Chain rule (probability)
Encyclopedia
In probability
theory, the chain rule permits the calculation of any member of the joint distribution
of a set of random variables using only conditional probabilities.
Consider an indexed set of sets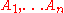 . To find the value of this member of the joint distribution, we can apply the definition of conditional probability to obtain:
. To find the value of this member of the joint distribution, we can apply the definition of conditional probability to obtain:
Repeating this process with each final term creates the product
For example:
The rule is useful in the study of Bayesian network
s, which describe a probability distribution in terms of conditional probabilities.
This rule is illustrated in the following example. Urn 1 has 1 black ball and 2 white balls and Urn 2 has 1 black ball and 3 white balls. Suppose we pick an urn at random and then select a ball from that urn. Let event A be choosing the first urn: P(A) = P(~A) = 1/2. Let event B be the chance we choose a white ball. Chance of choosing a white ball, given that we've chose the first urn, is P(B|A) = 2/3. Chance of choosing a white ball, given that we've chosen the second urn is P(B|~A) = 3/4. Event A, B would be their intersection; choosing the first urn and a white ball from it. The probability can be found by the chain rule for probability:
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
theory, the chain rule permits the calculation of any member of the joint distribution
Joint distribution
In the study of probability, given two random variables X and Y that are defined on the same probability space, the joint distribution for X and Y defines the probability of events defined in terms of both X and Y...
of a set of random variables using only conditional probabilities.
Consider an indexed set of sets
 . To find the value of this member of the joint distribution, we can apply the definition of conditional probability to obtain:
. To find the value of this member of the joint distribution, we can apply the definition of conditional probability to obtain:
Repeating this process with each final term creates the product
For example:
The rule is useful in the study of Bayesian network
Bayesian network
A Bayesian network, Bayes network, belief network or directed acyclic graphical model is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of random variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph . For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic...
s, which describe a probability distribution in terms of conditional probabilities.
This rule is illustrated in the following example. Urn 1 has 1 black ball and 2 white balls and Urn 2 has 1 black ball and 3 white balls. Suppose we pick an urn at random and then select a ball from that urn. Let event A be choosing the first urn: P(A) = P(~A) = 1/2. Let event B be the chance we choose a white ball. Chance of choosing a white ball, given that we've chose the first urn, is P(B|A) = 2/3. Chance of choosing a white ball, given that we've chosen the second urn is P(B|~A) = 3/4. Event A, B would be their intersection; choosing the first urn and a white ball from it. The probability can be found by the chain rule for probability:
-
 .
.