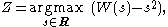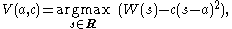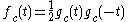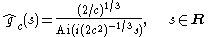Chernoff's distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, Chernoff's distribution, named after Herman Chernoff
, is the probability distribution
of the random variable
where W is a "two-sided" Wiener process
(or two-sided "Brownian motion
") satisfying W(0) = 0.
If
then V(0, c) has density
where gc has Fourier transform
given by
and where Ai it is the Airy function
. Thus fc is symmetric about 0 and the density ƒZ = ƒ1. Groeneboom (1989) shows that
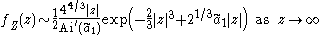
where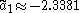 is the largest zero of the Airy function Ai and where
is the largest zero of the Airy function Ai and where 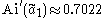 .
.
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, Chernoff's distribution, named after Herman Chernoff
Herman Chernoff
Herman Chernoff is an American applied mathematician, statistician and physicist formerly a professor at MIT and currently working at Harvard University.-Education:* Ph.D., Applied Mathematics, 1948. Brown University....
, is the probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of the random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
where W is a "two-sided" Wiener process
Wiener process
In mathematics, the Wiener process is a continuous-time stochastic process named in honor of Norbert Wiener. It is often called standard Brownian motion, after Robert Brown...
(or two-sided "Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
") satisfying W(0) = 0.
If
then V(0, c) has density
where gc has Fourier transform
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
given by
and where Ai it is the Airy function
Airy function
In the physical sciences, the Airy function Ai is a special function named after the British astronomer George Biddell Airy...
. Thus fc is symmetric about 0 and the density ƒZ = ƒ1. Groeneboom (1989) shows that
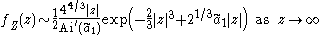
where
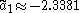 is the largest zero of the Airy function Ai and where
is the largest zero of the Airy function Ai and where 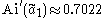 .
.