
Agreement in English law
Encyclopedia
English contract law
English contract law is a body of law regulating contracts in England and Wales. With its roots in the lex mercatoria and the activism of the judiciary during the industrial revolution, it shares a heritage with countries across the Commonwealth , and the United States...
, an agreement establishes the first stage in the existence of a contract. The three main elements of contractual formation are whether there is (1) offer and acceptance (agreement) (2) consideration (3) an intention to be legally bound
Intention to be legally bound
Intention to be legally bound is a technical term used in contract law, particularly English contract law, to denote a court's presumption that parties to an agreement wished it to be enforceable by a court...
.
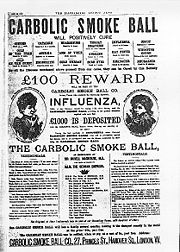
One of the most famous cases on forming a contract is Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Company, decided in nineteenth-century England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
. A medical firm advertised that its new wonder drug, a smoke ball, would cure people's flu
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
, and if it did not, buyers would receive £100. When sued, Carbolic argued the ad was not to be taken as a serious, legally binding offer
Offer and acceptance
Offer and acceptance analysis is a traditional approach in contract law used to determine whether an agreement exists between two parties. Agreement consists of an offer by an indication of one person to another of the offeror's willingness to enter into a contract on certain terms without...
. It was merely an invitation to treat
Invitation to treat
Invitation to treat is a contract law term. It comes from the Latin phrase invitatio ad offerendum and means "inviting an offer". Or as Andrew Burrows writes, an invitation to treat is...
, and a gimmick. But the court of appeal held that it would appear to a reasonable man that Carbolic had made a serious offer. People had given good "consideration" for it by going to the "distinct inconvenience" of using a faulty product. "Read the advertisement how you will, and twist it about as you will," said Lindley LJ, "here is a distinct promise expressed in language which is perfectly unmistakable".
Offer
The most important feature of a contract is that one party makes an offerOffer and acceptance
Offer and acceptance analysis is a traditional approach in contract law used to determine whether an agreement exists between two parties. Agreement consists of an offer by an indication of one person to another of the offeror's willingness to enter into a contract on certain terms without...
for a bargain that another accepts. This can be called a 'concurrence of wills' or a 'meeting of the minds' of two or more parties. There must be evidence
Evidence (law)
The law of evidence encompasses the rules and legal principles that govern the proof of facts in a legal proceeding. These rules determine what evidence can be considered by the trier of fact in reaching its decision and, sometimes, the weight that may be given to that evidence...
that the parties had each from an objective
Objectivity (philosophy)
Objectivity is a central philosophical concept which has been variously defined by sources. A proposition is generally considered to be objectively true when its truth conditions are met and are "mind-independent"—that is, not met by the judgment of a conscious entity or subject.- Objectivism...
perspective engaged in conduct manifesting their assent, and a contract will be formed when the parties have met such a requirement. An objective perspective means that it is only necessary that somebody gives the impression of offering or accepting contractual terms in the eyes of a reasonable person
Reasonable person
The reasonable person is a legal fiction of the common law that represents an objective standard against which any individual's conduct can be measured...
, not that they actually did want to contract.
Invitations to treat
Where a product in large quantities is advertised for in a newspaper or on a poster, it is generally regarded as an offer, however if the person who is to buy the advertised product is of importance, i.e. his personality etc., when buying e.g. land, it is merely an invitation to treat. In Carbolic Smoke Ball, the major difference was that a reward was included in the advertisement which is a general exception to the rule and is then treated as an offer. Whether something is classified as an offer or an invitation to treat depends on the type of agreement being made and the nature of the sale. In retail situations an item being present is normally considered an invitation to treat; this was established for items on display in shop windows in Fisher v Bell [1961] 1 QB 394 and for items on shelves in Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain v Boots Cash Chemists (Southern) Ltd [1953] 1 QB 401.Retail agreements can also be considered invitations to treat if there is simply not enough information in the initial statement for it to constitute an offer. In Partridge v Crittenden [1968] 1 WLR 1204 the defendant had placed an advertisement indicating that he had certain birds for sale, giving a price but no information about quantities. He was arrested under the Protection of Birds Act 1954 for 'offering such birds for sale'; it was ruled that since the advertisement did not specify the number of birds he had it could not constitute an offer; if it did he could have been legally bound to provide more birds than he possessed. The same principle was applied for catalogues in Grainger v Gough [1896] AC 325, when it was ruled that posting catalogues of items for sale to people did not constitute an offer since there was insufficient detail.
