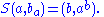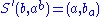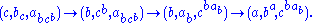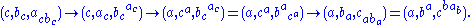Biquandle
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, biquandles and biracks are generalizations of quandles and racks. Whereas the hinterland of quandles and racks is the theory of classical knots
, that of the bi-versions, is the theory of virtual knot
s.
Biquandles and biracks have two binary operations on a set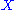 written
written 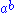 and
and 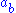 . These satisfy the following three axioms:
. These satisfy the following three axioms:
1.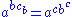
2.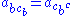
3.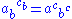
These identities appeared in 1992 in reference [FRS] where the object was called a species.
The superscript and subscript notation is useful here because it dispenses with the need for brackets. For example
if we write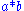 for
for 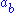 and
and 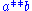 for
for 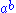 then the
then the
three axioms above become
1.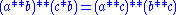
2.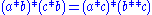
3.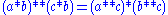
For other notations see .
If in addition the two operations are invertible, that is given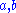 in the set
in the set 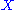 there are unique
there are unique 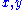 in the set
in the set 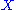 such that
such that 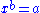 and
and 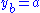 then the set
then the set 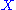 together with the two operations define a birack.
together with the two operations define a birack.
For example if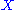 , with the operation
, with the operation 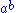 , is a rack then it is a birack if we define the other operation to be the identity
, is a rack then it is a birack if we define the other operation to be the identity
,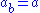 .
.
For a birack the function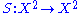 can be defined by
can be defined by
Then
1.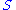 is a bijection
is a bijection
2.
In the second condition,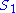 and
and 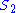 are defined by
are defined by 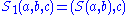 and
and 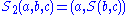 . This condition is sometimes known as the set-theoretic Yang-Baxter equation.
. This condition is sometimes known as the set-theoretic Yang-Baxter equation.
To see that 1. is true note that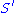 defined by
defined by
is the inverse to

To see that 2. is true let us follow the progress of the triple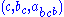 under
under 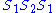 . So
. So
On the other hand,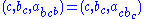 . Its progress under
. Its progress under 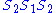 is
is
Any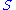 satisfying 1. 2. is said to be a switch (precursor of biquandles and biracks).
satisfying 1. 2. is said to be a switch (precursor of biquandles and biracks).
Examples of switches are the identity
, the twist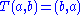 and
and 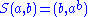 where
where 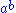 is the operation of a rack.
is the operation of a rack.
A switch will define a birack if the operations are invertible. Note that the identity switch does not do this.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, biquandles and biracks are generalizations of quandles and racks. Whereas the hinterland of quandles and racks is the theory of classical knots
Knot
A knot is a method of fastening or securing linear material such as rope by tying or interweaving. It may consist of a length of one or several segments of rope, string, webbing, twine, strap, or even chain interwoven such that the line can bind to itself or to some other object—the "load"...
, that of the bi-versions, is the theory of virtual knot
Virtual knot
In knot theory, a virtual knot is a generalization of the classical idea of knots in several ways that are all equivalent, introduced by .-Overview:...
s.
Biquandles and biracks have two binary operations on a set
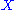 written
written 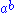 and
and 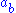 . These satisfy the following three axioms:
. These satisfy the following three axioms:1.
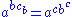
2.
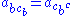
3.
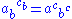
These identities appeared in 1992 in reference [FRS] where the object was called a species.
The superscript and subscript notation is useful here because it dispenses with the need for brackets. For example
if we write
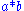 for
for 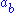 and
and 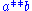 for
for 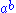 then the
then thethree axioms above become
1.
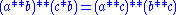
2.
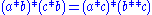
3.
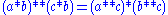
For other notations see .
If in addition the two operations are invertible, that is given
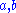 in the set
in the set 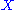 there are unique
there are unique 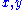 in the set
in the set 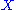 such that
such that 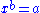 and
and 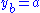 then the set
then the set 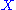 together with the two operations define a birack.
together with the two operations define a birack.For example if
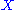 , with the operation
, with the operation 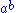 , is a rack then it is a birack if we define the other operation to be the identity
, is a rack then it is a birack if we define the other operation to be the identityIdentity (mathematics)
In mathematics, the term identity has several different important meanings:*An identity is a relation which is tautologically true. This means that whatever the number or value may be, the answer stays the same. For example, algebraically, this occurs if an equation is satisfied for all values of...
,
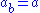 .
.For a birack the function
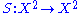 can be defined by
can be defined byThen
1.
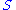 is a bijection
is a bijectionBijection
A bijection is a function giving an exact pairing of the elements of two sets. A bijection from the set X to the set Y has an inverse function from Y to X. If X and Y are finite sets, then the existence of a bijection means they have the same number of elements...
2.

In the second condition,
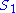 and
and 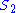 are defined by
are defined by 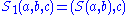 and
and 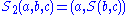 . This condition is sometimes known as the set-theoretic Yang-Baxter equation.
. This condition is sometimes known as the set-theoretic Yang-Baxter equation.To see that 1. is true note that
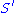 defined by
defined byis the inverse to

To see that 2. is true let us follow the progress of the triple
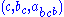 under
under 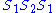 . So
. SoOn the other hand,
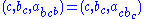 . Its progress under
. Its progress under 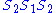 is
isAny
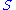 satisfying 1. 2. is said to be a switch (precursor of biquandles and biracks).
satisfying 1. 2. is said to be a switch (precursor of biquandles and biracks).Examples of switches are the identity
Identity (mathematics)
In mathematics, the term identity has several different important meanings:*An identity is a relation which is tautologically true. This means that whatever the number or value may be, the answer stays the same. For example, algebraically, this occurs if an equation is satisfied for all values of...
, the twist
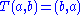 and
and 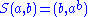 where
where 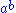 is the operation of a rack.
is the operation of a rack.A switch will define a birack if the operations are invertible. Note that the identity switch does not do this.