
Andreas von Ettingshausen
Encyclopedia
Andreas Freiherr von Ettingshausen (25 November 1796, Heidelberg
– 25 May 1878, Vienna
) was a German
mathematician and physicist
.
Ettingshausen studied philosophy
and jurisprudence
in Vienna
. In 1817, he joined the University of Vienna
and taught mathematics and physics. In 1819 he became professor of physics at the University of Innsbruck and 1821 professor of higher mathematics at the University of Vienna
. His lectures of that time marked a new era for the University of Vienna
, and they were published in 1827 in 2 volumes. In 1834 Ettingshausen became the chair of physics.
Ettingshausen was the first to design an electromagnetic machine
, which used the electrical induction for power generation. He promoted optics
and wrote a text book of physics. His method of lecturing was widely influential. In addition he wrote a book on combinatorial analysis (Vienna 1826). In 1866, he retired.
Among his lasting impacts in mathematics is the introduction of the notation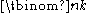 for the binomial coefficient
for the binomial coefficient
, which is the coefficient
of xk in the expansion of the binomial
(x+1)n and, more generally, the number of k-element subsets of an n-element set.
Heidelberg
-Early history:Between 600,000 and 200,000 years ago, "Heidelberg Man" died at nearby Mauer. His jaw bone was discovered in 1907; with scientific dating, his remains were determined to be the earliest evidence of human life in Europe. In the 5th century BC, a Celtic fortress of refuge and place of...
– 25 May 1878, Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
) was a German
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
mathematician and physicist
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who studies or practices physics. Physicists study a wide range of physical phenomena in many branches of physics spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic particles of which all ordinary matter is made to the behavior of the material Universe as a whole...
.
Ettingshausen studied philosophy
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
and jurisprudence
Jurisprudence
Jurisprudence is the theory and philosophy of law. Scholars of jurisprudence, or legal theorists , hope to obtain a deeper understanding of the nature of law, of legal reasoning, legal systems and of legal institutions...
in Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
. In 1817, he joined the University of Vienna
University of Vienna
The University of Vienna is a public university located in Vienna, Austria. It was founded by Duke Rudolph IV in 1365 and is the oldest university in the German-speaking world...
and taught mathematics and physics. In 1819 he became professor of physics at the University of Innsbruck and 1821 professor of higher mathematics at the University of Vienna
University of Vienna
The University of Vienna is a public university located in Vienna, Austria. It was founded by Duke Rudolph IV in 1365 and is the oldest university in the German-speaking world...
. His lectures of that time marked a new era for the University of Vienna
University of Vienna
The University of Vienna is a public university located in Vienna, Austria. It was founded by Duke Rudolph IV in 1365 and is the oldest university in the German-speaking world...
, and they were published in 1827 in 2 volumes. In 1834 Ettingshausen became the chair of physics.
Ettingshausen was the first to design an electromagnetic machine
Electric machine
The academic study of electric machines is the universal study of electric motors and electric generators. By the classic definition, electric machine is synonymous with electric motor or electric generator, all of which are electro-mechanical energy converters: converting electricity to mechanical...
, which used the electrical induction for power generation. He promoted optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
and wrote a text book of physics. His method of lecturing was widely influential. In addition he wrote a book on combinatorial analysis (Vienna 1826). In 1866, he retired.
Among his lasting impacts in mathematics is the introduction of the notation
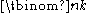 for the binomial coefficient
for the binomial coefficientBinomial coefficient
In mathematics, binomial coefficients are a family of positive integers that occur as coefficients in the binomial theorem. They are indexed by two nonnegative integers; the binomial coefficient indexed by n and k is usually written \tbinom nk , and it is the coefficient of the x k term in...
, which is the coefficient
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
of xk in the expansion of the binomial
Binomial
In algebra, a binomial is a polynomial with two terms —the sum of two monomials—often bound by parenthesis or brackets when operated upon...
(x+1)n and, more generally, the number of k-element subsets of an n-element set.

