
Approximate Bayesian computation
Encyclopedia
Approximate Bayesian computation (ABC) is a family of computational techniques in Bayesian statistics
. These simulation techniques operate on summary data (such as population mean, or variance) to make broad inferences with less computation than might be required if all available data were analyzed in detail. They are especially useful in situations where evaluation of the likelihood is computationally prohibitive, or whenever suitable likelihoods are not available.
ABC methods originated in population and evolutionary genetics but have recently also been introduced to the analysis of complex and stochastic dynamical systems.

where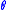 are the parameters of a probability model,
are the parameters of a probability model,  are the observed data, and
are the observed data, and 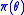 is the prior distribution of the parameters
is the prior distribution of the parameters 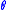 .
. 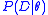 is the likelihood
is the likelihood
of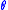 , that is the probability of observing the data
, that is the probability of observing the data  given the model with parameter
given the model with parameter 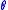 .
.
The explicit evaluation of the likelihood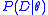 is avoided in ABC approaches by considering distances between observed and data simulated from a model with parameter
is avoided in ABC approaches by considering distances between observed and data simulated from a model with parameter 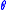 . For sufficiently complex models and large data sets the probability of happening upon a simulation run that yields precisely the same dataset as the one observed will be very small, often unacceptably so. So rather than considering the data we consider a summary statistic of the data,
. For sufficiently complex models and large data sets the probability of happening upon a simulation run that yields precisely the same dataset as the one observed will be very small, often unacceptably so. So rather than considering the data we consider a summary statistic of the data, 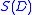 , and use a distance
, and use a distance 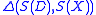 between the summary statistics of real and simulated data,
between the summary statistics of real and simulated data,  and
and  , respectively.
, respectively.
The generic ABC approach to infer the posterior probability distribution of a parameter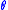 is as follows:
is as follows:
For sufficiently small the ABC procedure should deliver a good approximation to the true posterior, in particular if the summary statistic
sufficiently small the ABC procedure should deliver a good approximation to the true posterior, in particular if the summary statistic 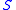 is a sufficient statistic of the probability model. If sufficient statistics do not exist or are hard to come by, setting up a satisfying and efficient ABC approach can be challenging.
is a sufficient statistic of the probability model. If sufficient statistics do not exist or are hard to come by, setting up a satisfying and efficient ABC approach can be challenging.
The generic procedure outlined above can be computationally inefficient but ABC and likelihood-free inferential procedures can be combined with the standard computational approaches used in Bayesian inference
such as Markov chain Monte Carlo
and Sequential Monte Carlo method approaches. In these frameworks ABC can be used to tackle otherwise computationally intractable problems.
While ABC and related likelihood-free methods have overwhelmingly been employed for parameter estimation, they can also be used for model selection
, as the whole apparatus of Bayesian model selection can be adapted to the ABC framework.
An increasing number of software implementations of ABC approaches exist.
Recent advances in ABC methodology, computational implementations and applications are discussed at the ABC in ... meetings:
ABC SysBio : A Tool for parameter inference and model selection in systems biology
(see also Theoretical Background).
ABC Toolbox: Inference for Population Genetics
.
msBayes : Comparative phylogeographic inference
Bayesian statistics
Bayesian statistics is that subset of the entire field of statistics in which the evidence about the true state of the world is expressed in terms of degrees of belief or, more specifically, Bayesian probabilities...
. These simulation techniques operate on summary data (such as population mean, or variance) to make broad inferences with less computation than might be required if all available data were analyzed in detail. They are especially useful in situations where evaluation of the likelihood is computationally prohibitive, or whenever suitable likelihoods are not available.
ABC methods originated in population and evolutionary genetics but have recently also been introduced to the analysis of complex and stochastic dynamical systems.
Overview
In standard Bayesian inference the posterior distribution is given by
where
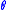 are the parameters of a probability model,
are the parameters of a probability model,  are the observed data, and
are the observed data, and 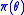 is the prior distribution of the parameters
is the prior distribution of the parameters 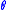 .
. 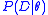 is the likelihood
is the likelihoodLikelihood
Likelihood is a measure of how likely an event is, and can be expressed in terms of, for example, probability or odds in favor.-Likelihood function:...
of
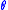 , that is the probability of observing the data
, that is the probability of observing the data  given the model with parameter
given the model with parameter 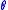 .
