
Alternative periodic tables
Encyclopedia
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
s differing significantly in their organization from the traditional depiction of the Periodic System. Several have been devised, often purely for didactic reasons, as not all correlations between the chemical elements are effectively captured by the standard periodic table. A 1974 review of the tables then known is considered a definitive work on the topic.
Aims
Alternative periodic tables are developed often to highlight or emphasize different chemical or physical properties of the elements which are not as apparent in traditional periodic tables. Some tables aim to emphasize both the nucleon and electronic structure of atoms. This can be done changing the spatial relationship or representation each element has with respect to another element in the table. Other tables aim to emphasize the chemical element isolations by humans over time.Major alternatives
Charles JanetCharles Janet
Charles Janet was a French engineer, company director, inventor and biologist.-Life and work:Janet graduated from the Ecole des Mines and worked for some years in munitions. He then married the daughter of the owner of a manufacturing company and worked for it for the rest of his life, finding...
's Left Step Periodic Table (1928) is considered to be the most significant alternative to the traditional depiction of the periodic system. It organizes elements according to orbital filling and is widely used by physicists. Its modern version, known as ADOMAH Periodic Table, (2006) is helpful for writing electron configurations.
H.G. Deming used the long periodic table in his textbook General Chemistry, which appeared in the USA for the first time in 1923 (Wiley), and was the first to designate the first two and the last five Main Groups with the notation "A", and the intervening Transition Groups with the notation "B".
This version of the periodic table was distributed for many years by the Sargent-Welch Scientific Company, Skokie, Illinois, USA.:
The numeration was chosen so that the characteristic oxides of the B groups would correspond to those of the A groups. The iron, cobalt, and nickel groups were designated neither A nor B. The Noble Gas Group was originally attached (by Deming) to the left side of the periodic table. The group was later switched to the right side and usually labeled as Group VlllA.
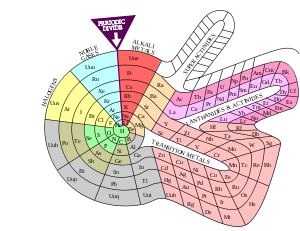
In Theodor Benfey's periodic table (1964), the elements form a two-dimensional spiral, starting from hydrogen, and folding their way around two islands, the transition metal
Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
s, and lanthanide
Lanthanide
The lanthanide or lanthanoid series comprises the fifteen metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57 through 71, from lanthanum through lutetium...
s and actinide
Actinide
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium...
s. A superactinide island is already slotted in. The Chemical Galaxy
Chemical Galaxy
Chemical Galaxy is a new representation by Philip Stewart of the periodic system of the elements, better known in tabular form as the periodic table, based on the cyclical nature of characteristics of the chemical elements...
(2004) is organized in a similar way.
In the extended periodic table, suggested by Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg was an American scientist who won the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for "discoveries in the chemistry of the transuranium elements", contributed to the discovery and isolation of ten elements, and developed the actinide concept, which led to the current arrangement of the...
in 1969, yet unknown elements are included up to atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
218. Helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
is placed in the group 2 elements.
The oldest periodic table is the short form table of Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev , was a Russian chemist and inventor. He is credited as being the creator of the first version of the periodic table of elements...
, which shows secondary chemical kinships. For example, the alkali metals and the coinage metals
Coinage metals
The coinage metals comprise, at minimum, those metallic chemical elements which have historically been used as components in alloys used to mint coins. The term is not perfectly defined, however, since a number of metals have been used to make "demonstration coins" which have never been used to...
(copper, silver, gold) are in the same column because both groups tend to have a valence of one. This format is still used by many, as shown by this contemporary Russian short form table which includes all elements and element names until roentgenium
Roentgenium
Roentgenium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Rg and atomic number 111. It is placed as the heaviest member of the group 11 elements, although a sufficiently stable isotope has not yet been produced in a sufficient amount that would confirm this position as a heavier...
.
Timmothy Stowe's physicist's periodic table is three-dimensional with the three axes representing the principal quantum number
Principal quantum number
In atomic physics, the principal quantum symbolized as n is the firstof a set of quantum numbers of an atomic orbital. The principal quantum number can only have positive integer values...
, orbital quantum number, and orbital magnetic quantum number
Magnetic quantum number
In atomic physics, the magnetic quantum number is the third of a set of quantum numbers which describe the unique quantum state of an electron and is designated by the letter m...
. Helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
is again a group 2 element.
Paul Giguere's 3-D periodic table consists of 4 billboards with the elements written on the front and the back. The first billboard has the group 1 elements on the front and the group 2 elements at the back, with hydrogen and helium omitted altogether. At a 90° angle the second billboard contains the groups 13 to 18 front and back. Two more billboard each making 90° angles contain the other elements.
In the research field of superatoms, clusters of atoms have properties of single atoms of another element. It is suggested to extend the periodic table with a second layer to be occupied with these cluster compounds. The latest addition to this multi-story table is the aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
cluster ion , which behaves like a multivalent germanium
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbors tin and silicon. The isolated element is a semiconductor, with an appearance most similar to elemental silicon....
atom.
Ronald L. Rich has proposed a periodic table where elements appear more than once when appropriate. He notes that hydrogen shares properties with group 1 elements based on valency
Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds...
, with group 17 elements because hydrogen is a non-metal but also with the carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
group based on similarities in chemical bonding to transition metals and a similar electronegativity
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ , is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance that its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus...
. In this rendition of the periodic table carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
and silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
also appear in the same group as titanium
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color....
and zirconium
Zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium...
.
An interesting new chemists' table ("Newlands Revisited") that solves many of the problems of position of hydrogen, helium and the lanthanides, etc., was published by EG Marks and JA Marks in 2010.
Further reading
- Hjørland, Birger (2011). The periodic table and the philosophy of classification. Knowledge Organization, 38(1), 9-21. Retrieved 2011-03-13 from: http://ucla.academia.edu/EricScerri/Papers/432740/Forum%5FThe%5FPhilosophy%5Fof%5FClassification
External links
- Robert Harrison's modern spiral periodic table
- Janet's Left Step Periodic Table
- Correction to Physicist periodic table offered by Jeries Rihani as MeitneriumMeitneriumMeitnerium is a chemical element with the symbol Mt and atomic number 109. It is placed as the heaviest member of group 9 in the periodic table but a sufficiently stable isotope is not known at this time which would allow chemical experiments to confirm its position, unlike its lighter...
occupies the position that HassiumHassiumHassium is a synthetic element with the symbol Hs and atomic number 108. It is the heaviest member of the group 8 elements. The element was first observed in 1984...
should have. - A Wired Article on Alternate Periodic Tables
- A Selection of Periodic Tables
- http://periodicspiral.com/ arranges the periodic table in a (hexagonal) spiral.
- Rotaperiod.com A new periodic table.
- Note on the T-shirt topology of the Z-spiral.
- New Periodic Table of the Elements this is in a square-triangular periodic arrangement.
- Periodic Table based on electron configurations
- Database of Periodic Tables
- Periodic Fractal of the Elements
- Bob Doyle Periodic Table of the Elements A regrouping by properties that suggests a maximum of 120 elements.
- Earth Scientist's Periodic Table

