
Climate classification
Encyclopedia
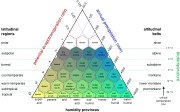
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
s. A climate classification may correlate closely with a biome
Biome
Biomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often referred to as ecosystems. Some parts of the earth have more or less the same kind of abiotic and biotic factors spread over a...
category, as climate is a major influence on biological life in a region. The most popular classification scheme is probably the Köppen climate classification
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by Crimea German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen himself, notably in 1918 and 1936...
scheme.
Climate classification systems include:
- Aridity indexAridity indexAn aridity index is a numerical indicator of the degree of dryness of the climate at a given location. A number of aridity indices have been proposed ; these indicators serve to identify, locate or delimit regions that suffer from a deficit of available water, a condition that can severely affect...
- Köppen climate classificationKöppen climate classificationThe Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by Crimea German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen himself, notably in 1918 and 1936...
- Holdridge Life Zone Classification SystemHoldridge life zonesThe Holdridge life zones system is a global bioclimatic scheme for the classification of land areas. It was first published by Leslie Holdridge in 1947, and updated in 1967. It is a relatively simple system based on few empirical data, giving objective mapping criteria...
See also
- BiomeBiomeBiomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often referred to as ecosystems. Some parts of the earth have more or less the same kind of abiotic and biotic factors spread over a...
- Ecological land classificationEcological land classificationEcological land classification is defined as being a cartographical delineation of distinct ecological areas, identified by their geology, topography, soils, vegetation, climate conditions, living species, habitats, water resources, as well as anthropic factors...
- EcozoneEcozoneAn ecozone is the broadest biogeographic division of the Earth's land surface, based on distributional patterns of terrestrial organisms.Ecozones delineate large areas of the Earth's surface within which organisms have been evolving in relative isolation over long periods of time, separated from...
- Geographical zoneGeographical zoneThe five main latitude regions of the Earth's surface comprise geographical zones, divided by the major circles of latitude. The differences between them relate to climate, and the behaviour of the Sun...
- Hardiness zoneHardiness zoneA hardiness zone is a geographically defined area in which a specific category of plant life is capable of growing, as defined by climatic conditions, including its ability to withstand the minimum temperatures of the zone...

