
Bergamottin
Encyclopedia
Bergamottin is a natural furanocoumarin
found principally in grapefruit juice
. It is also found in the oil of bergamot
, from which it was first isolated and from which its name is derived. To a lesser extent, bergamottin is also present in the essential oil
s of other citrus
fruits. Along with the chemically related compound 6’,7’-dihydroxybergamottin, it is believed to be responsible for the grapefruit juice effect in which the consumption of the juice affects the metabolism of a variety of pharmaceutical drugs.
. They are inhibitors
of some isoforms
of the cytochrome P450 enzyme, particularly CYP3A4
. This prevents oxidative metabolism of certain drugs by the enzyme, resulting in an elevated concentration of drug in the bloodstream.
Normally, the grapefruit juice effect is considered to be a negative interaction, and patients are often warned not to consume grapefruit or its juice when taking medication. However, some current research is focused on the potential benefits of cytochrome P450 inhibition. Bergamottin, dihydroxybergamottin, or synthetic analogs may be developed as drugs that are targeted to increase the oral bioavailability
of other drugs. Drugs that may have limited use because they are metabolized by CYP3A4
may become viable medications when taken with a CYP3A4 inhibitor because the dose required to achieve a necessary concentration in the blood would be lowered.

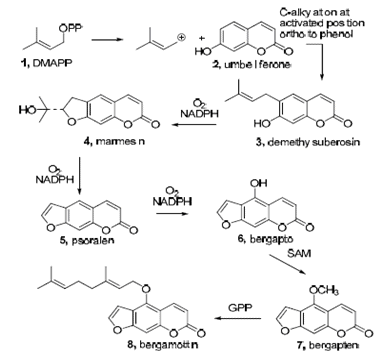
, more commonly known as DMAPP. The cyclization of an alkyl group occurs to form marmesin (4), which is done in the presence of NADPH and oxygen along with a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase catalyst. This process is then repeated twice more, first to remove the hydroxyisopropyl substituent from marmesin (4) to form psoralen (5), and then to add a hydroxyl group to form bergaptol (6). Bergaptol (6) is next methylated with SAM, S-Adenosyl methionine
, to form bergapten (7). The final step in this biosynthesis is the attachment of a GPP, or geranyl pyrophosphate
, to the newly methylated bergapten (7) to form the target molecule bergamottin (8).
Furanocoumarin
Furanocoumarins, or furocoumarins, are a class of organic chemical compounds produced by a variety of plants. They are biosynthesized partly through the phenylpropanoid pathway and the mevalonate pathway, which is biosynthesized by a coupling of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate and 7-hydroxycoumarin...
found principally in grapefruit juice
Grapefruit juice
Grapefruit juice is the fruit juice from grapefruits. It is rich in Vitamin C and ranges from sweet-tart to very sour. It is considered by some cultures to be a mystical tonic which promotes health and vigor. Certain civilizations have had holy men who live on Grapefruit juice alone...
. It is also found in the oil of bergamot
Bergamot orange
Citrus bergamia, the Bergamot orange, is a fragrant fruit the size of an orange, with a yellow colour similar to a lemon. Genetic research into the ancestral origins of extant citrus cultivars recently matched the bergamot as a likely hybrid of Citrus limetta and Citrus aurantium...
, from which it was first isolated and from which its name is derived. To a lesser extent, bergamottin is also present in the essential oil
Essential oil
An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile aroma compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils or aetherolea, or simply as the "oil of" the plant from which they were extracted, such as oil of clove...
s of other citrus
Citrus
Citrus is a common term and genus of flowering plants in the rue family, Rutaceae. Citrus is believed to have originated in the part of Southeast Asia bordered by Northeastern India, Myanmar and the Yunnan province of China...
fruits. Along with the chemically related compound 6’,7’-dihydroxybergamottin, it is believed to be responsible for the grapefruit juice effect in which the consumption of the juice affects the metabolism of a variety of pharmaceutical drugs.
Chemistry
Chemically, bergamottin and dihydroxybergamottin are linear furanocoumarins functionalized with side chains derived from geraniolGeraniol
Geraniol is a monoterpenoid and an alcohol. It is the primary part of rose oil, palmarosa oil, and citronella oil . It also occurs in small quantities in geranium, lemon, and many other essential oils. It appears as a clear to pale-yellow oil that is insoluble in water, but soluble in most common...
. They are inhibitors
Enzyme inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to enzymes and decreases their activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used as herbicides and pesticides...
of some isoforms
Protein isoform
A protein isoform is any of several different forms of the same protein. Different forms of a protein may be produced from related genes, or may arise from the same gene by alternative splicing. A large number of isoforms are caused by single-nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs, small genetic...
of the cytochrome P450 enzyme, particularly CYP3A4
CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 , a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is one of the most important enzymes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP3A4 is involved in the oxidation of the largest range of substrates of all the CYPs. As a result, CYP3A4 is present in...
. This prevents oxidative metabolism of certain drugs by the enzyme, resulting in an elevated concentration of drug in the bloodstream.
Normally, the grapefruit juice effect is considered to be a negative interaction, and patients are often warned not to consume grapefruit or its juice when taking medication. However, some current research is focused on the potential benefits of cytochrome P450 inhibition. Bergamottin, dihydroxybergamottin, or synthetic analogs may be developed as drugs that are targeted to increase the oral bioavailability
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is used to describe the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation, one of the principal pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. By definition, when a medication is administered...
of other drugs. Drugs that may have limited use because they are metabolized by CYP3A4
CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 , a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is one of the most important enzymes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP3A4 is involved in the oxidation of the largest range of substrates of all the CYPs. As a result, CYP3A4 is present in...
may become viable medications when taken with a CYP3A4 inhibitor because the dose required to achieve a necessary concentration in the blood would be lowered.

Biosynthesis of bergamottin
Bergamottin is derived from components originating in the shikimate pathway. The biosynthesis of this compound starts with the formation of the demethylsuberosin (3) product which is formed via the alkylation of the umbelliferone (2) compound. The alkylation of the umbelliferone is initiated with the use of dimethylallyl pyrophosphateDimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate product of both mevalonic acid pathway and DOXP/MEP pathway. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate and exists in virtually all life forms...
, more commonly known as DMAPP. The cyclization of an alkyl group occurs to form marmesin (4), which is done in the presence of NADPH and oxygen along with a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase catalyst. This process is then repeated twice more, first to remove the hydroxyisopropyl substituent from marmesin (4) to form psoralen (5), and then to add a hydroxyl group to form bergaptol (6). Bergaptol (6) is next methylated with SAM, S-Adenosyl methionine
S-Adenosyl methionine
S-Adenosyl methionine is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers. SAM was first discovered in Italy by G. L. Cantoni in 1952. It is made from adenosine triphosphate and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase . Transmethylation, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation are the...
, to form bergapten (7). The final step in this biosynthesis is the attachment of a GPP, or geranyl pyrophosphate
Geranyl pyrophosphate
Geranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate, cholesterol, terpenes and terpenoids....
, to the newly methylated bergapten (7) to form the target molecule bergamottin (8).


