
Cologarithm
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, the base-b cologarithm, sometimes shortened to colog, of a number is the base-b logarithm
of the reciprocal
of the number. It is equal to the negative base-b logarithm of the number.
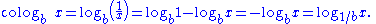
In chemistry
, a decimal cologarithm is indicated by the letter p (originally the Greek letter ρ).
For example, pK
= – log10 K and pH
= – log10 [H3O+].
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the base-b cologarithm, sometimes shortened to colog, of a number is the base-b logarithm
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
of the reciprocal
Multiplicative inverse
In mathematics, a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal for a number x, denoted by 1/x or x−1, is a number which when multiplied by x yields the multiplicative identity, 1. The multiplicative inverse of a fraction a/b is b/a. For the multiplicative inverse of a real number, divide 1 by the...
of the number. It is equal to the negative base-b logarithm of the number.
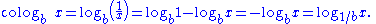
In chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, a decimal cologarithm is indicated by the letter p (originally the Greek letter ρ).
For example, pK
Acid dissociation constant
An acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions...
= – log10 K and pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
= – log10 [H3O+].

