Artificial enzyme
Encyclopedia
Enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
catalysis of chemical reactions occur with high selectivity and rate in a small part of the enzyme macromolecule known as the active site
Active site
In biology the active site is part of an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The majority of enzymes are proteins but RNA enzymes called ribozymes also exist. The active site of an enzyme is usually found in a cleft or pocket that is lined by amino acid residues that...
. There, the binding of a substrate
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
close to functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
s in the enzyme causes catalysis
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
by so-called proximity effects. It is therefore possible to create similar catalysts from small molecule
Small molecule
In the fields of pharmacology and biochemistry, a small molecule is a low molecular weight organic compound which is by definition not a polymer...
mimics of enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
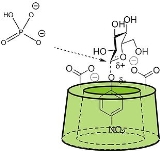
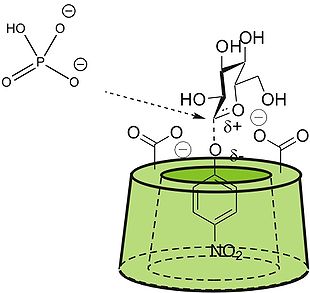
active sites by combining, in a small molecule, the ability to bind substrate with catalytic functional groups. Since the artificial enzymes need to bind molecules, they are made based on a host-molecule such as a cyclodextrin
Cyclodextrin
Cyclodextrins are a family of compounds made up of sugar molecules bound together in a ring ....
, crown ethers or calixarene
Calixarene
A calixarene is a macrocycle or cyclic oligomer based on a hydroxyalkylation product of a phenol and an aldehyde. The word calixarene is derived from calix or chalice because this type of molecule resembles a vase and from the word arene that refers to the aromatic building block...
etc.
A number of artificial enzymes have been reported catalysing various reactions with rate increases up to 103; this is nevertheless substantially lower than natural enzymes that typically causes rate increases above 106. One of the pioneers in artificial enzyme research is chemist Ronald Breslow
Ronald Breslow
Ronald C. D. Breslow is an American chemist from Rahway, New Jersey. He is currently University Professor at Columbia University, where he is based in the Department of Chemistry and affiliated with the Departments of Biological Sciences and Pharmacology; he has also been on the faculty of its...
.
New approaches based on amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s or peptide
Peptide
Peptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
s as characteristic molecular moieties have led to a significant expansion of the field of artificial enzymes or enzyme mimics. For instance, recent results by the group of Rob Liskamphttp://www.pharm.uu.nl/ffwuk.htm?/medchem/ have shown that scaffolded histidine residues can be used as mimics of certain metalloproteins and -enzymes. Especially the structural mimicry of certain copper proteins
Copper proteins
Copper proteins are proteins that contain one or more copper ions as prosthetic groups. The metal centres in the copper proteins can be classified into several types:...
(e.g. hemocyanin
Hemocyanin
Hemocyanins are respiratory proteins in the form of metalloproteins containing two copper atoms that reversibly bind a single oxygen molecule . Oxygenation causes a color change between the colorless Cu deoxygenated form and the blue Cu oxygenated form...
, tyrosinase
Tyrosinase
Tyrosinase also known as monophenol monooxygenase is an enzyme that catalyses the oxidation of phenols and is widespread in plants and animals...
and catechol oxidase
Catechol oxidase
Catechol oxidase is an enzyme that catalyses the oxidation of phenols such as catechol. Catechol oxidase is a copper-containing enzyme whose activity is similar to that of tyrosinase, a related class of copper oxidases....
), containing so-called type-3 copper binding sites, has been shown. This is a significant improvement since the use of scaffolded histidine residues is one step closer to the mimicry of enzymes by biological relevant species such as amino acids and peptideshttp://www.rsc.org/Publishing/Journals/CC/article.asp?doi=b709400k.

