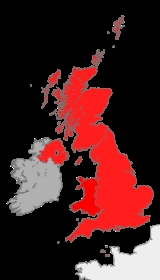
British Islands
Encyclopedia
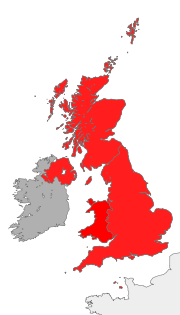
Law of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom has three legal systems. English law, which applies in England and Wales, and Northern Ireland law, which applies in Northern Ireland, are based on common-law principles. Scots law, which applies in Scotland, is a pluralistic system based on civil-law principles, with common law...
which since 1889 has referred collectively to the following four states:
- the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (formerly the United Kingdom of Great Britain and IrelandUnited Kingdom of Great Britain and IrelandThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the formal name of the United Kingdom during the period when what is now the Republic of Ireland formed a part of it....
); - the Bailiwick of Jersey;
- the Bailiwick of Guernsey (including AlderneyAlderneyAlderney is the most northerly of the Channel Islands. It is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown dependency. It is long and wide. The area is , making it the third-largest island of the Channel Islands, and the second largest in the Bailiwick...
, HermHermHerm is the smallest of the Channel Islands that is open to the public and is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey. Cars are banned from the small island just like its Channel Island neighbour, Sark. Unlike Sark, bicycles are also banned...
, and SarkSarkSark is a small island in the Channel Islands in southwestern English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. It is a royal fief, geographically located in the Channel Islands in the Bailiwick of Guernsey, with its own set of laws based on Norman law and its own parliament. It has a population...
); and - the Isle of ManIsle of ManThe Isle of Man , otherwise known simply as Mann , is a self-governing British Crown Dependency, located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, within the British Isles. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is...
.
The latter three territories are Crown dependencies
Crown dependency
The Crown Dependencies are British possessions of the Crown, as opposed to overseas territories of the United Kingdom. They comprise the Channel Island Bailiwicks of Jersey and Guernsey in the English Channel, and the Isle of Man in the Irish Sea....
and are not a part of the United Kingdom. The Parliament of the United Kingdom
Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body in the United Kingdom, British Crown dependencies and British overseas territories, located in London...
on occasions introduces legislation that is extended to the islands, normally by the use of Orders in Council. For this reason it has been found useful to have a collective term for the combined territories. Dating back to 1889, a statutory definition can be found in the Interpretation Act 1978
Interpretation Act 1978
The Interpretation Act 1978 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The Act makes provision for the interpretation of Acts of Parliament, Measures of the General Synod of the Church of England, Measures of the Church Assembly, subordinate legislation, "deeds and other instruments and...
.
The term United Kingdom and Islands is used in the Immigration Act 1971
Immigration Act 1971
The Immigration Act 1971 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom concerning immigration.The Act, as with the Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1962, and that of 1968, restricted immigration, especially primary immigration into the UK....
.
British passports issued in the UK have the wording "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland" on their cover. In the Crown dependencies, this is replaced by "British Islands – Bailiwick of Jersey", "British Islands – Bailiwick of Guernsey" or "British Islands – Isle of Man". These passports are issued to all British citizens resident in the jurisdiction in question.
Section 5 of the Interpretation Act 1978
Interpretation Act 1978
The Interpretation Act 1978 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The Act makes provision for the interpretation of Acts of Parliament, Measures of the General Synod of the Church of England, Measures of the Church Assembly, subordinate legislation, "deeds and other instruments and...
provides that "in any Act
Acts of Parliament in the United Kingdom
An Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom is a type of legislation called primary legislation. These Acts are passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom at Westminster, or by the Scottish Parliament at Edinburgh....
, unless the contrary intention appears" the expression "British Islands" is to be construed according to Schedule 1 of that Act, which contains the following paragraph:
Subject to paragraph 4(2) of Schedule 2, that paragraph of Schedule 1 applies, so far as applicable, to Acts passed after the year 1889.
Paragraph 4(2) provides:
The Irish Free State was established on ... and the Interpretation Act 1978 came into force on 1 January 1979.
The Interpretation Act 1978 applies to itself and to any Act passed after the commencement of that Act and, to the extent specified in Part I of Schedule 2, to Acts passed before the commencement of that Act.
See also
- British Islands Isle of Man (European Union) passport in PRADO (Council of the European Union Public Register of Authentic Document Online)
- British Islands Jersey (European Union) passport in PRADO
- British Isles naming disputeBritish Isles naming disputeThere is disagreement over the term "the British Isles", particularly with relation to Ireland. The term is defined in dictionaries as referring to Great Britain, Ireland and adjacent islands. However, the association between the word "British" and the United Kingdom causes the term to be regarded...
- Terminology of the British Isles
- List of islands of the British Isles
External links
- Interpretation Act, 1978 (unofficial text)

