Canonical signed digit
Encyclopedia
In computing
canonical-signed-digit (CSD) is a number system
for encoding a floating-point value in a two's complement
representation. This encoding contains 33% fewer zeros than the two's complement form, leading to efficient implementations of add/subtract networks in hardwired Digital signal processing
.
The representation uses a sequence of one or more of the symbols, -1, 0, +1 (alternatively -, 0 or +) with each position possibly representing the addition or subtraction of a power of 2. For instance 23 is represented as +0-00-, which expands to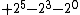 or
or 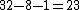
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
canonical-signed-digit (CSD) is a number system
Number system
In mathematics, a 'number system' is a set of numbers, , together with one or more operations, such as addition or multiplication....
for encoding a floating-point value in a two's complement
Two's complement
The two's complement of a binary number is defined as the value obtained by subtracting the number from a large power of two...
representation. This encoding contains 33% fewer zeros than the two's complement form, leading to efficient implementations of add/subtract networks in hardwired Digital signal processing
Digital signal processing
Digital signal processing is concerned with the representation of discrete time signals by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing...
.
The representation uses a sequence of one or more of the symbols, -1, 0, +1 (alternatively -, 0 or +) with each position possibly representing the addition or subtraction of a power of 2. For instance 23 is represented as +0-00-, which expands to
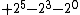 or
or