Bethlem myopathy
Encyclopedia
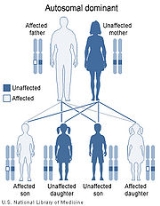
Bethlem myopathy is an autosomal dominant myopathy
, classified as a congenital form of muscular dystrophy
, that is caused by a variation in one of the three genes coding for type VI collagen
. These include COL6A1
, COL6A2
, and COL6A3
.
s.
Bethlem myopathy is an extremely rare disorder, with fewer than 100 families worldwide known to have it. It is sometimes known as "Leonard syndrome" after one of the presenting families. Contractures of the fingers are a typical symptom of Bethlem myopathy but not of the related Ullrich's myopathy (which does include contractures of arms and legs, as does Bethlem myopathy). Serum
creatine kinase
is elevated in Bethlem myopathy, as there is ongoing muscle cell death. Patients with Bethlem myopathy may expect a normal life span and continued mobility into adulthood. There is currently no cure for this disorder, but the contractures of the legs can be alleviated with heel-cord surgery followed by bracing and regular physical therapy. Repeated surgeries to lengthen the heel cords may be needed as the child grows to adulthood.

Myopathy
In medicine, a myopathy is a muscular disease in which the muscle fibers do not function for any one of many reasons, resulting in muscular weakness. "Myopathy" simply means muscle disease...
, classified as a congenital form of muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy is a group of muscle diseases that weaken the musculoskeletal system and hamper locomotion. Muscular dystrophies are characterized by progressive skeletal muscle weakness, defects in muscle proteins, and the death of muscle cells and tissue.In the 1860s, descriptions of boys who...
, that is caused by a variation in one of the three genes coding for type VI collagen
Collagen
Collagen is a group of naturally occurring proteins found in animals, especially in the flesh and connective tissues of mammals. It is the main component of connective tissue, and is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up about 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content...
. These include COL6A1
COL6A1
Collagen alpha-1 chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL6A1 gene.- Function :The collagens are a superfamily of proteins that play a role in maintaining the integrity of various tissues. Collagens are extracellular matrix proteins and have a triple-helical domain as their common...
, COL6A2
COL6A2
Collagen alpha-2 chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL6A2 gene.- Function :This gene encodes one of the three alpha chains of type VI collagen, a beaded filament collagen found in most connective tissues. The product of this gene contains several domains similar to von Willebrand...
, and COL6A3
COL6A3
Collagen alpha-3 chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL6A3 gene.- Function :This gene encodes the alpha 3 chain, one of the three alpha chains of type VI collagen, a beaded filament collagen found in most connective tissues. The alpha 3 chain of type VI collagen is much larger than...
.
Presentation
The onset of this disease begins in childhood, but its progression is extremely slow, with symptoms of weakness and walking difficulties usually not presenting until past age 50. Early symptoms include Gower's sign ("climbing" up the thighs with the hands when rising from the floor) and tiptoe-walking caused by the beginning of contractureContracture
A muscle contracture is a permanent shortening of a muscle or joint.. It is usually in response to prolonged hypertonic spasticity in a concentrated muscle area, such as is seen in the tightest muscles of people with conditions like spastic cerebral palsy....
s.
Bethlem myopathy is an extremely rare disorder, with fewer than 100 families worldwide known to have it. It is sometimes known as "Leonard syndrome" after one of the presenting families. Contractures of the fingers are a typical symptom of Bethlem myopathy but not of the related Ullrich's myopathy (which does include contractures of arms and legs, as does Bethlem myopathy). Serum
Blood serum
In blood, the serum is the component that is neither a blood cell nor a clotting factor; it is the blood plasma with the fibrinogens removed...
creatine kinase
Creatine kinase
Creatine kinase , also known as creatine phosphokinase or phospho-creatine kinase , is an enzyme expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and consumes adenosine triphosphate to create phosphocreatine and adenosine diphosphate...
is elevated in Bethlem myopathy, as there is ongoing muscle cell death. Patients with Bethlem myopathy may expect a normal life span and continued mobility into adulthood. There is currently no cure for this disorder, but the contractures of the legs can be alleviated with heel-cord surgery followed by bracing and regular physical therapy. Repeated surgeries to lengthen the heel cords may be needed as the child grows to adulthood.


