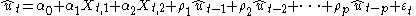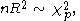Breusch–Godfrey test
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the Breusch–Godfrey test is used to assess the validity of some of the modelling assumptions inherent in applying regression-like
models to observed data series. In particular, it tests
for the presence of serial dependence
that has not been included in a proposed model structure and which, if present, would mean that incorrect conclusions would be drawn from other tests, or that sub-optimal estimates of model parameters are obtained if it is not taken into account. The regression models to which the test can be applied include cases where lagged values of the dependent variables are used as independent variables in the model's representation for later observations. This type of structure is common in econometric model
s.
An alternative name for the test is the Breusch–Godfrey serial correlation Lagrange multiplier test, where this indicates that the test in equivalent to one based on the idea of Lagrange multiplier testing.
The test is named after Trevor S. Breusch and Leslie G. Godfrey.
in the errors
in a regression model. It makes use of the residuals
from the model being considered in a regression analysis
, and a test statistic is derived from these. The null hypothesis
is that there is no serial correlation of any order up to p.
The test is more general than the Durbin–Watson statistic (or Durbin's h statistic), which is only valid for nonstochastic regressors and for testing the possibility of a first-order autoregressive model (e.g. AR(1)) for the regression errors. The BG test has none of these restrictions, and is statistically more powerful
than Durbin's h statistic.
of any form, for example
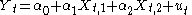
where the residuals might follow an AR(p) autoregressive scheme, as follows:
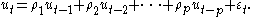
The simple regression model is first fitted by ordinary least squares
to obtain a set of sample residuals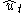 .
.
Breusch and Godfrey proved that, if the following auxiliary regression model is fitted
and if the usual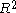 statistic is calculated for this model, then the following asymptotic approximation
statistic is calculated for this model, then the following asymptotic approximation
can be used for the distribution of the test statistic
when the null hypothesis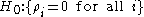 holds (that is, there is no serial correlation of any order up to p). Here n is the number of data-points available for the second regression, that for
holds (that is, there is no serial correlation of any order up to p). Here n is the number of data-points available for the second regression, that for 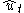 ,
,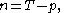
where T is the number of observations in the basic series . Note that the value of n depends on the number of lags of the error term (p).
, this test is performed by function bgtest, available in package lmtest.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the Breusch–Godfrey test is used to assess the validity of some of the modelling assumptions inherent in applying regression-like
Regression analysis
In statistics, regression analysis includes many techniques for modeling and analyzing several variables, when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables...
models to observed data series. In particular, it tests
Statistical hypothesis testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of making decisions using data, whether from a controlled experiment or an observational study . In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, according to a pre-determined threshold...
for the presence of serial dependence
Serial dependence
In statistics and signal processing, random variables in a time series have serial dependence if the value at some time t in the series is statistically dependent on the value at another time s...
that has not been included in a proposed model structure and which, if present, would mean that incorrect conclusions would be drawn from other tests, or that sub-optimal estimates of model parameters are obtained if it is not taken into account. The regression models to which the test can be applied include cases where lagged values of the dependent variables are used as independent variables in the model's representation for later observations. This type of structure is common in econometric model
Econometric model
Econometric models are statistical models used in econometrics. An econometric model specifies the statistical relationship that is believed to hold between the various economic quantities pertaining to a particular economic phenomenon under study...
s.
An alternative name for the test is the Breusch–Godfrey serial correlation Lagrange multiplier test, where this indicates that the test in equivalent to one based on the idea of Lagrange multiplier testing.
The test is named after Trevor S. Breusch and Leslie G. Godfrey.
Background
The Breusch–Godfrey serial correlation LM test is a test for autocorrelationAutocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
in the errors
Errors and residuals in statistics
In statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
in a regression model. It makes use of the residuals
Errors and residuals in statistics
In statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
from the model being considered in a regression analysis
Regression analysis
In statistics, regression analysis includes many techniques for modeling and analyzing several variables, when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables...
, and a test statistic is derived from these. The null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
is that there is no serial correlation of any order up to p.
The test is more general than the Durbin–Watson statistic (or Durbin's h statistic), which is only valid for nonstochastic regressors and for testing the possibility of a first-order autoregressive model (e.g. AR(1)) for the regression errors. The BG test has none of these restrictions, and is statistically more powerful
Statistical power
The power of a statistical test is the probability that the test will reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is actually false . The power is in general a function of the possible distributions, often determined by a parameter, under the alternative hypothesis...
than Durbin's h statistic.
Procedure
Consider a linear regressionLinear regression
In statistics, linear regression is an approach to modeling the relationship between a scalar variable y and one or more explanatory variables denoted X. The case of one explanatory variable is called simple regression...
of any form, for example
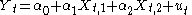
where the residuals might follow an AR(p) autoregressive scheme, as follows:
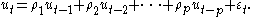
The simple regression model is first fitted by ordinary least squares
Ordinary least squares
In statistics, ordinary least squares or linear least squares is a method for estimating the unknown parameters in a linear regression model. This method minimizes the sum of squared vertical distances between the observed responses in the dataset and the responses predicted by the linear...
to obtain a set of sample residuals
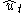 .
.Breusch and Godfrey proved that, if the following auxiliary regression model is fitted
and if the usual
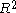 statistic is calculated for this model, then the following asymptotic approximation
statistic is calculated for this model, then the following asymptotic approximationAsymptotic distribution
In mathematics and statistics, an asymptotic distribution is a hypothetical distribution that is in a sense the "limiting" distribution of a sequence of distributions...
can be used for the distribution of the test statistic
when the null hypothesis
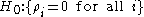 holds (that is, there is no serial correlation of any order up to p). Here n is the number of data-points available for the second regression, that for
holds (that is, there is no serial correlation of any order up to p). Here n is the number of data-points available for the second regression, that for 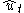 ,
,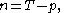
where T is the number of observations in the basic series . Note that the value of n depends on the number of lags of the error term (p).
Software
In RR (programming language)
R is a programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics. The R language is widely used among statisticians for developing statistical software, and R is widely used for statistical software development and data analysis....
, this test is performed by function bgtest, available in package lmtest.
See also
- Breusch–Pagan test