CIE 1960 color space
Encyclopedia
Chromaticity
Chromaticity is an objective specification of the quality of a color regardless of its luminance, that is, as determined by its hue and colorfulness ....
space devised by David MacAdam
David MacAdam
Dr. David Lewis MacAdam was an American physicist and color scientist who made important contributions to color science and technology in the fields of colorimetry, color discrimination, color photography and television, and color order.-Education:MacAdam grew up in Philadelphia, attended Lehigh...
.
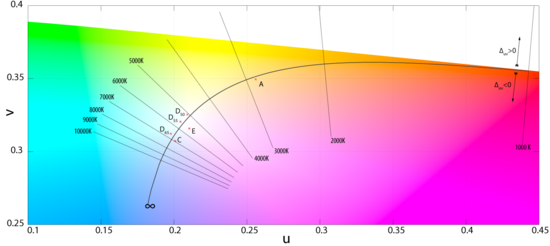
The CIE 1960 UCS does not define a luminance or lightness
Lightness (color)
Lightness is a property of a color, or a dimension of a color space, that is defined in a way to reflect the subjective brightness perception of a color for humans along a lightness–darkness axis. A color's lightness also corresponds to its amplitude.Various color models have an explicit term for...
component, but the Y tristimulus value of the XYZ color space or a lightness index similar to W* of the CIE 1964 color space are sometimes used.
Today, the CIE 1960 UCS is mostly used to calculate correlated color temperature, where the isothermal lines are perpendicular to the Planckian locus
Planckian locus
In physics and color science, the Planckian locus or black body locus is the path or locus that the color of an incandescent black body would take in a particular chromaticity space as the blackbody temperature changes...
. As a uniform chromaticity space, it has been superseded by the CIE 1976 UCS.
Background
Judd determined that a more uniform color spaceColor space
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components...
could be found by a simple projective transformation of the CIEXYZ tristimulus values:
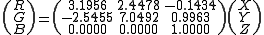
Judd was the first to employ this type of transformation, and many others were to follow. Converting this RGB space to chromaticities one finds

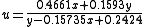
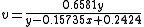
or equivalently (for comparative purposes with the equations to follow):
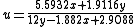
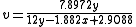
MacAdam simplified Judd's UCS for computational purposes:
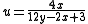
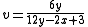
The Colorimetry committee of the CIE considered MacAdam's proposal at its 14th Session in Brussels for use in situations where more perceptual uniformity was desired than the (x,y) chromaticity space, and officially adopted it as the standard UCS the next year.
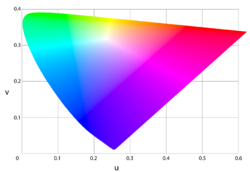
Relation to CIEXYZ
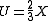
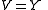
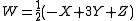
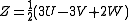
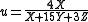
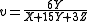
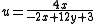
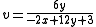

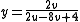
External links
- Free Windows utility to generate chromaticity diagrams. Delphi source included.

