CRAL-TRIO domain
Encyclopedia
CRAL-TRIO domain is a protein structural domain that binds small lipophilic molecules. This domain is named after cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein (CRALBP) and TRIO
guanine exchange factor.
CRALB protein carries 11-cis-retinol
or 11-cis-retinaldehyde. It modulates interaction of retinoids with visual cycle enzymes. TRIO is involved in coordinating actin remodeling
, which is necessary for cell migration and growth.
Other members of the family are alpha-tocopherol
transfer protein and phosphatidylinositol
-transfer protein (Sec14). They transport their substrates (alpha-tocopherol
and phosphatidylinositol
or phosphatidylcholine
, respectively) between different intracellular membranes. Family also include a guanine nucleotide exchange factor
that may function as an effector of RAC1
small G-protein.
The N-terminal domain of yeast ECM25 protein has been identified as containing a lipid binding CRAL-TRIO domain.
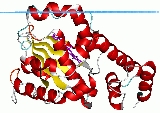
protein was the first CRAL-TRIO domain for which the structure was determined. The structure contains several alpha helices
as well as a beta sheet
composed of 6 strands. Strands 2,3,4 and 5 form a parallel beta sheet with strands 1 and 6 being anti-parallel. The structure also identified a hydrophobic binding pocket for lipid
binding.
; RLBP1
; RLBP1L1; RLBP1L2; SEC14L1
; SEC14L2
;
SEC14L3; SEC14L4; TTPA
;
TRIO (gene)
Triple functional domain protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIO gene.-Interactions:TRIO has been shown to interact with Filamin and RHOA.-Further reading:...
guanine exchange factor.
CRALB protein carries 11-cis-retinol
Retinol
Retinol is one of the animal forms of vitamin A. It is a diterpenoid and an alcohol. It is convertible to other forms of vitamin A, and the retinyl ester derivative of the alcohol serves as the storage form of the vitamin in animals....
or 11-cis-retinaldehyde. It modulates interaction of retinoids with visual cycle enzymes. TRIO is involved in coordinating actin remodeling
Actin remodeling
Actin remodeling is a biochemical process in cells. In actin remodeling, there is a cycle of actin monomers being polymerized, affecting the cell membrane, and being broken down into monomers again...
, which is necessary for cell migration and growth.
Other members of the family are alpha-tocopherol
Tocopherol
Tocopherols are a class of chemical compounds of which many have vitamin E activity. It is a series of organic compounds consisting of various methylated phenols...
transfer protein and phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol is a negatively charged phospholipid and a minor component in the cytosolic side of eukaryotic cell membranes....
-transfer protein (Sec14). They transport their substrates (alpha-tocopherol
Alpha-tocopherol
α-Tocopherol is a type of tocopherol with formula C29H50O2. It has E number "E307".α-Tocopherol is a form of vitamin E that is preferentially absorbed and accumulated in humans...
and phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol is a negatively charged phospholipid and a minor component in the cytosolic side of eukaryotic cell membranes....
or phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically...
, respectively) between different intracellular membranes. Family also include a guanine nucleotide exchange factor
Nucleotide exchange factor
Nucleotide exchange factors are proteins that stimulate the exchange of nucleoside diphosphates for nucleoside triphosphates bound to other proteins.-Function:...
that may function as an effector of RAC1
RAC1
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 also known as Rac1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAC1 gene. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined.- Function :Rac1 is...
small G-protein.
The N-terminal domain of yeast ECM25 protein has been identified as containing a lipid binding CRAL-TRIO domain.
Structure
The Sec14Sec14
Sec14p is a protein that in yeast is encoded by the Sec14 gene....
protein was the first CRAL-TRIO domain for which the structure was determined. The structure contains several alpha helices
Alpha helix
A common motif in the secondary structure of proteins, the alpha helix is a right-handed coiled or spiral conformation, in which every backbone N-H group donates a hydrogen bond to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid four residues earlier...
as well as a beta sheet
Beta sheet
The β sheet is the second form of regular secondary structure in proteins, only somewhat less common than the alpha helix. Beta sheets consist of beta strands connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet...
composed of 6 strands. Strands 2,3,4 and 5 form a parallel beta sheet with strands 1 and 6 being anti-parallel. The structure also identified a hydrophobic binding pocket for lipid
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
binding.
Human proteins containing this domain
C20orf121; MOSPD2; PTPN9PTPN9
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN9 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase family...
; RLBP1
RLBP1
Retinaldehyde-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RLBP1 gene.-External links:* -Further reading:...
; RLBP1L1; RLBP1L2; SEC14L1
SEC14L1
SEC14-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEC14L1 gene.-Further reading:...
; SEC14L2
SEC14L2
SEC14-like protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEC14L2 gene.-Further reading:...
;
SEC14L3; SEC14L4; TTPA
TTPA
Alpha-tocopherol transfer protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TTPA gene.-External links:**...
;

