Central Counterparty Clearing
Encyclopedia
Central Counterparty Clearing (CCC) is a process by which financial transactions in equities are cleared by a single (i.e., "central") counterparty. Please see Clearing (finance)
for general information about clearing. This article contains specifics about the process as it applies to non-centrally cleared equity markets in the U.S.
In the United States
, there is a separation between the Clearing Broker and the Depository. This means that there will be multiple clearing brokers that have to reconcile shares and money against other clearing brokers. It also means that the clearing brokers bear the risk of default on the leg of the transaction that they are servicing. Contrast this with the options market with its Options Clearing Corporation
, which is a true central clearing counterparty and which bears all default risk (by distributing it evenly among its members).
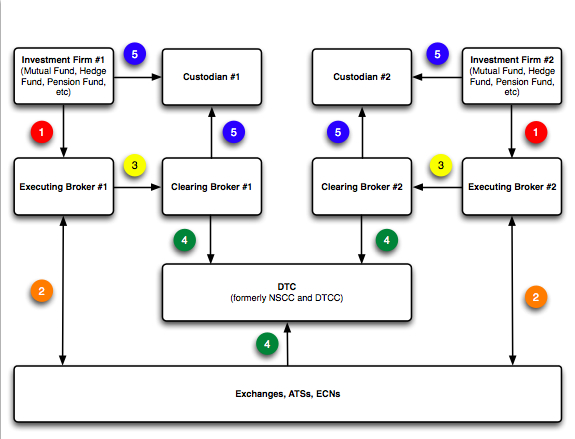
To better understand Central Counterparty Clearing (CCC), a relatively new process, in the U.S. equity markets, first consider the lifecycle of a trade before Central Counterparty Clearing:
On Settlement Date (which is usually up to 3 days after Trade Date, the date when the actual trade occurred), the Clearing Brokers will deliver/receive the match amount of shares/money to settle the trade with both Investment firms.
Other links:
Clearing (finance)
In banking and finance, clearing denotes all activities from the time a commitment is made for a transaction until it is settled. Clearing is necessary because the speed of trades is much faster than the cycle time for completing the underlying transaction....
for general information about clearing. This article contains specifics about the process as it applies to non-centrally cleared equity markets in the U.S.
In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, there is a separation between the Clearing Broker and the Depository. This means that there will be multiple clearing brokers that have to reconcile shares and money against other clearing brokers. It also means that the clearing brokers bear the risk of default on the leg of the transaction that they are servicing. Contrast this with the options market with its Options Clearing Corporation
Options Clearing Corporation
Options Clearing Corporation or OCC, founded in 1973, is the world's largest equity derivatives clearing organization, providing central counterparty clearing and settlement services to 14 exchanges and platforms for options, financial and commodity futures, security futures and securities...
, which is a true central clearing counterparty and which bears all default risk (by distributing it evenly among its members).
To better understand Central Counterparty Clearing (CCC), a relatively new process, in the U.S. equity markets, first consider the lifecycle of a trade before Central Counterparty Clearing:

- Orders are routed from the investment firms (one is a buyer, the other is a seller) to their respective Executing Brokers.
- The Executing Brokers send the orders to the appropriate Marketplace for the security being traded. The Marketplaces respond with executions ("fills").
- The Executing Brokers send the fills to the Clearing Broker that was designated by the investment firms. Many Executing Brokers are themselves Clearing Brokers, a term which is called "self-clearing".
- The Marketplace(s) and the Clearing Brokers compare their shares/money to make sure that they match. This is referred to as "Street-Side matching".
- The Investment Managers inform their respective Custodians what they should expect to receive/deliver from the Clearing Brokers, and the Custodians perform this comparison. This is referred to as "Customer-Side matching". This occurs the day of the trade (T+0).
On Settlement Date (which is usually up to 3 days after Trade Date, the date when the actual trade occurred), the Clearing Brokers will deliver/receive the match amount of shares/money to settle the trade with both Investment firms.
External links
Firms providing Central Counterparty Clearing (may be incomplete):- ISJ (Investor Services Journal magazine and dot tv information service)
- Electronic Securities Processing (ESP)
- Firefly
- UNX
Other links:
- Independent report by the Tabb Group, which they charge for
- http://www.quadriserv.com/newsdocs/20100913.pdf Good, Bad, or Inevitable? A whitepaper on the Introduction of CCP's in Securities Lending (PDF)

