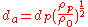Aerodynamic diameter is a physical property of a particle in a viscous
fluidIn physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
such as air. In general, particles have irregular shapes with actual geometric diameters that are difficult to measure. Aerodynamic diameter is an expression of a particle's aerodynamic behavior as if it were a perfect sphere with unit-
densityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
and diameter equal to the aerodynamic diameter. Such a model has the same terminal settling velocity.
Aerodynamic diameter is commonly applied to particulate pollutants and inhaled drugs to predict where in the respiratory tract such particles will deposit.
Calculations
Drug particles for pulmonary delivery are typically characterized by aerodynamic diameter rather than geometric diameter. The velocity at which the drug settles is proportional to the aerodynamic diameter, d
a.
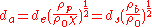
where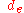 = equivalent volume diameter
= equivalent volume diameter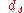 = Stokes’s equivalent diameter
= Stokes’s equivalent diameter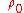 = standard particle density (1g/cc).
= standard particle density (1g/cc).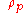 = particle material density
= particle material densityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
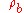 = bulk material density
= bulk material densityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
(less than 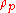 if porosity)
if porosity) = shape factor
= shape factorShape factor can refer to one of number of values in physics, engineering, or image analysis. Typically, a shape factor refers to a value that is affected by an object's shape but is independent of its dimensions.In physics:...
.
For spherical species, χ = 1.
Aerodynamic diameter is the diameter of a sphere of unit density (1g/cc) that has the same gravitational settling velocity as the particle in question.
It's given as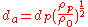
The source of this article is
wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. The text of this article is licensed under the
GFDL.

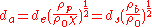
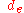 = equivalent volume diameter
= equivalent volume diameter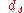 = Stokes’s equivalent diameter
= Stokes’s equivalent diameter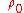 = standard particle density (1g/cc).
= standard particle density (1g/cc).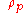 = particle material density
= particle material density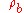 = bulk material density
= bulk material density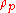 if porosity)
if porosity) = shape factor
= shape factor