Capoeira toques
Encyclopedia
In the game of capoeira
, toques are the rhythm
s played on the berimbau
. Many toques are associated with a specific game (i.e. style and speed of play), although organizations differ on how to play each toque. Capoeira toques have their roots in African rhythmic music
, which was modified and further developed among the slaves of Brazil
.
who was responsible for significant developments to modern capoeira.
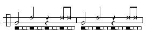
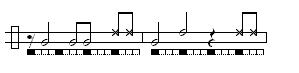
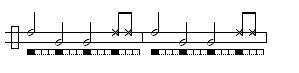
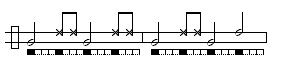
Images are given below to illustrate the structure of this common toque.
The basic: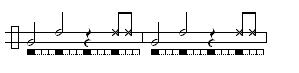
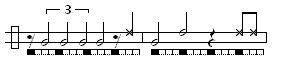
Some common variations played by the viola:
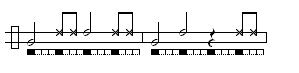
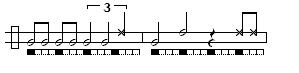

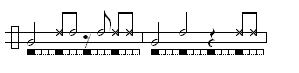
A note on notation:
4e85
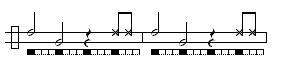
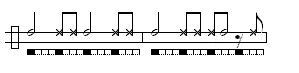
Variations are the same as above, but with High and Low tones swapped.
’s fast, explosive game seen often in exhibitions.
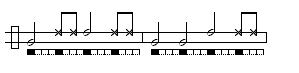
It usually switches between one of a set of variations and a repeated common measure.
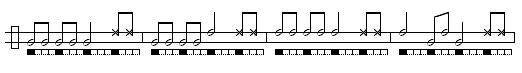
Phrase 1: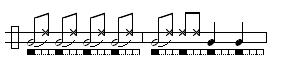
Phrase 2: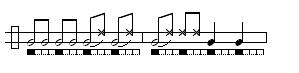
Phrase 3: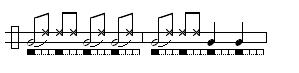
Phrase 4: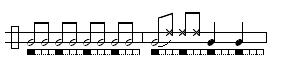
Three Versions Below:
NB. This toque is also called Santa Maria de Angola in some circumstances and is identical to São Bento Grande de Mestre Bimba. What differentiates toques in instances like this is the particular purpose for which it is being played.
Mestre Suassuna: "The game of miudinho is generating controversy because it is being misinterpreted. People are thinking it's a new capoeira, and it's nothing like that. I simply rescued an older capoeira, modernized the manner of playing it, changed the sequences... the name miudinho arose because I was observing that capoeiristas were playing very distant from each other and in our time we played very close; thus, I said to people, 'I want the game more minute, closer, play very tiny.' Then, I created a toque on the berimbau. Miudinho is not a new capoeira, it's a different manner to display capoeira. Just like the games of Iuna and São Bento Grande exist, the game of miudinho exists."
Capoeira
Capoeira is a Brazilian art form that combines elements of martial arts, sports, and music. It was created in Brazil mainly by descendants of African slaves with Brazilian native influences, probably beginning in the 16th century...
, toques are the rhythm
Rhythm
Rhythm may be generally defined as a "movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions." This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time may be applied to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or...
s played on the berimbau
Berimbau
The berimbau is a single-string percussion instrument, a musical bow, from Brazil. The berimbau's origins are not entirely clear, but there is not much doubt about its African origin, as no Indigenous Brazilian or European people use musical bows, and very similar instruments are played in the...
. Many toques are associated with a specific game (i.e. style and speed of play), although organizations differ on how to play each toque. Capoeira toques have their roots in African rhythmic music
Music of Africa
Africa is a vast continent and its regions and nations have distinct musical traditions. The music of North Africa for the most part has a different history from sub-Saharan African music traditions....
, which was modified and further developed among the slaves of Brazil
Slavery in Brazil
Slavery in Brazil shaped the country's social structure and ethnic landscape. During the colonial epoch and for over six decades after the 1822 independence, slavery was a mainstay of the Brazilian economy, especially in mining, cotton, and sugar cane production.Brazil obtained an estimated 35% of...
.
Important toques
Some of the more important toques are described below, including; traditional toques, and those created or popularised by Mestre BimbaMestre Bimba
Manuel dos Reis Machado, commonly called Mestre Bimba , was a mestre of the Afro-Brazilian martial art capoeira.-Early life:Machado is said to have had two birth certificates, dated 1899 and 1900, respectively...
who was responsible for significant developments to modern capoeira.
Angola
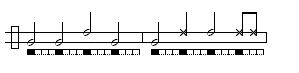
Considered the oldest and most traditional toque. Used for the Angola game, a slow performance where players demonstrate balance and corporal expression. Used with the São Bento Pequeno toque. Tempo can range from slow to moderately fast.Images are given below to illustrate the structure of this common toque.
The basic:

Some common variations played by the viola:






