
Cholinergic urticaria
Encyclopedia
Cholinergic urticaria is a subcategory of physical urticaria
(aka hives) that is a skin rash brought on by a hypersensitive reaction to body heat. Symptoms follow any stimulus to sweat such as exercise (sometimes called exercise-induced urticaria, see Exercise urticaria
), heat from the sun (which could also indicate solar urticaria), saunas, hot showers (reaction to water can also indicate water urticaria), spicy foods which may cause an increase in body temperature or even stress due to blushing or anger. Some people only have symptoms during the winter months where their body temperature rises when it is unacclimatized to heat. Consistently exercising to break a sweat before the onset of cold weather, and through the winter months may reduce the symptoms greatly.
One of the main causes of cholinergic urticaria is stress, especially among teenagers. Therapy can sometimes aid in treatment. Severe cases of cholinergic urticaria can prove to be extremely problematic for the victim as it is difficult for those affected to walk outside or even work.
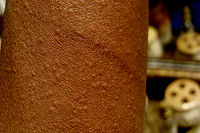 The visible hives (sometimes called heat bumps) appear as a multitude of small 2–3 mm welts typically surrounded by patches of red skin. The affected area will often feel warm and can be extremely itchy or exhibit a burning sensation. Typically the rash occurs on the upper trunk and the arms but can appear on other parts of the body. The rash may be worse in areas where clothing restricts the skin's ability to cool itself such as hat brims, waist bands, tight collars, backpack straps, the wrist watch area, etc. This can be compounded since many people with cholinergic urticaria also have pressure urticaria, in which pressure on the skin causes a reaction.
The visible hives (sometimes called heat bumps) appear as a multitude of small 2–3 mm welts typically surrounded by patches of red skin. The affected area will often feel warm and can be extremely itchy or exhibit a burning sensation. Typically the rash occurs on the upper trunk and the arms but can appear on other parts of the body. The rash may be worse in areas where clothing restricts the skin's ability to cool itself such as hat brims, waist bands, tight collars, backpack straps, the wrist watch area, etc. This can be compounded since many people with cholinergic urticaria also have pressure urticaria, in which pressure on the skin causes a reaction.
The rash typically develops within a few minutes of a rise in body temperature but can take longer to appear visibly on the skin. The visible rash is often preceded by a general warming of the skin or itchiness. The hives last from a half an hour to several hours with a mean time of 80 minutes, with the duration often contingent on the severity of the outbreak.
The sudden rash, if not proved by doctors to be an allergy, and if accompanied by strangely unrelated symptoms such as migraines, slight arthritis, mood swings, depression, indulgence in addictive and/or self abusive activities such alcohol for example, including sudden increase or decrease in weight loss due to loss of appetite (which was looked over due to depression or major alter in a persons life), could suggest hyperthyroidism
or hypothyroidism
.
Aspirin can sometimes worsen symptoms as may other drugs.
(atopic dermatitis
), allergic conjunctivitis
, allergic rhinitis
or asthma
. These other atopic reactions can sometimes be triggered by the urticaria attack. There is some evidence that in at least some individuals the condition is hereditary.
The age of onset is anywhere from 10-30 and the condition may occur spontaneously in people with no history of the condition. People who are chronically affected by the condition will sometimes go through phases of no reactions and phases where their skin is hypersensitive. These phases may relate to the season, diet changes, or other environmental factors, but often have no obvious cause. Most people who are afflicted by this condition maintain a tendency for outbreaks for several years (anywhere from 3–30 years) before it finally disappears.
The name cholinergic urticaria comes from studies where some people with the disorder produce a rash when injected with the neurochemical acetylcholine
; however, it is not clear how acetylcholine
is involved in the reaction.
Some patients with cholinergic urticaria have been seen to have an IgE mediated allergy to their own sweat - it is not clear whether this is due to the disorder having sub-types.
.
