
Affine pricing
Encyclopedia
In economics
, affine pricing is a situation where buying more than zero of a good gains a fixed benefit or cost, and each purchase after that gains a per-unit benefit or cost.
Where:
T is the total price paid,
q is the quantity in units purchased,
p is a constant price per unit,
k is the fixed cost,
the affine price is then calculated by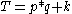
In mathematical language, the price is an affine function (sometimes also linear function
) of the quantity bought.
An example would be a cell phone contract where a base price is paid each month with a per-minute price for calls.
Sliding-scale price contracts achieve a similar effect, although the terms are stated differently. The price decreases with volume produced, achieving the same financial transfer over time, but the transaction is always based on units sold, with the fixed cost amortized into the price of each unit.
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, affine pricing is a situation where buying more than zero of a good gains a fixed benefit or cost, and each purchase after that gains a per-unit benefit or cost.
Where:
T is the total price paid,
q is the quantity in units purchased,
p is a constant price per unit,
k is the fixed cost,
the affine price is then calculated by
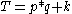
In mathematical language, the price is an affine function (sometimes also linear function
Linear function
In mathematics, the term linear function can refer to either of two different but related concepts:* a first-degree polynomial function of one variable;* a map between two vector spaces that preserves vector addition and scalar multiplication....
) of the quantity bought.
An example would be a cell phone contract where a base price is paid each month with a per-minute price for calls.
Sliding-scale price contracts achieve a similar effect, although the terms are stated differently. The price decreases with volume produced, achieving the same financial transfer over time, but the transaction is always based on units sold, with the fixed cost amortized into the price of each unit.

