
Amavadin
Encyclopedia

Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature...
-containing anion found in three species of poisonous Amanita
Amanita
The genus Amanita contains about 600 species of agarics including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide. This genus is responsible for approximately 95% of the fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own...
mushrooms: A. muscaria
Amanita muscaria
Amanita muscaria, commonly known as the fly agaric or fly amanita , is a poisonous and psychoactive basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita...
, A. regalis, and A. velatipes. Amavadin was first isolated and identified in 1972 by Kneifel and Bayer. This anion, which appears as a blue solution, is an eight-coordinate vanadium complex
Complex (chemistry)
In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex, is an atom or ion , bonded to a surrounding array of molecules or anions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents...
. A Ca2+ cation is often used to crystallize amavadin to obtain a good quality X-ray diffraction. Oxidized amavadin can be isolated as its PPh4+ salt. The oxidized form contains vanadium(V), which can be used to obtain an NMR spectrum.
Preparation
The formation of amavadin begins with the formation of two tetradentate ligandLigand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
s.
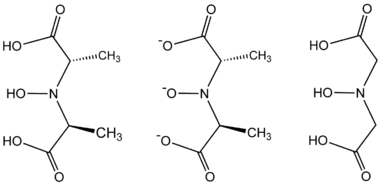
- 2 HON(CH(CH3)CO2H)2 + VO2+ → [V{NO[CH(CH3)CO2]2}2]2− + H2O + 4 H+
Structure and properties
The ligand found in amavadin was first synthesized in 1954. Amavadin contains vanadium(IV). Initially, amavadin was thought to have a vanadyl, VO2+, center. In 1993, it was discovered by crystallographic characterization that amavadin is not a vanadyl ionVanadyl ion
The vanadyl or oxovanadium cation, [VO]2+, is a blue-coloured vanadium oxocation. It is one of the most stable diatomic ions known and forms a wide range of complexes.-Compounds containing the vanadyl ion:* vanadyl, VO2...
compound. Instead, it is an octacoordinated vanadium(IV) complex. This complex is bonded to two tetradentate ligands derived from N-hydroxyimino-2,2'-dipropionic acid, H3(HIDPA), ligands. The ligands coordinate through the nitrogen and the three oxygen centers.
Amavadin is a C2-symmetric anion with a 2− charge. The twofold axis bisects the vanadium atom perpendicular to the two NO ligands. The anion features five chiral centers, one at vanadium and the four carbon atoms having S stereochemistry. There are two possible diastereomers for the ligands, (S,S)-(S,S)-Δ and (S,S)-(S,S)-Λ.
Biological function
The biological function of amavadin is still unknown, yet it has been thought that it uses H2O2 and acts as a peroxidasePeroxidase
Peroxidases are a large family of enzymes that typically catalyze a reaction of the form:For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides...
to aid the regeneration of damaged tissues. Amavadin may serve as a toxin for protection of the mushroom.

