
Charge-exchange ionization
Encyclopedia
Charge-exchange ionization (also known as charge-transfer ionization) is a gas phase reaction between an ion
and an atom
or molecule
in which the charge of the ion is transferred to the neutral species.
For example
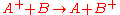 .
.
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
and an atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
or molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
in which the charge of the ion is transferred to the neutral species.
For example
 .
.

