
Apparent infection rate
Encyclopedia
Apparent infection rate is an estimate of the rate of progress of a disease, based on proportional measures of the extent of infection at different times.
Firstly, a proportional measure of the extent of infection is chosen as the disease extent metric. For example, the metric might be the proportion of leaf area affected by mildew, or the proportion of plants in a population showing dieback lesions. Measures of disease extent are then taken over time, and a mathematical model
is fit. The model is based upon two assumptions:
There is a single model parameter r, which is the apparent infection rate. It can be calculated analytically using the formula
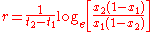
where
Firstly, a proportional measure of the extent of infection is chosen as the disease extent metric. For example, the metric might be the proportion of leaf area affected by mildew, or the proportion of plants in a population showing dieback lesions. Measures of disease extent are then taken over time, and a mathematical model
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
is fit. The model is based upon two assumptions:
- the progress of the infection is constrained by the amount of tissue that remains to be infected; and
- if it were not so constrained, the extent of infection would exhibit exponential growthExponential growthExponential growth occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value...
.
There is a single model parameter r, which is the apparent infection rate. It can be calculated analytically using the formula
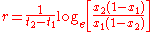
where
- r is the apparent infection rate
- t1 is the time of the first measurement
- t2 is the time of the second measurement
- x1 is the proportion of infection measured at time t1
- x2 is the proportion of infection measured at time t2

