
Blind equalization
Encyclopedia
Blind equalization is a digital signal processing
technique in which the transmitted
signal
is inferred (equalized
) from the received
signal, while making use only of the transmitted signal statistics. Hence, the use of the word blind in the name.
Blind equalization is essentially blind deconvolution
applied to digital communications. Nonetheless, the emphasis in blind equalization is on online
estimation
of the equalizer filter
, which is the inverse of the channel
impulse response
, rather than the estimation of the channel impulse response itself. This is due to blind deconvolution common mode of usage in digital communications systems, as a mean to extract the continuously transmitted signal from the received signal, with the channel impulse response being of secondary intrinsic importance.
The estimated equalizer is then convolved
with the received signal to yield an estimation of the transmitted signal.
channel with impulse response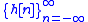 , the noiseless model relates the received signal
, the noiseless model relates the received signal  to the transmitted signal
to the transmitted signal 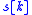 via
via

The blind equalization problem can now be formulated as follows; Given the received signal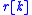 , find a filter
, find a filter  , called an equalization filter, such that
, called an equalization filter, such that

where is an estimation of
is an estimation of  .
.
The solution to the blind equalization problem is not unique. In fact, it may be determined only up to a signed scale factor and an arbitrary time delay. That is, if
to the blind equalization problem is not unique. In fact, it may be determined only up to a signed scale factor and an arbitrary time delay. That is, if 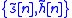 are estimations of the transmitted signal and channel impulse response, respectively, then
are estimations of the transmitted signal and channel impulse response, respectively, then 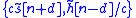 give rise to the same received signal
give rise to the same received signal  for any real scale factor
for any real scale factor  and integral time delay
and integral time delay 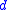 . In fact, by symmetry, the roles of
. In fact, by symmetry, the roles of  and
and  are Interchangeable.
are Interchangeable.
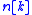 , representing additive noise, is included. The model is therefore
, representing additive noise, is included. The model is therefore

However, as one usually has access to only a finite number of samples from the received signal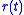 , further restrictions must be imposed over the above models to render the blind equalization problem tractable.
, further restrictions must be imposed over the above models to render the blind equalization problem tractable.
One such assumption, common to all algorithms described below is to assume that the channel has finite impulse response
,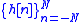 , where
, where  is an arbitrary natural number.
is an arbitrary natural number.
This assumption may be justified on physical grounds, since the energy of any real signal must be finite, and therefore its impulse response must tend to zero. Thus it may be assumed that all coefficients beyond a certain point are negligibly small.
, the problem becomes trivial.
algorithm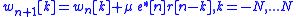
with

