
Center for Computational Biology
Encyclopedia
Computational biology
Computational biology involves the development and application of data-analytical and theoretical methods, mathematical modeling and computational simulation techniques to the study of biological, behavioral, and social systems...
methods for modeling, representation, analysis and visualization of biological shape that are applicable across spatial scales and biological systems.
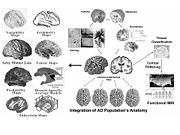
The Computational Brain Atlas is developed by the CCB as part of the NCBC initiative. This atlas illustrates the potential of utilizing a broad integrated approach to translational science
Translational science
Translational science is a cross disciplinary scientific research that is motivated by the need for practical applications that help people. The term is used mostly in the health sciences and refers to things like the discovery of new drugs that directly help improve human health...
. The figure to the right shows how combining structural and functional neuroimaging
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging includes the use of various techniques to either directly or indirectly image the structure, function/pharmacology of the brain...
data (e.g., Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
, Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
), genetics data (e.g., racial, familial and spontaneous genetic mutations) and phenotypic data (e.g., age, race, cognition) helps generate an integral atlas framework that serves as a common space for representing biological information across modalities, scales and species.

