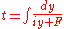Cash accumulation equation
Encyclopedia
The cash accumulation equation is an equation which calculates how much money will be in a bank account
, at any point in time. The account pays interest
, and is being fed a steady trickle of money.
the equation is
and so the sum of money grows exponentially. Differentiating this we derive
and eliminating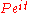 between eqns (1) and (2) yields
between eqns (1) and (2) yields
That is to say, eqn (1) is a solution of eqn (3).
 dollars/year. This is effected by making a small change to eqn (3) as follows
dollars/year. This is effected by making a small change to eqn (3) as follows
and accordingly we need to solve the equation
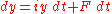
From a table of integrals, the solution is
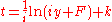
where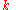 is the constant of integration. The initial sum deposited was
is the constant of integration. The initial sum deposited was 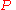 so we know one point on the curve :
so we know one point on the curve :
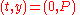
and making this substitution we find that

Using this expression for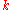 , and recalling that
, and recalling that
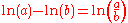
gives us the solution :
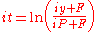
This is the neatest form of the cash accumulation equation, as we are calling it, but it not the most useful form. Using the exponential instead of the logarithmic function, the equation can be written out like this :
 .
.
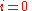 , and specifically the expression
, and specifically the expression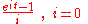
One way of evaluating this is to write out the Maclaurin expansion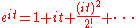
At a glance we can subtract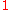 from this series and divide by
from this series and divide by 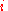 , to find out that
, to find out that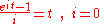
With this result the cash accumulation equation now reads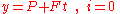
Thus the cash sum just increases linearly, as expected, if no interest is being paid.
 . Upon making this substitution, eqn (4) becomes simply
. Upon making this substitution, eqn (4) becomes simply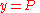
Evidently is negative, and money is being withdrawn rather than deposited. Specifically, the interest is being withdrawn as fast as it is being earned.
is negative, and money is being withdrawn rather than deposited. Specifically, the interest is being withdrawn as fast as it is being earned.
An alternative interpretation of this special case is that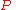 is negative - the account is overdrawn - and money is being fed in at a rate which just meets the interest charges. A force of interest value is always positive.
is negative - the account is overdrawn - and money is being fed in at a rate which just meets the interest charges. A force of interest value is always positive.
Bank account
A Bank account is a financial account recording the financial transactions between the customer and the bank and the resulting financial position of the customer with the bank .-Account types:...
, at any point in time. The account pays interest
Interest
Interest is a fee paid by a borrower of assets to the owner as a form of compensation for the use of the assets. It is most commonly the price paid for the use of borrowed money, or money earned by deposited funds....
, and is being fed a steady trickle of money.
Compound interest
We will approach the development of this equation by first considering the simpler case, that of just placing a lump sum in an account and then making no additions to the sum. With the usual notation, namely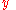 | = the current sum (dollars) | |
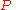 | = principal (dollars) | |
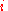 | = force of interest (per year) | |
 | = time (years) |
the equation is
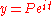 | eqn(1) |
and so the sum of money grows exponentially. Differentiating this we derive
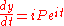 | eqn(2) |
and eliminating
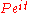 between eqns (1) and (2) yields
between eqns (1) and (2) yields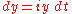 | eqn(3) |
That is to say, eqn (1) is a solution of eqn (3).
Cash infeed
Having achieved this we are ready to start feeding money into the account, at a rate of dollars/year. This is effected by making a small change to eqn (3) as follows
dollars/year. This is effected by making a small change to eqn (3) as follows
and accordingly we need to solve the equation
From a table of integrals, the solution is
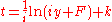
where
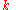 is the constant of integration. The initial sum deposited was
is the constant of integration. The initial sum deposited was 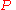 so we know one point on the curve :
so we know one point on the curve :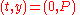
and making this substitution we find that

Using this expression for
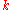 , and recalling that
, and recalling that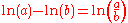
gives us the solution :
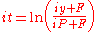
This is the neatest form of the cash accumulation equation, as we are calling it, but it not the most useful form. Using the exponential instead of the logarithmic function, the equation can be written out like this :
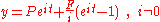 | eqn(4) |
First special case
From this new perspective, eqn (1) is just a special case of eqn (4) - namely with .
.Second special case
For completeness we will consider the case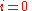 , and specifically the expression
, and specifically the expression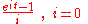
One way of evaluating this is to write out the Maclaurin expansion
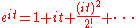
At a glance we can subtract
 from this series and divide by
from this series and divide by 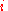 , to find out that
, to find out that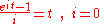
With this result the cash accumulation equation now reads
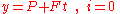
Thus the cash sum just increases linearly, as expected, if no interest is being paid.
Third special case
The only other special case to mention is . Upon making this substitution, eqn (4) becomes simply
. Upon making this substitution, eqn (4) becomes simply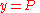
Evidently
 is negative, and money is being withdrawn rather than deposited. Specifically, the interest is being withdrawn as fast as it is being earned.
is negative, and money is being withdrawn rather than deposited. Specifically, the interest is being withdrawn as fast as it is being earned.An alternative interpretation of this special case is that
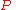 is negative - the account is overdrawn - and money is being fed in at a rate which just meets the interest charges. A force of interest value is always positive.
is negative - the account is overdrawn - and money is being fed in at a rate which just meets the interest charges. A force of interest value is always positive.