A note on notation:
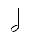 = Open berimbau tone. The arame is struck with the dobrão open and the cabaça away from the stomach for a low note, or dobrão pressing firmly for a high note. In this notation, notes that are unfilled are played unmuted rather than representing a half note.
= Open berimbau tone. The arame is struck with the dobrão open and the cabaça away from the stomach for a low note, or dobrão pressing firmly for a high note. In this notation, notes that are unfilled are played unmuted rather than representing a half note.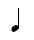 = Muted berimbau note (cabaça is held against the body).
= Muted berimbau note (cabaça is held against the body).
4e85
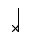 = A buzz (strike the arame with the dobrão resting lightly on the arame and the cabaça against the body)
= A buzz (strike the arame with the dobrão resting lightly on the arame and the cabaça against the body)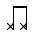
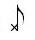 Double and single eighth notes. An eight note is 1/2 a beat.
Double and single eighth notes. An eight note is 1/2 a beat.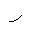 = A slur (press the dobrão against the arame without striking with the other hand)
= A slur (press the dobrão against the arame without striking with the other hand)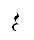 = A quarter note rest (1 beat)
= A quarter note rest (1 beat)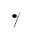 = An eighth note rest (1/2 a beat)
= An eighth note rest (1/2 a beat) = Shows the basic pulse underneath the bar for comparison. Four boxes = 1 beat
= Shows the basic pulse underneath the bar for comparison. Four boxes = 1 beat
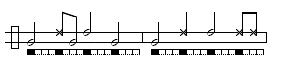
São Bento pequeno
Also known as São Bento pequeno or Inverted Angola (because it replaces the high note of the Angola toque with the low and vice versa). A close, fast game. São Bento Pequeno is also sometimes played as a contra-toque (an inversion the gunga) by the medio berimbau.
Variations are the same as above, but with High and Low tones swapped.
São Bento grande
This is a very fast game played with ample movements. Leg sweeps and take downs are common in this game. The toque is identical to São Bento Pequeno, except that the 1/4 note pause is replaced by an additional solto note (i.e. the open note struck below the level of the coin) and the tempo is faster.
Santa Maria
A toque used for the not often seen 'money', game where the players try to pick up a coin purse placed in the center of the roda with their mouths, the melody imitates the corrido Santa Maria, Mãe de Deus. The corrido Apanha Laranja no Chão Tico Tico (não leva com mão, só com pé ou com bico) gives general rule for the game: use your mouth and feet, not your hands.
Cavalaria
Originally used to alert players that the police were coming, the toque imitates the galloping of horses (and some say it sounds like a police siren)
Samba de Roda
This rhythm comes from the traditional Sambas de Roda of Bahia and is perhaps the oldest of the toques listed. It's used as a toque variation for the berimbau viola, as well as for a post-roda celebration.
São Bento grande de Bimba
Often called São Bento grande de Regional or just Regional. Mestre BimbaMestre Bimba
Manuel dos Reis Machado, commonly called Mestre Bimba , was a mestre of the Afro-Brazilian martial art capoeira.-Early life:Machado is said to have had two birth certificates, dated 1899 and 1900, respectively...
’s fast, explosive game seen often in exhibitions.

Iúna
Iúna is an old viola guitar toque used in the sambas of the Recôncavo, Bahia. Bimba, who himself was an accomplished master of the viola de samba, brought it into capoeira as a toque on berimbau. Some say it is also in imitation of the Iúna bird's song. This toque may signal a medium paced game with emphasis almost entirely on acrobatics and usually played with ample distance between partners. Traditionally this game is only played by graduados (experienced students) and in many schools may only be played when a Mestre is present.It usually switches between one of a set of variations and a repeated common measure.
Phrase 1:

Phrase 2:

Phrase 3:

Phrase 4:

Banguela
In many schools played extremely close and with much deception. Some schools play this as a slower, safer Regional game.
Idalina
A slow, but powerful game. Another of Mestre Bimba's toques, the accompanying game is played with knives/razors.

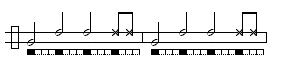
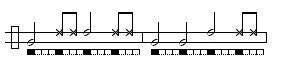
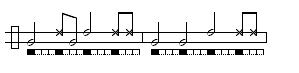
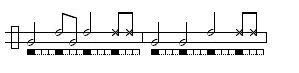
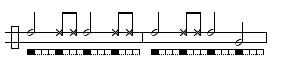
Amazonas/Santa Maria (de Angola)
Amazonas: A welcoming toque used to greet visiting Mestres and guests in some Regional and Contemporânea schools. It has no traditionally associated game though Mestre Camisa is currently developing a game that mimics the movements of animals.Three Versions Below:



NB. This toque is also called Santa Maria de Angola in some circumstances and is identical to São Bento Grande de Mestre Bimba. What differentiates toques in instances like this is the particular purpose for which it is being played.
Miudinho
Created by Mestre Suassuna. Like Angola, but faster. There is only sometimes clapping or singing.Mestre Suassuna: "The game of miudinho is generating controversy because it is being misinterpreted. People are thinking it's a new capoeira, and it's nothing like that. I simply rescued an older capoeira, modernized the manner of playing it, changed the sequences... the name miudinho arose because I was observing that capoeiristas were playing very distant from each other and in our time we played very close; thus, I said to people, 'I want the game more minute, closer, play very tiny.' Then, I created a toque on the berimbau. Miudinho is not a new capoeira, it's a different manner to display capoeira. Just like the games of Iuna and São Bento Grande exist, the game of miudinho exists."


