Axenfeld syndrome
Encyclopedia
Axenfeld syndrome is the name given to a rare autosomal dominant disorder, which affects the development of the teeth, eyes, and abdominal region.
who studied anterior segment disorders, especially those such as Rieger Syndrome and the Axenfeld Anomaly.
The term "Rieger syndrome" is sometimes used to indicate an association with glaucoma
.. Rieger Syndrome is by medical definition determined by the presence of malformations of the teeth, the underdevelopment of the anterior segment of the eye, along with the manifestations caused by the Axenfeld anomaly . In addition to these occurrences, a prominent Schwalbe's line
, an opaque ring around the cornea known as posterior embryotoxin, Glaucoma
and hypolasia of the iris can occur in the eye. Other defects such as a lower than average height and stature, a stunt in the development of the mid-facial features and mental deficiencies may be observed.
, the malformation is not limited to the eye, as Axenfeld syndrome when associated with the PITX2
genetic mutation usually presents congenital malformations of the face, teeth, and skeletal system.
The most characteristic feature affecting the eye is a distinct corneal posterior arcuate ring, known as an "embryotoxon". The iris is commonly adherent to the Schwalbe's line
(posterior surface of the cornea).
Analysis of genetic samples from affected patients could result in the discovery of one of the three known genetic mutations which cause the syndrome. About 40% of Axenfeld-Rieger sufferers display mutations in one of the genes known as PAX6
, PITX2
and FOXC1.
The OMIM classification is as follows:
Detection of any of these mutations can give patients a clear diagnosis and post and antenatal procedures such as Preimplantation genetic diagnosis
, Chorionic villus sampling
and Amniocentesis
can be offered to patients. From here, it is a decision for the prospective parent to decide whether they wish to use the genetic diagnosis that they have acquired to prevent the condition from being passed on to future generations.
 The molecular genetics
The molecular genetics
of Axenfeld syndrome are poorly understood, and centers on three genes identified by cloning of chromosomal breakpoints from patients.
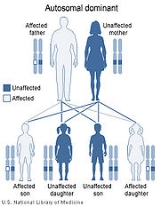
This disorder is inheritable as an autosomal dominant trait, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
, and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder when inherited from a parent who has the disorder. As shown in the diagram, this gives a 50/50 chance of offspring inheriting the condition.
Eponym
It is named after the German ophthalmologist Theodor AxenfeldTheodor Axenfeld
Karl Theodor Paul Polykarpus Axenfeld was a German ophthalmologist who was born in Smyrna in the Ottoman Empire to a German minister. As a child his family moved back to Germany in the town of Godesberg. He received his medical doctorate in 1890 from the University of Marburg...
who studied anterior segment disorders, especially those such as Rieger Syndrome and the Axenfeld Anomaly.
The term "Rieger syndrome" is sometimes used to indicate an association with glaucoma
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disorder in which the optic nerve suffers damage, permanently damaging vision in the affected eye and progressing to complete blindness if untreated. It is often, but not always, associated with increased pressure of the fluid in the eye...
.. Rieger Syndrome is by medical definition determined by the presence of malformations of the teeth, the underdevelopment of the anterior segment of the eye, along with the manifestations caused by the Axenfeld anomaly . In addition to these occurrences, a prominent Schwalbe's line
Schwalbe's line
Schwalbe's line is the anatomical line found on the interior surface of the eye's cornea, and delineates the outer limit of the corneal endothelium layer. Specifically, it represents the termination of Descemet's membrane. In many cases it can be seen via gonioscopy....
, an opaque ring around the cornea known as posterior embryotoxin, Glaucoma
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disorder in which the optic nerve suffers damage, permanently damaging vision in the affected eye and progressing to complete blindness if untreated. It is often, but not always, associated with increased pressure of the fluid in the eye...
and hypolasia of the iris can occur in the eye. Other defects such as a lower than average height and stature, a stunt in the development of the mid-facial features and mental deficiencies may be observed.
Diagnosis
Although most recognized for its correlation with the onset of glaucomaGlaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disorder in which the optic nerve suffers damage, permanently damaging vision in the affected eye and progressing to complete blindness if untreated. It is often, but not always, associated with increased pressure of the fluid in the eye...
