted into a tooth from any side (proximal, facial or lingual), the depth of the hole is defined by the axial wall of the hole.
Buccal refers to the side of a tooth that is adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the cheek
Cheek
Cheeks constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. They may also be referred to as jowls. "Buccal" means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve...
, as opposed to lingual or palatal, which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the tongue
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly...
or palate
Palate
The palate is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but, in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separate. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior...
, respectively. Although technically referring only to posterior teeth (where the cheeks are present instead of lips, use of this term may extend to all teeth, anterior and posterior), this term may be employed to describe the facial surface of (or directions in relation to) anterior teeth as well.
Cervical, which simply means neck in Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
(as in cervical vertebrae
Cervical vertebrae
In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also...
), refers to the narrowing of the contours of the tooth surface at or near the CEJ
Cementoenamel junction
The cementoenamel junction, frequently abbreviated as the CEJ, is an anatomical border identified on a tooth. It is the location where the enamel, which covers the anatomical crown of a tooth, and the cementum, which covers the anatomical root of a tooth, meet...
, where the crown meets the root. When referring to direction in relation to entities on or of the crown, it is nearly synonymous with both apical and gingival.
Coronal refers to the direction towards the crown of a tooth, as opposed to apical, which refers to the direction towards the tip(s) of the root(s). It may also refer to something relating to the crown, such as coronal forces.
Distal refers to the direction towards the last tooth in each quadrant of a dental arch, as opposed to mesial, which refers to the direction towards the anterior midline
Dental midline
The dental midline is a term that refers to the midsagittal line of maxillary and mandibular dental arches possessing teeth of ideal size, shape and position, when situated in maximum intercuspation. Each arch also possesses its own midline, which can be used to refer to the location of contact...
. Each tooth can be described as having a distal surface and, for posterior teeth, a distobuccal (DB) and a distolingual (DL) corner or cusp
Cusp (dentistry)
A cusp is an occlusal or incisal eminence on a tooth.Canine teeth, otherwise known as cuspids, each possess a single cusp, while premolars, otherwise known as bicuspids, possess two each. Molars normally possess either four or five cusps...
.
Facial refers to the side of a tooth that is adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the cheek
Cheek
Cheeks constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. They may also be referred to as jowls. "Buccal" means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve...
or lip
Lip
Lips are a visible body part at the mouth of humans and many animals. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech...
s, as opposed to lingual or palatal, which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the tongue
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly...
or palate
Palate
The palate is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but, in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separate. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior...
, respectively. This term is an umbrella term
Umbrella term
An umbrella term is a word that provides a superset or grouping of concepts that all fall under a single common category. Umbrella term is also called a hypernym. For example, cryptology is an umbrella term that encompasses cryptography and cryptanalysis, among other fields...
for both the term buccal and labial.
Gingival refers to the direction towards the gingiva
Gingiva
The gingiva , or gums, consists of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth.-General description:...
(gums), synonymous with cervical and similar to apical. However, locations on teeth already more apical to the interface of the crown and root, referred to as the CEJ
Cementoenamel junction
The cementoenamel junction, frequently abbreviated as the CEJ, is an anatomical border identified on a tooth. It is the location where the enamel, which covers the anatomical crown of a tooth, and the cementum, which covers the anatomical root of a tooth, meet...
, tend not to be described using this term, as it would lead to confusion, as the exact definition is ambiguous. Additionally, this term would not be used when referring to a tooth ex vivo
Ex vivo
Ex vivo means that which takes place outside an organism. In science, ex vivo refers to experimentation or measurements done in or on tissue in an artificial environment outside the organism with the minimum alteration of natural conditions...
.
Incisal refers either to the direction towards the biting edge of anterior teeth or to something relating to this edge, such as the terms incisal guidance or incisal edge. This is the sister term to occlusal, which related to the analogous location on posterior teeth.
Inferior, as usual, refers to the direction towards the feet of a human's body, as opposed to superior, which refers to the direction towards the head. However, use of these terms should enjoy only limited usage when discussing features of a tooth, as, for example, something more inferior on a mandibular tooth will be situated more superior on a maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
ry tooth, as they exhibit an inverted relationship. It is for this reason that the terms coronal and apical are substituted.
Labial refers to the side of a tooth that is adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the lip
Lip
Lips are a visible body part at the mouth of humans and many animals. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech...
, as opposed to lingual or palatal, which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the tongue
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly...
or palate
Palate
The palate is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but, in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separate. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior...