Often it is handled just with limiting one's exposure to triggers such as strenuous exercise or heat. For some, the reaction can be limited by making sure to wear light breathable clothing allowing the body to remain cool. Also, gradually warming the body with light exercise first can help limit the effects in some people. Since an attack can often be felt coming on, it can sometimes be halted by rapid cooling, such as applying cold water or an ice pack to the skin. This treatment can also result in an adverse reaction, depending on the sensitivity of the person affected. Sudden temperature change is a known trigger for cholinergic urticaria. Exercising consistently to break a sweat before the onset of cold weather and throughout the winter significantly reduces the symptoms in some cases.
s such as Loratadine
, Desloratadine
, Cetirizine
, Levocetirizine
and Fexofenadine
. These drugs are H1-receptor antagonists, and when taken prophylactically on a regular basis will mask the symptoms of Cholinergic Urticaria in the majority of patients. In some recalcitrant cases, doctors advise increasing the dose above manufacturer guidelines. Should non-sedating therapy not prove successful, the sedating antihistamine drug Hydroxyzine
is often trialled, however it may not be well tolerated due to the main side effect of drowsiness.
For some people, H2-receptor antagonist
s such as Cimetidine
and Ranitidine
can also help control symptoms either protectively or by lessening symptoms when an attack occurs. When taken in combination with an H1 antagonist it has been shown to have a synergistic effect which is more effective than either treatment alone. The use of ranitidine (or other H2 antagonist) for urticaria is considered an off-label use, since these drugs are primarily used for the treatment of peptic ulcer
disease (PUD) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Tricyclic antidepressant
s such as Doxepin
, also are often potent H1 and H2 antagonists and may have a role in therapy, although side effects limit their use.
Anabolic Steroids such as Danazol
have in some cases proven effective in treating Cholinergic Urticaria - it is thought that this is due to the drug's beneficial effect on protease inhibitors such as alpha 1-antichymotrypsin
.
The anti-IgE monoclonal antibody Omalizumab
has been seen in some cases to cause symptom reduction or resolution, research into this drug's efficacy and method of action on urticarial conditions is ongoing.
There are some reports that anticholinergic
agents such as Butylscopolamine are effective in treating the disorder.
None of these treatments are surefire means of controlling attacks. Some people prove to be treatment resistant, and medications can suddenly cease being as effective as they once were. In these instances, changes to a treatment plan can sometimes help. It can be difficult to determine appropriate medications since some require a day or two to build up to effective levels, and since the condition is intermittent and outbreaks typically clear up without any treatment.
can sometimes lessen severity and occurrence. Additionally, methods similar to psychological pain management can be used to shift focus away from the discomfort and itchiness during an attack.
Many people suffering from chronic conditions like urticaria use some form of alternative medicine
such as meditation, acupuncture, or chinese herbs. There are little to no data to support the effectiveness of most of these therapies. Urticaria is often intermittent and idiopathic and can be caused by stress, which amplifies the placebo effect
. As such, many alternative treatments may seem to work great when in reality it is only a combination of the placebo effect and a chance remission
in the disease.
Diet changes are often tried by people with urticaria in attempts to stop what is presumed to be a food allergy. Also, people often try changing their laundry detergents, shampoos, soaps, etc. While food and other allergies can cause hive outbreaks, cholinergic urticaria and other urticaria outbreaks often occur on their own with no connection to food or other allergy. Urticaria's intermittent nature can fool people into thinking that it is caused by an allergy to food or product.
Urticaria
Urticaria is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives is frequently caused by allergic reactions; however, there are many non-allergic causes...
(aka hives) that is a skin rash brought on by a hypersensitive reaction to body heat. Symptoms follow any stimulus to sweat such as exercise (sometimes called exercise-induced urticaria, see Exercise urticaria
Exercise urticaria
Exercise urticaria is a form of urticaria that happens during or after exercise, e.g. jogging or running. Urticaria is an allergic reaction in the skin characterized by itching -- as well as possible rash, swelling or hives -- on the legs, arms, torso or neck...
), heat from the sun (which could also indicate solar urticaria), saunas, hot showers (reaction to water can also indicate water urticaria), spicy foods which may cause an increase in body temperature or even stress due to blushing or anger. Some people only have symptoms during the winter months where their body temperature rises when it is unacclimatized to heat. Consistently exercising to break a sweat before the onset of cold weather, and through the winter months may reduce the symptoms greatly.
One of the main causes of cholinergic urticaria is stress, especially among teenagers. Therapy can sometimes aid in treatment. Severe cases of cholinergic urticaria can prove to be extremely problematic for the victim as it is difficult for those affected to walk outside or even work.