, the malformation is not limited to the eye, as Axenfeld syndrome when associated with the PITX2
PITX2
Paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 2 also known as pituitary homeobox 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PITX2 gene.- Function :...
genetic mutation usually presents congenital malformations of the face, teeth, and skeletal system.
The most characteristic feature affecting the eye is a distinct corneal posterior arcuate ring, known as an "embryotoxon". The iris is commonly adherent to the Schwalbe's line
Schwalbe's line
Schwalbe's line is the anatomical line found on the interior surface of the eye's cornea, and delineates the outer limit of the corneal endothelium layer. Specifically, it represents the termination of Descemet's membrane. In many cases it can be seen via gonioscopy....
(posterior surface of the cornea).
Analysis of genetic samples from affected patients could result in the discovery of one of the three known genetic mutations which cause the syndrome. About 40% of Axenfeld-Rieger sufferers display mutations in one of the genes known as PAX6
PAX6
Paired box protein Pax-6 also known as aniridia type II protein or oculorhombin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PAX6 gene.- Function :PAX6 is a member of the Pax gene family...
, PITX2
PITX2
Paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 2 also known as pituitary homeobox 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PITX2 gene.- Function :...
and FOXC1.
The OMIM classification is as follows:
| Type | OMIM | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | PITX2 PITX2 Paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 2 also known as pituitary homeobox 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PITX2 gene.- Function :... |
|
| Type 2 | possibly FOXO1A | |
| Type 3 | FOXC1 | |
| DeHauwere syndrome | Unknown |
Detection of any of these mutations can give patients a clear diagnosis and post and antenatal procedures such as Preimplantation genetic diagnosis
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis
In medicine and genetics pre-implantation genetic diagnosis refers to procedures that are performed on embryos prior to implantation, sometimes even on oocytes prior to fertilization. PGD is considered another way to prenatal diagnosis...
, Chorionic villus sampling
Chorionic villus sampling
Chorionic villus sampling , sometimes misspelled "chorionic villous sampling", is a form of prenatal diagnosis to determine chromosomal or genetic disorders in the fetus. It entails sampling of the chorionic villus and testing it...
and Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections, in which a small amount of amniotic fluid, which contains fetal tissues, is sampled from the amnion or amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus, and the fetal DNA is examined for...
can be offered to patients. From here, it is a decision for the prospective parent to decide whether they wish to use the genetic diagnosis that they have acquired to prevent the condition from being passed on to future generations.
Pathophysiology

Molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is the field of biology and genetics that studies the structure and function of genes at a molecular level. The field studies how the genes are transferred from generation to generation. Molecular genetics employs the methods of genetics and molecular biology...
of Axenfeld syndrome are poorly understood, and centers on three genes identified by cloning of chromosomal breakpoints from patients.
This disorder is inheritable as an autosomal dominant trait, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder when inherited from a parent who has the disorder. As shown in the diagram, this gives a 50/50 chance of offspring inheriting the condition.
See also
- GlaucomaGlaucomaGlaucoma is an eye disorder in which the optic nerve suffers damage, permanently damaging vision in the affected eye and progressing to complete blindness if untreated. It is often, but not always, associated with increased pressure of the fluid in the eye...
- SHORT syndromeSHORT syndromeSHORT syndrome is a medical condition in which affected individuals have multiple birth defects in different organ systems.It was characterized in 1975.-Presentation:...
- AutosomeAutosomeAn autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
- Chorionic villus samplingChorionic villus samplingChorionic villus sampling , sometimes misspelled "chorionic villous sampling", is a form of prenatal diagnosis to determine chromosomal or genetic disorders in the fetus. It entails sampling of the chorionic villus and testing it...
- AmniocentesisAmniocentesisAmniocentesis is a medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections, in which a small amount of amniotic fluid, which contains fetal tissues, is sampled from the amnion or amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus, and the fetal DNA is examined for...
- Preimplantation genetic diagnosisPreimplantation genetic diagnosisIn medicine and genetics pre-implantation genetic diagnosis refers to procedures that are performed on embryos prior to implantation, sometimes even on oocytes prior to fertilization. PGD is considered another way to prenatal diagnosis...

