
Bloch spectrum
Encyclopedia
The Bloch spectrum is a concept in quantum mechanics
in the field of theoretical physics
; this concept addresses certain energy spectra considerations.
Let H be the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation
operator
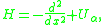
where Uα is a periodic function
of period α. The Bloch spectrum of H is defined as the set of values E for which all the solutions of (H − E)φ = 0 are bounded on the whole real axis. The Bloch spectrum consists of the half-line E0 < E from which certain closed intervals [E2j−1, E2j] (j = 1, 2, ...) are omitted. These are forbidden bands (or gaps) so the (E2j−2, E2j−1) are allowed bands.
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
in the field of theoretical physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
; this concept addresses certain energy spectra considerations.
Let H be the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation
Schrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation was formulated in 1926 by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger. Used in physics , it is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time....
operator
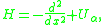
where Uα is a periodic function
Periodic function
In mathematics, a periodic function is a function that repeats its values in regular intervals or periods. The most important examples are the trigonometric functions, which repeat over intervals of length 2π radians. Periodic functions are used throughout science to describe oscillations,...
of period α. The Bloch spectrum of H is defined as the set of values E for which all the solutions of (H − E)φ = 0 are bounded on the whole real axis. The Bloch spectrum consists of the half-line E0 < E from which certain closed intervals [E2j−1, E2j] (j = 1, 2, ...) are omitted. These are forbidden bands (or gaps) so the (E2j−2, E2j−1) are allowed bands.

