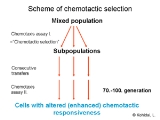
Chemotactic selection
Encyclopedia
Chemotaxis
receptors
are expressed in the surface membrane with diverse dynamics, some of them have long-term characteristics as they are determined genetically, others have short-term moiety as their assembly is induced ad hoc in the presence of the ligand. The diverse feature of the chemotaxis receptors and ligands provides the possibility to select chemotactic responder cells with a simple chemotaxis assay
. By chemotactic selection we can determine whether a still not characterized molecule acts via the long- or the short-term receptor pathway. Recent results proved that chemokines (e.g. IL-8
, RANTES
) are working on long-term chemotaxis receptors, while vasoactive peptides (e.g. endothelin
) act more on the short-term ones. Term chemotactic selection is also used to design a technique which separates eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells upon their chemotactic responsiveness to selector ligands.

Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis is the phenomenon in which somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food by swimming towards the highest concentration of food molecules,...
receptors
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a receptor is a molecule found on the surface of a cell, which receives specific chemical signals from neighbouring cells or the wider environment within an organism...
are expressed in the surface membrane with diverse dynamics, some of them have long-term characteristics as they are determined genetically, others have short-term moiety as their assembly is induced ad hoc in the presence of the ligand. The diverse feature of the chemotaxis receptors and ligands provides the possibility to select chemotactic responder cells with a simple chemotaxis assay
Chemotaxis assay
Chemotaxis assays are experimental tools for evaluation of chemotactic ability of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells.A wide variety of techniques are known and applied for such reason...
. By chemotactic selection we can determine whether a still not characterized molecule acts via the long- or the short-term receptor pathway. Recent results proved that chemokines (e.g. IL-8
IL-8
IL-8 can refer to:* Interleukin 8, a chemokine of the immune system* Illinois' 8th congressional district* Illinois Route 8...
, RANTES
RANTES
Chemokine ligand 5 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CCL5 gene. It is also known as RANTES .- Function :...
) are working on long-term chemotaxis receptors, while vasoactive peptides (e.g. endothelin
Endothelin
Endothelins are proteins that constrict blood vessels and raise blood pressure. They are normally kept in balance by other mechanisms, but when they are over-expressed, they contribute to high blood pressure and heart disease....
) act more on the short-term ones. Term chemotactic selection is also used to design a technique which separates eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells upon their chemotactic responsiveness to selector ligands.


