
Chameleon particle
Encyclopedia
The "chameleon" is a postulated scalar particle with a non-linear self-interaction which gives the particle an effective mass that depends on its environment: the presence of other fields. It would have a small mass in much of intergalactic space, but a large mass in terrestrial experiments, making it difficult to detect. The chameleon is a possible candidate for dark energy
and dark matter
, and may contribute to cosmic inflation
.
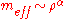 , where
, where  .
.
Chameleons also couple to photons, allowing photons and chameleons to oscillate between each other in the presence of an external magnetic field.
Chameleons can be confined in hollow containers because their mass increases rapidly as they penetrate the container wall, causing them to reflect. One strategy to search experimentally for chameleons is to direct photons into a cavity, confining the chameleons produced, and then to switch off the light source. Chameleons would be indicated by the presence of an afterglow as they decay back into photons.
The GammeV experiment is a search for axions, but has been used to look for chameleons too. It consists of a cylindrical chamber inserted in a 5T
magnetic field. The ends of the chamber are glass windows, allowing light from a laser to enter and afterglow to exit.
Dark energy
In physical cosmology, astronomy and celestial mechanics, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted theory to explain recent observations that the universe appears to be expanding...
and dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
, and may contribute to cosmic inflation
Cosmic inflation
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation or just inflation is the theorized extremely rapid exponential expansion of the early universe by a factor of at least 1078 in volume, driven by a negative-pressure vacuum energy density. The inflationary epoch comprises the first part...
.
Hypothetical properties
In most theories, chameleons have a mass that scales as some power of the local energy density: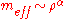 , where
, where  .
.Chameleons also couple to photons, allowing photons and chameleons to oscillate between each other in the presence of an external magnetic field.
Chameleons can be confined in hollow containers because their mass increases rapidly as they penetrate the container wall, causing them to reflect. One strategy to search experimentally for chameleons is to direct photons into a cavity, confining the chameleons produced, and then to switch off the light source. Chameleons would be indicated by the presence of an afterglow as they decay back into photons.
Experimental searches
A number of experiments have attempted to detect chameleons along with axions.The GammeV experiment is a search for axions, but has been used to look for chameleons too. It consists of a cylindrical chamber inserted in a 5T
Tesla (unit)
The tesla is the SI derived unit of magnetic field B . One tesla is equal to one weber per square meter, and it was defined in 1960 in honour of the inventor, physicist, and electrical engineer Nikola Tesla...
magnetic field. The ends of the chamber are glass windows, allowing light from a laser to enter and afterglow to exit.