where is an appropriate positive adaptation step and
is an appropriate positive adaptation step and  is a suitable nonlinear function.
is a suitable nonlinear function.
in order to compute the equalizer.
Digital signal processing
Digital signal processing is concerned with the representation of discrete time signals by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing...
technique in which the transmitted
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications a transmitter or radio transmitter is an electronic device which, with the aid of an antenna, produces radio waves. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating...
signal
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
is inferred (equalized
Equalizer (communications)
In telecommunication, the equalizer is a device that attempts to reverse the distortion incurred by a signal transmitted through a channel.- Digital communications :...
) from the received
Receiver (Information Theory)
The receiver in information theory is the receiving end of a communication channel. It receives decoded messages/information from the sender, who first encoded them. Sometimes the receiver is modeled so as to include the decoder. Real-world receivers like radio receivers or telephones can not be...
signal, while making use only of the transmitted signal statistics. Hence, the use of the word blind in the name.
Blind equalization is essentially blind deconvolution
Blind deconvolution
In image processing and applied mathematics, blind deconvolution is a deconvolution technique that permits recovery of the target scene from a single or set of "blurred" images in the presence of a poorly determined or unknown point spread function ....
applied to digital communications. Nonetheless, the emphasis in blind equalization is on online
Online algorithm
In computer science, an online algorithm is one that can process its input piece-by-piece in a serial fashion, i.e., in the order that the input is fed to the algorithm, without having the entire input available from the start. In contrast, an offline algorithm is given the whole problem data from...
estimation
Estimation
Estimation is the calculated approximation of a result which is usable even if input data may be incomplete or uncertain.In statistics,*estimation theory and estimator, for topics involving inferences about probability distributions...
of the equalizer filter
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, which is the inverse of the channel
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
impulse response
Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
, rather than the estimation of the channel impulse response itself. This is due to blind deconvolution common mode of usage in digital communications systems, as a mean to extract the continuously transmitted signal from the received signal, with the channel impulse response being of secondary intrinsic importance.
The estimated equalizer is then convolved
Convolution
In mathematics and, in particular, functional analysis, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions f and g, producing a third function that is typically viewed as a modified version of one of the original functions. Convolution is similar to cross-correlation...
with the received signal to yield an estimation of the transmitted signal.
Noiseless model
Assuming a linear time invariantLTI system theory
Linear time-invariant system theory, commonly known as LTI system theory, comes from applied mathematics and has direct applications in NMR spectroscopy, seismology, circuits, signal processing, control theory, and other technical areas. It investigates the response of a linear and time-invariant...
channel with impulse response
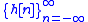 , the noiseless model relates the received signal
, the noiseless model relates the received signal  to the transmitted signal
to the transmitted signal 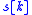 via
via
The blind equalization problem can now be formulated as follows; Given the received signal
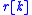 , find a filter
, find a filter  , called an equalization filter, such that
, called an equalization filter, such that
where
 is an estimation of
is an estimation of  .
.The solution
 to the blind equalization problem is not unique. In fact, it may be determined only up to a signed scale factor and an arbitrary time delay. That is, if
to the blind equalization problem is not unique. In fact, it may be determined only up to a signed scale factor and an arbitrary time delay. That is, if 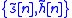 are estimations of the transmitted signal and channel impulse response, respectively, then
are estimations of the transmitted signal and channel impulse response, respectively, then 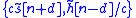 give rise to the same received signal
give rise to the same received signal  for any real scale factor
for any real scale factor  and integral time delay
and integral time delay  . In fact, by symmetry, the roles of
. In fact, by symmetry, the roles of  and
and  are Interchangeable.
are Interchangeable.Noisy model
In the noisy model, an additional term,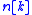 , representing additive noise, is included. The model is therefore
, representing additive noise, is included. The model is therefore
Algorithms
Many algorithms for the solution of the blind equalization problem have been suggested over the years.However, as one usually has access to only a finite number of samples from the received signal
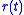 , further restrictions must be imposed over the above models to render the blind equalization problem tractable.
, further restrictions must be imposed over the above models to render the blind equalization problem tractable.One such assumption, common to all algorithms described below is to assume that the channel has finite impulse response
Finite impulse response
A finite impulse response filter is a type of a signal processing filter whose impulse response is of finite duration, because it settles to zero in finite time. This is in contrast to infinite impulse response filters, which have internal feedback and may continue to respond indefinitely...
,
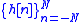 , where
, where  is an arbitrary natural number.
is an arbitrary natural number.This assumption may be justified on physical grounds, since the energy of any real signal must be finite, and therefore its impulse response must tend to zero. Thus it may be assumed that all coefficients beyond a certain point are negligibly small.
Minimum phase
If the channel impulse response is assumed to be minimum phaseMinimum phase
In control theory and signal processing, a linear, time-invariant system is said to be minimum-phase if the system and its inverse are causal and stable....
, the problem becomes trivial.
Bussgang methods
Bussgang methods make use of the Least mean squares filterLeast mean squares filter
Least mean squares algorithms are a class of adaptive filter used to mimic a desired filter by finding the filter coefficients that relate to producing the least mean squares of the error signal . It is a stochastic gradient descent method in that the filter is only adapted based on the error at...
algorithm
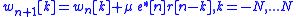
with

where
 is an appropriate positive adaptation step and
is an appropriate positive adaptation step and  is a suitable nonlinear function.
is a suitable nonlinear function.Polyspectra techniques
Polyspectra techniques utilize higher order statisticsHigher-order statistics
Higher-order statistics are descriptive measures of, among other things, qualities of probability distributions and sample distributions, and are, themselves, extensions of first- and second-order measures to higher orders. Skewness and kurtosis are examples of this...
in order to compute the equalizer.
See also
- EqualizationEqualizationEqualization, is the process of adjusting the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal. The most well known use of equalization is in sound recording and reproduction but there are many other applications in electronics and telecommunications. The circuit or equipment used...
- Independent component analysisIndependent component analysisIndependent component analysis is a computational method for separating a multivariate signal into additive subcomponents supposing the mutual statistical independence of the non-Gaussian source signals...
- Principal components analysisPrincipal components analysisPrincipal component analysis is a mathematical procedure that uses an orthogonal transformation to convert a set of observations of possibly correlated variables into a set of values of uncorrelated variables called principal components. The number of principal components is less than or equal to...
- Blind deconvolutionBlind deconvolutionIn image processing and applied mathematics, blind deconvolution is a deconvolution technique that permits recovery of the target scene from a single or set of "blurred" images in the presence of a poorly determined or unknown point spread function ....
- Linear predictive codingLinear predictive codingLinear predictive coding is a tool used mostly in audio signal processing and speech processing for representing the spectral envelope of a digital signal of speech in compressed form, using the information of a linear predictive model...

