
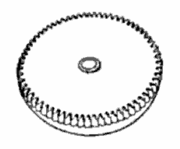
Barrel (horology)
Encyclopedia
Mechanical watch
A mechanical watch is a watch that uses a mechanical mechanism to measure the passage of time, as opposed to modern quartz watches which function electronically. It is driven by a spring which must be wound periodically...
es and clock
Clock
A clock is an instrument used to indicate, keep, and co-ordinate time. The word clock is derived ultimately from the Celtic words clagan and clocca meaning "bell". A silent instrument missing such a mechanism has traditionally been known as a timepiece...
s, a barrel is a cylindrical metal box closed by a cover, with a ring of gear teeth around it, containing a spiral spring called the mainspring
Mainspring
A mainspring is a spiral torsion spring of metal ribbon that is the power source in mechanical watches and some clocks. Winding the timepiece, by turning a knob or key, stores energy in the mainspring by twisting the spiral tighter. The force of the mainspring then turns the clock's wheels as it...
, which provides power to run the timepiece. The barrel turns on an arbor (axle). The spring is hooked to the barrel at its outer end and to the arbor at its inner end. The barrel teeth engage the first pinion
Pinion
A pinion is a round gear used in several applications:*usually the smallest gear in a gear drive train, although in the case of John Blenkinsop's Salamanca, the pinion was rather large...
of the wheel train
Wheel train (horology)
In horology, a wheel train is the gear train of a mechanical watch or clock. Although the term is used for other types of gear trains, the long history of mechanical timepieces has created a traditional terminology for their gear trains which is not used in other applications of gears.Watch...
of the watch, usually the center wheel. Barrels rotate slowly: for a watch mainspring barrel, the rate is usually one rotation every 8 hours.
Types of barrels:
- Plain Barrel: i.e. without teeth, used in fusee watches and clocks. A chain, or cord, was wound around the plain barrel, connecting it to the fusee.
- Going barrel: the form used in modern watches, is wound by turning the arbor and drives the watch movement by a ring of teeth around the barrel. This enables the mainspring to continue running the watch while it is being wound. Invented by Jean-Antoine LépineJean-Antoine LépineJean-Antoine Lépine , was a revolutionary and inventive French watch and clockmaker, who contributed with crucial inventions for watchmaking still used nowadays...
.
- Hanging Barrel: a version of the going barrel that to save space is supported by the movement only at its upper end.
- Motor or safety barrel: used in pocketwatches around 1900, a reverse variant of the going barrel in which the spring is wound by turning the barrel, and turns the watch movement by the central arbor. The purpose of this arrangement was that if the spring breaks, destructive recoil forces would not be applied to the vulnerable gear trainGear trainA gear train is formed by mounting gears on a frame so that the teeth of the gears engage. Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, this provides a smooth transmission of rotation from one gear to the next.The transmission of...
.