- Chapelton v Barry UDC
- Spencer v Harding (1870) LR 5 CP 561
- Harvey v FaceyHarvey v FaceyHarvey v Facey [1893] , [1893] AC 552 is a contract law case decided by the United Kingdom Judicial Committee of the Privy Council which in 1893 held final legal jurisdiction over most of the British Caribbean. Its importance in case law is that it defined the difference between an offer and an...
[1893] AC 552
Auctions
- Warlow v Harrison (1859) 1 E & E 309; 120 ER 925
- Harris v Nickerson
- Payne v CavePayne v CavePayne v Cave 3 TR 148 is an old English contract law case, which stands for the proposition that an auctioneer's request for bids is not an offer which can be accepted by the highest bidder.-Facts:...
- Barry v Davies (t/a Heathcote Ball & Co) [2001] 1 All ER 944
- Sale of Goods Act 1979Sale of Goods Act 1979The Sale of Goods Act 1979 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which regulates English contract law and UK commercial law in respect of goods that are sold and bought. The Act consolidates the original Sale of Goods Act 1893 and subsequent legislation, which in turn had codified and...
, s 57(2)
Revocation
- Routledge v Grant (1828) 4 Bing 653; 130 ER 920
- Byrne v Van TienhovenByrne v Van TienhovenByrne v Van Tienhoven [1880] 5 CPD 344 is a leading English contract law case on the issue of revocation in relation to the postal rule. In it Lindley J of the High Court Common Pleas Division ruled that an offer is only revoked by direct communication with the offeree, and that the postal rule...
(1880) 5 CPD 344 - Dickinson v DoddsDickinson v DoddsDickinson v Dodds 2 Ch D 463 is an English contract law case, heard by the Court of Appeal, Chancery Division, that held that notification by a third party of an offer's withdrawal is effective just like a withdrawal by the person who made an offer....
[1876] 2 Ch D 463 - Errington v Errington [1952] 1 KB 290
Counter offers
- Hyde v WrenchHyde v WrenchHyde v Wrench [1840] is a leading English contract law case on the issue of counter-offers and their relation to initial offers. In it Lord Langdale ruled that any counter-offer cancels the original offer.-Facts:...
(1840) 3 Bea 334 - Stevenson, Jacques & Co v McLeanStevenson, Jacques & Co v McLeanStevenson, Jacques & Co v McLean 5 QBD 346 is an English contract law case concerning the rules on communication of acceptance by telegraph. Its approach contrasts to the postal rule.-Facts:...
(1880) 5 QBD 346
Prescribed method of acceptance
- Manchester Diocesan Council for Education v Commercial Investments Ltd [1969] 3 All ER 1593
Knowledge and reliance on offer
- Williams v CarwardineWilliams v CarwardineWilliams v Carwardine [1833] is an English contract law case which concerns how a contract comes about through the offer of a reward. It also raises interesting questions about the necessity of reliance on an offer in the formation of a contract.-Facts:...
(1833) 5 C & P 566; 172 ER 1101 - Gibbons v ProctorGibbons v ProctorGibbons v Proctor [1891] 64 LT 594 , is an English contract law case that deals with an offer, via advertisement, and whether or not a person who doesn't know of the offer can accept the offer if he completes the conditions of the offer.-Facts:A police officer supplied information for which a...
- R v ClarkeR v ClarkeR v Clarke 40 CLR 227 is court case decided by the Australian High Court in the law of contract.-Facts:The claimant wanted to compel the Crown to pay a reward it had offered for information leading to the conviction of a murderer. The claimant gave the information. But he gave it while he was...
