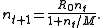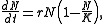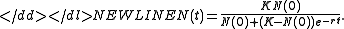Beverton-Holt model
Encyclopedia
The Beverton–Holt model is a classic discrete-time population model
which gives the expected
number n t+1 (or density) of individuals in generation t + 1 as a function of the number of individuals in the previous generation,
Here R0 is interpreted as the proliferation rate per generation and K = (R0 − 1) M is the carrying capacity
of the environment. The Beverton–Holt model was introduced in the context of fisheries
by Beverton
& Holt
(1957). Subsequent work has derived the model under other assumptions such as contest competition
(Brännström & Sumpter 2005) or within-year resource limited competition (Geritz & Kisdi 2004). The Beverton–Holt model can be generalized to include scramble competition
(see the Ricker model
, the Hassell model and the Maynard Smith
–Slatkin model). It is also possible to include a parameter reflecting the spatial clustering of individuals (see Brännström & Sumpter 2005).
Despite being nonlinear, the model can be solved explicitly, since it is in fact an inhomogeneous linear equation in 1/n.
The solution is
Population modeling
A population model is a type of mathematical model that is applied to the study of population dynamics.Models allow a better understanding of how complex interactions and processes work. Modeling of dynamic interactions in nature can provide a manageable way of understanding how numbers change over...
which gives the expected
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
number n t+1 (or density) of individuals in generation t + 1 as a function of the number of individuals in the previous generation,
Here R0 is interpreted as the proliferation rate per generation and K = (R0 − 1) M is the carrying capacity
Carrying capacity
The carrying capacity of a biological species in an environment is the maximum population size of the species that the environment can sustain indefinitely, given the food, habitat, water and other necessities available in the environment...
of the environment. The Beverton–Holt model was introduced in the context of fisheries
Fisheries management
Fisheries management draws on fisheries science in order to find ways to protect fishery resources so sustainable exploitation is possible. Modern fisheries management is often referred to as a governmental system of appropriate management rules based on defined objectives and a mix of management...
by Beverton
Ray Beverton
Raymond John Heaphy Beverton, CBE, FRS was an important founder of fisheries science. He is best known for the book On the Dynamics of Exploited Fish Populations which he wrote with Sidney Holt. The book is a cornerstone of modern fisheries science and remains much used today...
& Holt
Sidney Holt
Sidney J. Holt is an important founder of fisheries science. He is best known for the book On the Dynamics of Exploited Fish Populations which he published with Ray Beverton in 1957. The book is a cornerstone of modern fisheries science and remains much used today. Holt served with the FAO in 1953...
(1957). Subsequent work has derived the model under other assumptions such as contest competition
Competition (biology)
Competition is an interaction between organisms or species, in which the fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another. Limited supply of at least one resource used by both is required. Competition both within and between species is an important topic in ecology, especially community ecology...
(Brännström & Sumpter 2005) or within-year resource limited competition (Geritz & Kisdi 2004). The Beverton–Holt model can be generalized to include scramble competition
Scramble competition
In general terms, scramble competition is a type of competition in which equally rationed yet perpetually limited resources within an environment result in decreased survival rates for all competitors...
(see the Ricker model
Ricker model
The Ricker model, named after Bill Ricker, is a classic discrete population model which gives the expected number a t+1 of individuals in generation t + 1 as a function of the number of individuals in the previous generation,Here r is interpreted as an intrinsic growth rate and k as...
, the Hassell model and the Maynard Smith
John Maynard Smith
John Maynard Smith,His surname was Maynard Smith, not Smith, nor was it hyphenated. F.R.S. was a British theoretical evolutionary biologist and geneticist. Originally an aeronautical engineer during the Second World War, he took a second degree in genetics under the well-known biologist J.B.S....
–Slatkin model). It is also possible to include a parameter reflecting the spatial clustering of individuals (see Brännström & Sumpter 2005).
Despite being nonlinear, the model can be solved explicitly, since it is in fact an inhomogeneous linear equation in 1/n.
The solution is
-
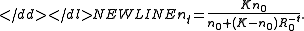
Because of this structure, the model can be considered as the discrete-time analogue of the continuous-time logistic equation for population growthPopulation growthPopulation growth is the change in a population over time, and can be quantified as the change in the number of individuals of any species in a population using "per unit time" for measurement....
introduced by Verhulst; for comparison, the logistic equation is
and its solution is
-