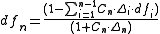Bootstrapping (finance)
Encyclopedia
Bootstrapping is a method for constructing a (zero-coupon) fixed-income yield curve
from the prices of a set of coupon-bearing products by forward substitution.
Using these zero-coupon products it becomes possible to derive par swap
rates (forward and spot) for all maturities by making a few assumptions (including linear interpolation). The term structure of spot returns is recovered from the bond yields by solving for them recursively, this iterative process is called the Bootstrap Method.
Given that, in general, we lack data points in a yield curve
(there are only a fixed number of products in the market) and more importantly these have varying coupon frequencies, it makes sense to construct a curve of zero-coupon instruments from which we can price any yield, whether forward or spot, without the need of more external information.
A generic "algorithm
" is described below; for more detail see Yield curve: Construction of the full yield curve from market data.
Tools
Yield curve
In finance, the yield curve is the relation between the interest rate and the time to maturity, known as the "term", of the debt for a given borrower in a given currency. For example, the U.S. dollar interest rates paid on U.S...
from the prices of a set of coupon-bearing products by forward substitution.
Using these zero-coupon products it becomes possible to derive par swap
Swap
- Finance :* Swap , a derivative in which two parties agree to exchange one stream of cash flows against another* Barter- Technology :* Swap space, related to a computer's virtual memory subsystem...
rates (forward and spot) for all maturities by making a few assumptions (including linear interpolation). The term structure of spot returns is recovered from the bond yields by solving for them recursively, this iterative process is called the Bootstrap Method.
Given that, in general, we lack data points in a yield curve
Yield curve
In finance, the yield curve is the relation between the interest rate and the time to maturity, known as the "term", of the debt for a given borrower in a given currency. For example, the U.S. dollar interest rates paid on U.S...
(there are only a fixed number of products in the market) and more importantly these have varying coupon frequencies, it makes sense to construct a curve of zero-coupon instruments from which we can price any yield, whether forward or spot, without the need of more external information.
A generic "algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
" is described below; for more detail see Yield curve: Construction of the full yield curve from market data.
General Methodology
- Define set of yielding products, these will generally be coupon-bearing bonds
- Derive discount factors for all terms, these are the internal rates of return of the bonds
- 'Bootstrap' the zero-coupon curve step-by-step.
For each stage of the iterative process, we are interested in deriving the n-year zero-coupon bond yield, also known as the internal rate of return of the zero-coupon bond. As there are no intermediate payments on this bond, (all the interest and principal is realised at the end of n years) it is sometimes called the n-year spot rate. To derive this rate we observe that the theoretical price of a bond can be calculated as the present value of the cash flows to be received in the future. In the case of swap rates, we want the par bond rate (Swaps are priced at par when created) and therefore we require that the present value of the future cash flows and principal be equal to 100%.
therefore
(this formula is precisely forward substitution)
- where
is the coupon rate of the n-year bond
is the length, or day count fraction, of the period
, in years
is the discount factor for that time period
is the discount factor for the entire period, from which we derive the zero-rate.
External links
Discussion- Bootstrapping, investopedia.com
Tools
- Excel Bootstrapper, janroman.dhis.org
- Bootstrapping Step-By-Step, bus.umich.edu