Symptoms
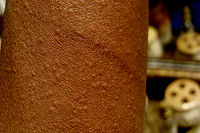
The rash typically develops within a few minutes of a rise in body temperature but can take longer to appear visibly on the skin. The visible rash is often preceded by a general warming of the skin or itchiness. The hives last from a half an hour to several hours with a mean time of 80 minutes, with the duration often contingent on the severity of the outbreak.
The sudden rash, if not proved by doctors to be an allergy, and if accompanied by strangely unrelated symptoms such as migraines, slight arthritis, mood swings, depression, indulgence in addictive and/or self abusive activities such alcohol for example, including sudden increase or decrease in weight loss due to loss of appetite (which was looked over due to depression or major alter in a persons life), could suggest hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the term for overactive tissue within the thyroid gland causing an overproduction of thyroid hormones . Hyperthyroidism is thus a cause of thyrotoxicosis, the clinical condition of increased thyroid hormones in the blood. Hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis are not synonymous...
or hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of hypothyroidism worldwide but it can be caused by other causes such as several conditions of the thyroid gland or, less commonly, the pituitary gland or...
.
Aspirin can sometimes worsen symptoms as may other drugs.
Frequency
Cholinergic urticaria is a fairly common type of hives and is often comorbid with other forms of urticaria, especially chronic urticaria. The prevalence of the disorder is also higher in people who have other atopic conditions such as eczemaEczema
Eczema is a form of dermatitis, or inflammation of the epidermis . In England, an estimated 5.7 million or about one in every nine people have been diagnosed with the disease by a clinician at some point in their lives.The term eczema is broadly applied to a range of persistent skin conditions...
(atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory, chronically relapsing, non-contagious and pruritic skin disorder...
), allergic conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva due to allergy. Although allergens differ between patients, the most common cause is hay fever. Symptoms consist of redness , oedema of the conjunctiva, itching and increased lacrimation...
, allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis, also known as pollenosis or hay fever, is an allergic inflammation of the nasal airways.It occurs when an allergen, such as pollen, dust or animal dander is inhaled by an individual with a sensitized immune system...
or asthma
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
. These other atopic reactions can sometimes be triggered by the urticaria attack. There is some evidence that in at least some individuals the condition is hereditary.
The age of onset is anywhere from 10-30 and the condition may occur spontaneously in people with no history of the condition. People who are chronically affected by the condition will sometimes go through phases of no reactions and phases where their skin is hypersensitive. These phases may relate to the season, diet changes, or other environmental factors, but often have no obvious cause. Most people who are afflicted by this condition maintain a tendency for outbreaks for several years (anywhere from 3–30 years) before it finally disappears.
Physiology
All urticarias are caused by an elevated histamine release by the body's mast cells. With cholinergic urticaria the exact triggering mechanism for this response is unknown, but it is assumed to be related to the body's thermoregulatory response.The name cholinergic urticaria comes from studies where some people with the disorder produce a rash when injected with the neurochemical acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
The chemical compound acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system in many organisms including humans...
; however, it is not clear how acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
The chemical compound acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system in many organisms including humans...
is involved in the reaction.
Some patients with cholinergic urticaria have been seen to have an IgE mediated allergy to their own sweat - it is not clear whether this is due to the disorder having sub-types.
Treatment
Cholinergic urticaria can be very difficult to treat. Most treatment plans for cholinergic urticaria involve being aware of one's triggers, but this can be difficult since there is often comorbidity with other forms of urticaria and some urticaria is idiopathicIdiopathic
Idiopathic is an adjective used primarily in medicine meaning arising spontaneously or from an obscure or unknown cause. From Greek ἴδιος, idios + πάθος, pathos , it means approximately "a disease of its own kind". It is technically a term from nosology, the classification of disease...
.
Often it is handled just with limiting one's exposure to triggers such as strenuous exercise or heat. For some, the reaction can be limited by making sure to wear light breathable clothing allowing the body to remain cool. Also, gradually warming the body with light exercise first can help limit the effects in some people. Since an attack can often be felt coming on, it can sometimes be halted by rapid cooling, such as applying cold water or an ice pack to the skin. This treatment can also result in an adverse reaction, depending on the sensitivity of the person affected. Sudden temperature change is a known trigger for cholinergic urticaria. Exercising consistently to break a sweat before the onset of cold weather and throughout the winter significantly reduces the symptoms in some cases.