.The explicit evaluation of the likelihood
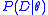 is avoided in ABC approaches by considering distances between observed and data simulated from a model with parameter
is avoided in ABC approaches by considering distances between observed and data simulated from a model with parameter 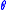 . For sufficiently complex models and large data sets the probability of happening upon a simulation run that yields precisely the same dataset as the one observed will be very small, often unacceptably so. So rather than considering the data we consider a summary statistic of the data,
. For sufficiently complex models and large data sets the probability of happening upon a simulation run that yields precisely the same dataset as the one observed will be very small, often unacceptably so. So rather than considering the data we consider a summary statistic of the data, 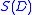 , and use a distance
, and use a distance 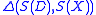 between the summary statistics of real and simulated data,
between the summary statistics of real and simulated data,  and
and  , respectively.
, respectively.The generic ABC approach to infer the posterior probability distribution of a parameter
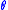 is as follows:
is as follows:-
- Sample a candidate parameter vector
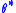 from some proposal distribution
from some proposal distribution 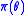 .
. - Simulate a dataset
 from the model with parameter
from the model with parameter 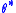 .
. - If
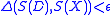 then accept
then accept 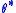 as a sample from the posterior.
as a sample from the posterior.
- Sample a candidate parameter vector
For
 sufficiently small the ABC procedure should deliver a good approximation to the true posterior, in particular if the summary statistic
sufficiently small the ABC procedure should deliver a good approximation to the true posterior, in particular if the summary statistic 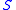 is a sufficient statistic of the probability model. If sufficient statistics do not exist or are hard to come by, setting up a satisfying and efficient ABC approach can be challenging.
is a sufficient statistic of the probability model. If sufficient statistics do not exist or are hard to come by, setting up a satisfying and efficient ABC approach can be challenging.The generic procedure outlined above can be computationally inefficient but ABC and likelihood-free inferential procedures can be combined with the standard computational approaches used in Bayesian inference
Bayesian inference
In statistics, Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference. It is often used in science and engineering to determine model parameters, make predictions about unknown variables, and to perform model selection...
such as Markov chain Monte Carlo
Markov chain Monte Carlo
Markov chain Monte Carlo methods are a class of algorithms for sampling from probability distributions based on constructing a Markov chain that has the desired distribution as its equilibrium distribution. The state of the chain after a large number of steps is then used as a sample of the...
and Sequential Monte Carlo method approaches. In these frameworks ABC can be used to tackle otherwise computationally intractable problems.
While ABC and related likelihood-free methods have overwhelmingly been employed for parameter estimation, they can also be used for model selection
Model selection
Model selection is the task of selecting a statistical model from a set of candidate models, given data. In the simplest cases, a pre-existing set of data is considered...
, as the whole apparatus of Bayesian model selection can be adapted to the ABC framework.
An increasing number of software implementations of ABC approaches exist.
Recent advances in ABC methodology, computational implementations and applications are discussed at the ABC in ... meetings:
- In 2009 ABC in Paris started this series at Université Paris Dauphine.
- In 2011 ABC in London is on the 5th of May at Imperial College London.
- In 2012 the event will be held in Rome at Università degli Studi Roma Tre.
See also
- Markov chain Monte CarloMarkov chain Monte CarloMarkov chain Monte Carlo methods are a class of algorithms for sampling from probability distributions based on constructing a Markov chain that has the desired distribution as its equilibrium distribution. The state of the chain after a large number of steps is then used as a sample of the...
- Sequential Monte Carlo Method
- Empirical Bayes
Software
DIYABC : "Do it yourself ABC".ABC SysBio : A Tool for parameter inference and model selection in systems biology
Systems biology
Systems biology is a term used to describe a number of trends in bioscience research, and a movement which draws on those trends. Proponents describe systems biology as a biology-based inter-disciplinary study field that focuses on complex interactions in biological systems, claiming that it uses...
(see also Theoretical Background).
ABC Toolbox: Inference for Population Genetics
Population genetics
Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of the four main evolutionary processes: natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and gene flow. It also takes into account the factors of recombination, population subdivision and population...
.
msBayes : Comparative phylogeographic inference