(1927) 40 CLR 227
Battle of the forms
- Butler Machine Tool Co Ltd v Ex-cello Cpn (England) Ltd [1979] 1 WLR 401
Acceptance in case of tenders
- Harvela Investments Ltd v Royal Trust Co of Canada [1986] AC 207
- Blackpool & Fylde Aero Club v Blackpool Borough CouncilBlackpool & Fylde Aero Club v Blackpool Borough CouncilBlackpool & Fylde Aero Club v Blackpool Borough Council [1990] is a leading English contract law case on the issue of offer and acceptance in relation to Call for bids...
[1990] 1 WLR 1195
Silence a condition of acceptance
- Felthouse v Bindley (1862) 11 CBNS 869
- Consumer Protection (Distance Selling) Regulations 2000Consumer Protection (Distance Selling) Regulations 2000The Consumer Protection Regulations 2000, SI 2000/2334, incorporates Directive into law of the United Kingdom. They apply to contracts "concluded between a supplier and a consumer under an organised distance sales or services provision scheme run by the supplier who, for the purposes of the...
(SI 2000/2334) Reg 24
Post or telegram
- Adams v Lindsell [1818] EWHC KB J59
- Henthorn v Fraser [1892] 2 Ch 27
- Holwell Securities Ltd v. Hughes [1974] 1 WLR 155
Telex
- Entores Ltd v Miles Far East CorporationEntores Ltd v Miles Far East CorporationEntores Ltd v Miles Far East Corporation [1955] is a landmark English Court of Appeal decision in contract law on the moment of acceptance of a contract over telex. Denning LJ found that the regular postal rule did not apply for instantaneous means of communications such as a telex...
[1955] 2 QB 327 - Brinkibon Ltd v Stahag Stahl mbH [1983] 2 AC 34
- The BrimnesThe BrimnesTenax Steamship Co v Owners of the Motor Vessel Brimnes [1974] is an English contract law case on agreement. It decided that communication of withdrawal of an offer by telex is effective when it could be read, rather than when it is in fact read....
[1975] QB 929
Revocation of Acceptance
- Hudson ‘Retraction of Letters of Acceptance’ (1966) 82 Law Quarterly Review 169
Certainty and completeness
If the terms of the contract are uncertain or incomplete, the parties cannot have reached an agreement in the eyes of the law. An agreement to agree does not constitute a contract, and an inability to agree on key issues, which may include such things as priceContract price
A contract price is the price listed in the contract for the good or services to be received in return.-Common law:In contract law, the contract price is a material term. The contract price is the price for the goods or services to be received in the contract. The contract price helps to ...
or safety, may cause the entire contract to fail. However, a court will attempt to give effect to commercial contracts where possible, by construing a reasonable construction of the contract (Hillas and Co Ltd v Arcos Ltd).
Courts may also look to external standards, which are either mentioned explicitly in the contract or implied by common practice in a certain field. In addition, the court may also imply a term; if price is excluded, the court may imply a reasonable price, with the exception of land, and second-hand goods, which are unique.
If there are uncertain or incomplete clauses in the contract, and all options in resolving its true meaning have failed, it may be possible to sever and void just those affected clauses if the contract includes a severability clause. The test of whether a clause is severable is an objective test—whether a reasonable person would see the contract standing even without the clauses.
- Sale of Goods Act 1979Sale of Goods Act 1979The Sale of Goods Act 1979 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which regulates English contract law and UK commercial law in respect of goods that are sold and bought. The Act consolidates the original Sale of Goods Act 1893 and subsequent legislation, which in turn had codified and...
ss 8(2) 9
See also
- English tort lawEnglish tort lawEnglish tort law concerns civil wrongs, as distinguished from criminal wrongs, in the law of England and Wales. Some wrongs are the concern of the state, and so the police can enforce the law on the wrongdoers in court – in a criminal case...
- Consideration in English law
- Powell v LeePowell v LeePowell v Lee 99 LT 284 was an English contract law case. The ruling established that acceptance of an offer must be communicated to offeror by offeree himself or authorized agent. -Facts:...
(1908) 99 LT 284

