
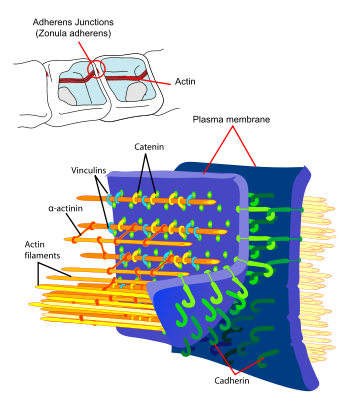
Adherens junction
Encyclopedia
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
cytoskeleton.
They can appear as bands encircling the cell (zonula adherens) or as spots of attachment to the extracellular matrix (adhesion plaques).
A similar cell junction in non-epithelial cells is the fascia adherens
Fascia adherens
Fascia Adherens is a ribbon like structure that stabilizes non-epithelial tissue. Is similar to the Zonula Adherens or Adherens junction of epithelial cells but it's not belt-like. It's a broad intercellular junction in the longitudinal sections of an intercalated disk of cardiac muscle anchoring...
. It is structurally the same, but appears in ribbonlike patterns that do not completely encircle the cells. One example is in cardiomyocytes.
Proteins
Adherens junctions are composed of the following proteins:- cadherins. The cadherins are a family of transmembrane proteins that form homodimers in a calcium-dependent manner with other cadherin molecules on adjacent cells.
- p120 (sometimes called delta cateninDelta cateninDelta-1-catenin and Delta-2-catenin are members of a subfamily of proteins with ten Armadillo-repeats. Delta-2-catenin is expressed in the brain where it is important for normal cognitive development. Like beta-catenin and gamma-catenin, delta-catenins seem to interact with presenilins...
) binds the juxtamembrane region of the cadherin. - β-catenin or gamma-catenin (plakoglobinPlakoglobinJunction plakoglobin, also known as gamma-catenin or JUP, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JUP gene.- Function :...
) binds the catenin-binding region of the cadherin. - α-catenin binds the cadherin indirectly via β-catenin or plakoglobinPlakoglobinJunction plakoglobin, also known as gamma-catenin or JUP, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JUP gene.- Function :...
and links the actin cytoskeleton with cadherin.
Models
Adherens junctions were, for many years, thought to share the characteristic of anchor cellAnchor cell
The anchor cell is a cell in nematodes such as Caenorhabditis elegans. It is important in the development of the reproductive system, as it is required for the production of the tube of cells that allows embryos to pass from the uterus through the vulva to the outside of the worm.During the...
s through their cytoplasmic actin
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
filaments.
The accepted model has been that adherens junctions serve as a bridge
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span physical obstacles such as a body of water, valley, or road, for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle...
connecting the actin cytoskeleton of neighboring cells through direct interaction. However, scientists have not been able to isolate the quaternary complex of cadherin-βcatenin-αcatenin-actin in vitro
In vitro
In vitro refers to studies in experimental biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological context in order to permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms. Colloquially, these experiments...
. Recent data (2005) demonstrate that membrane associated actin is several fold less stable compared to components of the adherens junctional complex.
Additionally, the authors found that monomeric α-catenin preferentially binds to the cadherin junction complex through β-catenin. Dimeric α-catenin preferentially binds to actin and suppresses Arp2/3 complex
Arp2/3 complex
Arp2/3 complex is a seven-subunit protein that plays a major role in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. It is a major component of the actin cytoskeleton and is found in most in actin cytoskeleton-containing eukaryotic cells....
-mediated actin branching, thus acting as a molecular switch to regulate actin polymerization.
Adherens junctions may serve as a regulatory module to maintain the actin contractile ring with which it is associated in microscopic studies.

