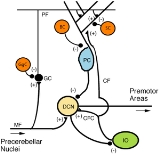
Climbing fiber
Encyclopedia
Climbing fibers are the name given to a series of neuron
al projections from the inferior olivary nucleus
located in the medulla oblongata
.
These axon
s pass through the pons
and enter the cerebellum
via the inferior cerebellar peduncle
where they form synapse
s with the deep cerebellar nuclei and Purkinje cell
s. Each climbing fiber will form synapses with 1-10 Purkinje cells.
Early in development, Purkinje cells are innervated by multiple climbing fibers, but as the cerebellum matures, these inputs gradually become eliminated resulting in a single climbing fiber input per Purkinje cell.
These fibers provide very powerful, excitatory input to the cerebellum which results in the generation of complex spike excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in Purkinje cells. In this way climbing fibers (CFs) perform a central role in motor behaviors.
Climbing fiber activation is thought to serve as a motor error signal sent to the cerebellum, and is an important signal for motor timing.
These climbing fibers carry information from various sources such as the spinal cord
, vestibular system
, red nucleus
, superior colliculus
, reticular formation
and sensory and motor cortices.
Although in the central nervous system, these fibers are able to undergo to remarkable regenerative modifications in response to injuries, being able to generate new branches by sprouting to innervate surrounding Purkinje cells if these lose their CF innervation. This kind of injury-induced sprouting has been shown to need the growth associated protein GAP-43.
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
al projections from the inferior olivary nucleus
Inferior olivary nucleus
The inferior olivary nucleus is the largest nucleus situated in the olivary body, part of the medulla oblongata.-Function:It is closely associated with the cerebellum, meaning that it is involved in control and coordination of movements, sensory processing and cognitive tasks likely by encoding the...
located in the medulla oblongata
Medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata is the lower half of the brainstem. In discussions of neurology and similar contexts where no ambiguity will result, it is often referred to as simply the medulla...
.
These axon
Axon
An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma....
s pass through the pons
Pons
The pons is a structure located on the brain stem, named after the Latin word for "bridge" or the 16th-century Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio . It is superior to the medulla oblongata, inferior to the midbrain, and ventral to the cerebellum. In humans and other bipeds this means it...
and enter the cerebellum
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language, and in regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established...
via the inferior cerebellar peduncle
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
The upper part of the posterior district of the medulla oblongata is occupied by the inferior cerebellar peduncle , a thick rope-like strand situated between the lower part of the fourth ventricle and the roots of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.Each cerebellar inferior peduncle connects the...
where they form synapse
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell...
s with the deep cerebellar nuclei and Purkinje cell
Purkinje cell
For the cells of the electrical conduction system of the heart, see Purkinje fibersPurkinje cells, or Purkinje neurons , are a class of GABAergic neurons located in the cerebellar cortex...
s. Each climbing fiber will form synapses with 1-10 Purkinje cells.
Early in development, Purkinje cells are innervated by multiple climbing fibers, but as the cerebellum matures, these inputs gradually become eliminated resulting in a single climbing fiber input per Purkinje cell.
These fibers provide very powerful, excitatory input to the cerebellum which results in the generation of complex spike excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in Purkinje cells. In this way climbing fibers (CFs) perform a central role in motor behaviors.
Climbing fiber activation is thought to serve as a motor error signal sent to the cerebellum, and is an important signal for motor timing.
These climbing fibers carry information from various sources such as the spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
, vestibular system
Vestibular system
The vestibular system, which contributes to balance in most mammals and to the sense of spatial orientation, is the sensory system that provides the leading contribution about movement and sense of balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes the labyrinth of...
, red nucleus
Red nucleus
The red nucleus is a structure in the rostral midbrain involved in motor coordination. It comprises a caudal magnocellular and a rostral parvocellular part.-Function:...
, superior colliculus
Superior colliculus
The optic tectum or simply tectum is a paired structure that forms a major component of the vertebrate midbrain. In mammals this structure is more commonly called the superior colliculus , but, even in mammals, the adjective tectal is commonly used. The tectum is a layered structure, with a...
, reticular formation
Reticular formation
The reticular formation is a part of the brain that is involved in actions such as awaking/sleeping cycle, and filtering incoming stimuli to discriminate irrelevant background stimuli...
and sensory and motor cortices.
Although in the central nervous system, these fibers are able to undergo to remarkable regenerative modifications in response to injuries, being able to generate new branches by sprouting to innervate surrounding Purkinje cells if these lose their CF innervation. This kind of injury-induced sprouting has been shown to need the growth associated protein GAP-43.

