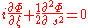Airy beam
Encyclopedia
An Airy beam is a non-diffracting waveform which gives the appearance of curving as it travels.
As the beam propagates, it does not diffract, i.e., does not spread out. The Airy beam also has the characteristic of freely accelerating. As it propagates, it bends so as to form a parabolic arc.
The Airy waveform was first theorized in 1979 by M. V. Berry and N. L. Balz. They demonstrated a nonspreading Airy wave packet solution to the Schrödinger equation.
In 2007 researchers from the University of Central Florida were able to create and observe an Airy beam for the first time in both one- and two-dimensional configurations. The members of the team were Georgios Siviloglou, John Broky, Aristide Dogariu, and Demetrios Christodoulides.
:
Has the following Airy nondispersive solution:

where
to have an Airy distribution. The result was recorded by a CCD camera.
Physical Description
A cross section of an Airy beam would reveal an area of principal intensity, with a series of adjacent, less luminous areas trailing off to infinity. In real applications, the beam is truncated so as to have a finite composition.As the beam propagates, it does not diffract, i.e., does not spread out. The Airy beam also has the characteristic of freely accelerating. As it propagates, it bends so as to form a parabolic arc.
History
The term "Airy beam" derives from the Airy integral, developed in the 1830s by Sir George Biddell Airy to explain optical caustics such as those appearing in a rainbow.The Airy waveform was first theorized in 1979 by M. V. Berry and N. L. Balz. They demonstrated a nonspreading Airy wave packet solution to the Schrödinger equation.
In 2007 researchers from the University of Central Florida were able to create and observe an Airy beam for the first time in both one- and two-dimensional configurations. The members of the team were Georgios Siviloglou, John Broky, Aristide Dogariu, and Demetrios Christodoulides.
Mathematical Description
The potential free Schrödinger equationSchrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation was formulated in 1926 by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger. Used in physics , it is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time....
:
Has the following Airy nondispersive solution:

where
-
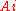 is the airy functionAiry functionIn the physical sciences, the Airy function Ai is a special function named after the British astronomer George Biddell Airy...
is the airy functionAiry functionIn the physical sciences, the Airy function Ai is a special function named after the British astronomer George Biddell Airy...
. -
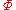 is the electric fieldElectric fieldIn physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
is the electric fieldElectric fieldIn physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
envelope -
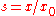 represents a dimensionless traverse coordinate
represents a dimensionless traverse coordinate -
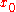 is an arbitrary traverse scale
is an arbitrary traverse scale -
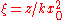 is a normalized propagation distance
is a normalized propagation distance -
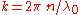
Experimental Observation
Georgios Sivilioglou, et al. successfully fabricated an Airy beam in 2007. A beam with a Gaussian distribution was modulated by a spatial light modulatorSpatial light modulator
A spatial light modulator is an object that imposes some form of spatially-varying modulation on a beam of light. A simple example is an overhead projector transparency. Usually when the phrase SLM is used, it means that the transparency can be controlled by a computer. In the 1980s, large SLMs...
to have an Airy distribution. The result was recorded by a CCD camera.