Clothing
Clothing is one of the most important ways to control your body temperature, and thus control any itching flare ups. In all cases, the less clothing you wear, the better it is to keep your body cool. Shorts, tank tops, ankle socks, quarter socks, bikini briefs, and thongs are all great for controlling this condition. Tank tops are great because they allow the armpits to breathe versus crew neck tshirts which keep you warmer. Boxers are loose and can provide a cooling effect, but ultimately is a lot of material and therefore holds in heat. Dressing in layers is very important, so that a light set of clothing is always accessible. The type of fabric is also very important. A breatheable moisture wicking material is generally best. Cotton, nylons, polyesters and wool are notorious for holding in moisture and heat. Alternative fabrics which wick moisture away are ideal, such as coolmax, dri-fit, supplex, etc.Pharmacotherapy
Drug treatment is typically in the form of non-sedating antihistamineAntihistamine
An H1 antagonist is a histamine antagonist of the H1 receptor that serves to reduce or eliminate effects mediated by histamine, an endogenous chemical mediator released during allergic reactions...
s such as Loratadine
Loratadine
Loratadine is a second-generation H1 histamine antagonist drug used to treat allergies. Structurally, it is closely related to tricyclic antidepressants such as imipramine, and distantly related to the atypical antipsychotic quetiapine. It is marketed by Schering-Plough under several trade names...
, Desloratadine
Desloratadine
Desloratadine is a drug used to treat allergies. It is marketed under several trade names such as NeoClarityn, Claramax, Clarinex, Larinex, Aerius, Dazit, Azomyr and Delot...
, Cetirizine
Cetirizine
Cetirizine , a second-generation antihistamine, is a major metabolite of hydroxyzine, and a racemic selective H1 receptor inverse agonist used in the treatment of allergies, hay fever, angioedema, and urticaria.-Availability:...
, Levocetirizine
Levocetirizine
Levocetirizine is a third-generation non-sedative antihistamine, developed from the second-generation antihistamine cetirizine. Chemically, levocetirizine is the active enantiomer of cetirizine. It is the L-enantiomer of the cetirizine racemate. Levocetirizine works by blocking histamine receptors...
and Fexofenadine
Fexofenadine
Fexofenadine is an antihistamine drug used in the treatment of hayfever and similar allergy symptoms...
. These drugs are H1-receptor antagonists, and when taken prophylactically on a regular basis will mask the symptoms of Cholinergic Urticaria in the majority of patients. In some recalcitrant cases, doctors advise increasing the dose above manufacturer guidelines. Should non-sedating therapy not prove successful, the sedating antihistamine drug Hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzine is a first-generation antihistamine of the diphenylmethane and piperazine classes. It was first synthesized by Union Chimique Belge in 1956 and was marketed by Pfizer in the United States later the same year, and is still in widespread use today....
is often trialled, however it may not be well tolerated due to the main side effect of drowsiness.
For some people, H2-receptor antagonist
H2-receptor antagonist
The H2 receptor antagonists are a class of drugs used to block the action of histamine on parietal cells in the stomach, decreasing the production of acid by these cells. H2 antagonists are used in the treatment of dyspepsia, although they have been surpassed in popularity by the more effective ...
s such as Cimetidine
Cimetidine
Cimetidine INN is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist that inhibits the production of acid in the stomach. It is largely used in the treatment of heartburn and peptic ulcers. It is marketed by GlaxoSmithKline under the trade name Tagamet...
and Ranitidine
Ranitidine
Ranitidine is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production. It is commonly used in treatment of peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease . Ranitidine is also used alongside fexofenadine and other antihistamines for the treatment of skin conditions...
can also help control symptoms either protectively or by lessening symptoms when an attack occurs. When taken in combination with an H1 antagonist it has been shown to have a synergistic effect which is more effective than either treatment alone. The use of ranitidine (or other H2 antagonist) for urticaria is considered an off-label use, since these drugs are primarily used for the treatment of peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer
A peptic ulcer, also known as PUD or peptic ulcer disease, is the most common ulcer of an area of the gastrointestinal tract that is usually acidic and thus extremely painful. It is defined as mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 0.5 cm...
disease (PUD) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants are heterocyclic chemical compounds used primarily as antidepressants. The TCAs were first discovered in the early 1950s and were subsequently introduced later in the decade; they are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms...
s such as Doxepin
Doxepin
Doxepin is a psychotropic agent with tricyclic antidepressant and anxiolytic properties, known under many brand-names such as Aponal, the original preparation by Boehringer-Mannheim, now part of the Roche group; Adapine, Doxal , Deptran, Sinquan and Sinequan...
