Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency
Encyclopedia
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency (CPS I deficiency) is an autosomal
recessive metabolic disorder that causes ammonia
to accumulate in the blood. Ammonia, which is formed when proteins are broken down in the body, is toxic if the levels become too high. The nervous system
is especially sensitive to the effects of excess ammonia.
In some affected individuals, signs and symptoms of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency may be less severe, and may not appear until later in life.

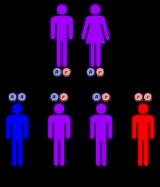
CPS I deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
disorders. The urea cycle is a sequence of reactions that occurs in liver
cells. This cycle processes excess nitrogen
, generated when protein is used by the body, to make a compound called urea that is excreted by the kidneys.
In carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency, the enzyme that regulates the urea cycle is damaged or missing. The urea cycle cannot proceed normally, and nitrogen accumulates in the bloodstream in the form of ammonia. Ammonia is especially damaging to the nervous system, and excess ammonia causes neurological problems and other signs and symptoms of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive metabolic disorder that causes ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
to accumulate in the blood. Ammonia, which is formed when proteins are broken down in the body, is toxic if the levels become too high. The nervous system
Nervous system
The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous...
is especially sensitive to the effects of excess ammonia.
Symptoms
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency often becomes evident in the first few days of life. An infant with this condition may be lacking in energy (lethargic) or unwilling to eat, and have a poorly controlled breathing rate or body temperature. Some babies with this disorder may experience seizures or unusual body movements, or go into a coma. Complications of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency may include developmental delay and mental retardation.In some affected individuals, signs and symptoms of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency may be less severe, and may not appear until later in life.
Genetics

CPS I deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
Pathophysiology
Mutations in the CPS1 gene cause carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency belongs to a class of genetic diseases called urea cycleUrea cycle
The urea cycle is a cycle of biochemical reactions occurring in many animals that produces urea from ammonia . This cycle was the first metabolic cycle discovered , five years before the discovery of the TCA cycle...
disorders. The urea cycle is a sequence of reactions that occurs in liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
cells. This cycle processes excess nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, generated when protein is used by the body, to make a compound called urea that is excreted by the kidneys.
In carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency, the enzyme that regulates the urea cycle is damaged or missing. The urea cycle cannot proceed normally, and nitrogen accumulates in the bloodstream in the form of ammonia. Ammonia is especially damaging to the nervous system, and excess ammonia causes neurological problems and other signs and symptoms of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency.

