Atelosteogenesis, type II
Encyclopedia
Atelosteogenesis, type II is a severe disorder of cartilage
and bone
development. It is extremely rare, and infants with the disorder are usually stillborn
, however those that that survive birth
die soon after from respiratory failure
.
s and leg
s, a narrow chest, and a prominent, rounded abdomen
. This disorder is also characterized by an opening in the roof of the mouth (cleft palate), distinctive facial features, an inward- and downward-turning foot (clubfoot), and unusually positioned thumbs (hitchhiker thumbs).
The signs and symptoms of atelosteogenesis, type 2 are similar to those of another skeletal disorder called diastrophic dysplasia
. Atelosteogenesis, type 2 tends to be more severe, however.
 Atelosteogenesis, type 2 is one of a spectrum of skeletal disorders caused by mutations in the SLC26A2
Atelosteogenesis, type 2 is one of a spectrum of skeletal disorders caused by mutations in the SLC26A2
gene. The protein
made by this gene is essential for the normal development of cartilage and for its conversion to bone. Mutations in the SLC26A2 gene disrupt the structure of developing cartilage, preventing bones from forming properly and resulting in the skeletal problems characteristic of atelosteogenesis, type 2.
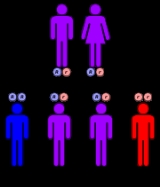
This condition is an autosomal recessive disorder, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - must be inherited for a child to be born with the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are not affected by disorder, but are carriers of one copy of the altered gene.
Cartilage
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in many areas in the bodies of humans and other animals, including the joints between bones, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the elbow, the knee, the ankle, the bronchial tubes and the intervertebral discs...
and bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
development. It is extremely rare, and infants with the disorder are usually stillborn
Stillbirth
A stillbirth occurs when a fetus has died in the uterus. The Australian definition specifies that fetal death is termed a stillbirth after 20 weeks gestation or the fetus weighs more than . Once the fetus has died the mother still has contractions and remains undelivered. The term is often used in...
, however those that that survive birth
Birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring. The offspring is brought forth from the mother. The time of human birth is defined as the time at which the fetus comes out of the mother's womb into the world...
die soon after from respiratory failure
Respiration (physiology)
'In physiology, respiration is defined as the transport of oxygen from the outside air to the cells within tissues, and the transport of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction...
.
Symptoms
Infants born with this condition have very short armArm
In human anatomy, the arm is the part of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow joints. In other animals, the term arm can also be used for analogous structures, such as one of the paired forelimbs of a four-legged animal or the arms of cephalopods...
s and leg
Leg
Łęg may refer to the following places in Poland:*A former name for the town of Ełk *Part of the Czyżyny district of Kraków*Łęg, Pleszew County in Greater Poland Voivodeship...
s, a narrow chest, and a prominent, rounded abdomen
Abdomen
In vertebrates such as mammals the abdomen constitutes the part of the body between the thorax and pelvis. The region enclosed by the abdomen is termed the abdominal cavity...
. This disorder is also characterized by an opening in the roof of the mouth (cleft palate), distinctive facial features, an inward- and downward-turning foot (clubfoot), and unusually positioned thumbs (hitchhiker thumbs).
The signs and symptoms of atelosteogenesis, type 2 are similar to those of another skeletal disorder called diastrophic dysplasia
Diastrophic dysplasia
Diastrophic dysplasia is an autosomal recessive dysplasia which affects cartilage and bone development....
. Atelosteogenesis, type 2 tends to be more severe, however.
Genetics

SLC26A2
The SLC26A2 protein is a member of the solute carrier family. In humans, this transporter is encoded by the SLC26A2 gene.- Function :The diastrophic dysplasia sulfate transporter is a transmembrane glycoprotein implicated in the pathogenesis of several human chondrodysplasias...
gene. The protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
made by this gene is essential for the normal development of cartilage and for its conversion to bone. Mutations in the SLC26A2 gene disrupt the structure of developing cartilage, preventing bones from forming properly and resulting in the skeletal problems characteristic of atelosteogenesis, type 2.
This condition is an autosomal recessive disorder, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - must be inherited for a child to be born with the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are not affected by disorder, but are carriers of one copy of the altered gene.