, also are often potent H1 and H2 antagonists and may have a role in therapy, although side effects limit their use.
Anabolic Steroids such as Danazol
Danazol
Danazol is a derivative of the synthetic steroid ethisterone, a modified testosterone. Also known as 17alpha-ethinyl testosterone. Before becoming available as a generic drug, Danazol was marketed as Danocrine in the United States. It was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the...
have in some cases proven effective in treating Cholinergic Urticaria - it is thought that this is due to the drug's beneficial effect on protease inhibitors such as alpha 1-antichymotrypsin
Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin
Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin is an alpha globulin glycoprotein that is a member of the serpin superfamily.It inhibits the activity of certain enzymes called proteases, such as cathepsin G that is found in neutrophils, and chymases found in mast cells, by cleaving them into a different shape or...
.
The anti-IgE monoclonal antibody Omalizumab
Omalizumab
Omalizumab is a humanized antibody drug approved for patients with moderate-to-severe or severe allergic asthma, which is caused by hypersensitivity reactions to certain harmless environmental substances...
has been seen in some cases to cause symptom reduction or resolution, research into this drug's efficacy and method of action on urticarial conditions is ongoing.
There are some reports that anticholinergic
Anticholinergic
An anticholinergic agent is a substance that blocks the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the central and the peripheral nervous system. An example of an anticholinergic is dicycloverine, and the classic example is atropine....
agents such as Butylscopolamine are effective in treating the disorder.
None of these treatments are surefire means of controlling attacks. Some people prove to be treatment resistant, and medications can suddenly cease being as effective as they once were. In these instances, changes to a treatment plan can sometimes help. It can be difficult to determine appropriate medications since some require a day or two to build up to effective levels, and since the condition is intermittent and outbreaks typically clear up without any treatment.
Alternative and complementary medicine
Although the disease may be physiological in origin, psychological treatments such as stress managementStress management
Stress management is the alteration of stress and especially chronic stress often for the purpose of improving everyday functioning.Stress produces numerous symptoms which vary according to persons, situations, and severity. These can include physical health decline as well as depression. According...
can sometimes lessen severity and occurrence. Additionally, methods similar to psychological pain management can be used to shift focus away from the discomfort and itchiness during an attack.
Many people suffering from chronic conditions like urticaria use some form of alternative medicine
Alternative medicine
Alternative medicine is any healing practice, "that does not fall within the realm of conventional medicine." It is based on historical or cultural traditions, rather than on scientific evidence....
such as meditation, acupuncture, or chinese herbs. There are little to no data to support the effectiveness of most of these therapies. Urticaria is often intermittent and idiopathic and can be caused by stress, which amplifies the placebo effect
Placebo effect
Placebo effect may refer to:* Placebo effect, the tendency of any medication or treatment, even an inert or ineffective one, to exhibit results simply because the recipient believes that it will work...
. As such, many alternative treatments may seem to work great when in reality it is only a combination of the placebo effect and a chance remission
Post hoc ergo propter hoc
Post hoc ergo propter hoc, Latin for "after this, therefore because of this," is a logical fallacy that states, "Since that event followed this one, that event must have been caused by this one." It is often shortened to simply post hoc and is also sometimes referred to as false cause,...
in the disease.
Diet changes are often tried by people with urticaria in attempts to stop what is presumed to be a food allergy. Also, people often try changing their laundry detergents, shampoos, soaps, etc. While food and other allergies can cause hive outbreaks, cholinergic urticaria and other urticaria outbreaks often occur on their own with no connection to food or other allergy. Urticaria's intermittent nature can fool people into thinking that it is caused by an allergy to food or product.