, respectively. Although technically referring only to anterior teeth (where the lips are present instead of cheeks), use of the term buccal may extend to all teeth, anterior and posterior.
Lingual refers to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the tongue, as opposed to buccal, labial or facial which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the cheek or lips, respectively. Although this term is technically specific to the mandible, it enjoys extensive use in reference to the maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
as well (see Palatal.)
Mandibular refers to entities related to the mandible.
Marginal may be used to refer to a number of different 'margins' that are involved in dentistry. The edge of tooth structure that is prepared to meet the edge of a prosthetic crown
Crown (dentistry)
A crown is a type of dental restoration which completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. Crowns are often needed when a large cavity threatens the ongoing health of a tooth. They are typically bonded to the tooth using a dental cement. Crowns can be made from many materials, which...
is called a margin, as is the aforementioned edge of the crown; an example of this usage would be "a poorly fitting crown might exhibit marginal leakage." The gingiva
Gingiva
The gingiva , or gums, consists of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth.-General description:...
and bone that abut the teeth are referred to as 'marginal', as in marginal periodontitis. The bulk of tooth structure on the occlusal surface at the point of contact of posterior teeth is referred to as the marginal ridge.
Maxillary refers to entities related to the maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
.

Dental midline
The dental midline is a term that refers to the midsagittal line of maxillary and mandibular dental arches possessing teeth of ideal size, shape and position, when situated in maximum intercuspation. Each arch also possesses its own midline, which can be used to refer to the location of contact...
in a dental arch, as opposed to distal, which refers to the direction towards the last tooth in each quadrant. Each tooth can be described as having a mesial surface and, for posterior teeth, a mesiobuccal (MB) and a mesiolingual (ML) corner or cusp
Cusp (dentistry)
A cusp is an occlusal or incisal eminence on a tooth.Canine teeth, otherwise known as cuspids, each possess a single cusp, while premolars, otherwise known as bicuspids, possess two each. Molars normally possess either four or five cusps...
.
Occlusal
Occlusion (dentistry)
Occlusion, in a dental context, means simply the contact between teeth. More technically, it is the relationship between the maxillary and mandibular teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or at rest....
refers either to the direction towards the biting surface of posterior teeth or to something relating to this surface, such as the terms occlusal interference or occlusal surface. This is the sister term to incisal, which related to the analogous location on anterior teeth. Restorations are designated by their location on a tooth, and abbreviated as such. Thus, for example, an amalgam
Amalgam (dentistry)
Amalgam is an alloy containing mercury. The term is commonly used for the amalgam employed as material for dental fillings, which consists of mercury , silver , tin , copper , and other trace metals...
restoration on the distal-occlusal of a tooth would be termed a DO amalgam.
Palatal refers to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the palate
Palate
The palate is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but, in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separate. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior...
, as opposed to buccal, labial or facial which refer to the side of a tooth adjacent to (or the direction towards) the inside of the cheek or lips, respectively. This term is strictly used in the maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
.
Posterior refers to the direction towards the back of an individual's head, as opposed to anterior, which refers to the directions towards an individual's lips. The term posterior teeth
Posterior teeth
In dentistry, the term posterior teeth can refer to:*Premolars in upper or lower jaw*Molars in upper or lower jaw...
refers to premolar
Premolar
The premolar teeth or bicuspids are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two cusps. Premolars can be considered as a 'transitional tooth' during chewing, or...
s and molars
Molar (tooth)
Molars are the rearmost and most complicated kind of tooth in most mammals. In many mammals they grind food; hence the Latin name mola, "millstone"....
, as opposed to incisor
Incisor
Incisors are the first kind of tooth in heterodont mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and mandible below.-Function:...
s and canines
Canine tooth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, fangs, or eye teeth, are relatively long, pointed teeth...
, which are anterior teeth.
Proximal refers to the surfaces of teeth that normally lie adjacent to another tooth. It is an umbrella term
Umbrella term
An umbrella term is a word that provides a superset or grouping of concepts that all fall under a single common category. Umbrella term is also called a hypernym. For example, cryptology is an umbrella term that encompasses cryptography and cryptanalysis, among other fields...
which includes both mesial and distal, such as when referring to the proximal surfaces of teeth.
Superior, as usual, refers to the direction towards the head of a human's body, as opposed to inferior, which refers to the direction towards the feet. However, use of these terms should enjoy only limited usage when discussing features of a tooth, as, for example, something more superior on a mandibular tooth will be situated more inferior on a maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
ry tooth, as they exhibit an inverted relationship. It is for this reason that the terms coronal and apical are substituted.

